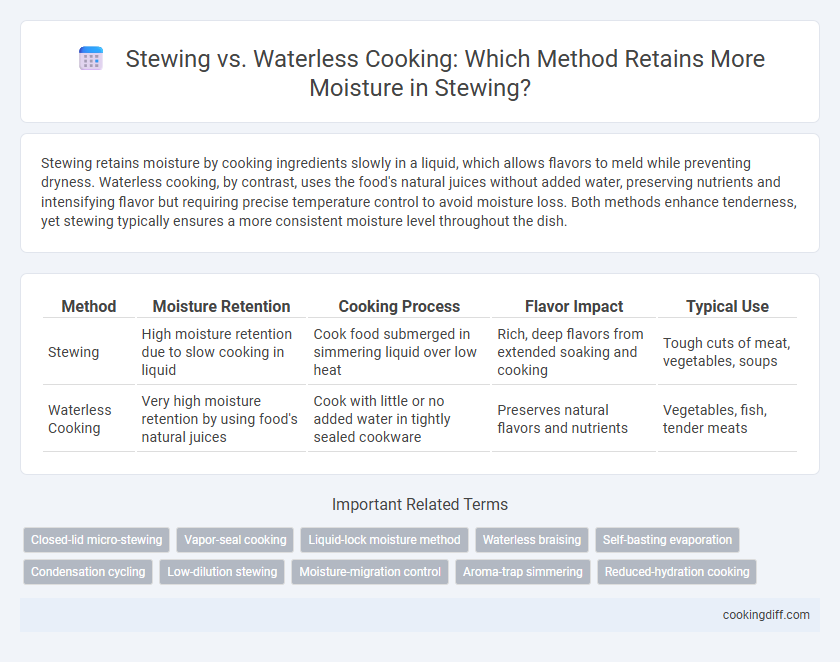
Stewing retains moisture by cooking ingredients slowly in a liquid, which allows flavors to meld while preventing dryness. Waterless cooking, by contrast, uses the food's natural juices without added water, preserving nutrients and intensifying flavor but requiring precise temperature control to avoid moisture loss. Both methods enhance tenderness, yet stewing typically ensures a more consistent moisture level throughout the dish.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Moisture Retention | Cooking Process | Flavor Impact | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stewing | High moisture retention due to slow cooking in liquid | Cook food submerged in simmering liquid over low heat | Rich, deep flavors from extended soaking and cooking | Tough cuts of meat, vegetables, soups |
| Waterless Cooking | Very high moisture retention by using food's natural juices | Cook with little or no added water in tightly sealed cookware | Preserves natural flavors and nutrients | Vegetables, fish, tender meats |
Introduction to Stewing and Waterless Cooking
Stewing is a slow cooking method that involves submerging ingredients in a flavorful liquid, allowing them to cook gently over low heat to retain moisture and develop rich flavors. Waterless cooking uses the natural moisture of the food and requires little to no added liquid, cooking ingredients in a tightly sealed pot to preserve nutrients and moisture effectively. Both techniques aim to enhance moisture retention, but stewing relies on added liquids while waterless cooking harnesses internal food moisture.
Understanding Moisture Retention in Cooking Methods
Stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid, which helps preserve moisture by preventing evaporation during the cooking process. Waterless cooking relies on the natural moisture of ingredients, enhancing nutrient retention while minimizing water loss through sealed cooking environments.
- Stewing retains moisture effectively - Submerging ingredients in liquid creates a barrier that limits water evaporation and keeps food tender.
- Waterless cooking maximizes moisture use - Using minimal or no added water traps steam inside a sealed pot, preserving the food's natural juices.
- Moisture retention impacts texture and flavor - Better moisture control results in juicier, more flavorful dishes with enhanced nutrient preservation.
Understanding the differences in moisture retention helps optimize cooking techniques for desired culinary results.
How Stewing Preserves Moisture in Food
How does stewing preserve moisture in food compared to waterless cooking? Stewing involves cooking food slowly in a liquid at low temperatures, creating a sealed environment that traps steam and prevents moisture loss. This method ensures that the food absorbs the cooking liquid, enhancing juiciness and flavor retention more effectively than waterless cooking techniques.
Waterless Cooking: Principles and Moisture Control
Waterless cooking utilizes sealed cookware and low heat to cook food in its natural juices, minimizing moisture loss and preserving nutrients. This method relies on the steam generated from the food itself, eliminating the need for added water, which enhances moisture retention compared to traditional stewing.
By maintaining a controlled internal environment, waterless cooking prevents evaporation and concentrates flavors, resulting in tender and succulent dishes. The reduction in moisture escape ensures that proteins and vegetables remain juicier and more flavorful than in conventional stewing methods.
Nutrient Preservation in Stewing vs Waterless Cooking
Stewing excels in nutrient preservation by gently cooking ingredients in liquid, which helps retain water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. The slow cooking process minimizes nutrient loss compared to high-heat methods.
Waterless cooking preserves nutrients by using the natural moisture of the food and cooking at lower temperatures without added water, which reduces vitamin leaching. However, stewing's use of broth captures nutrients that might otherwise be lost, enhancing the overall nutritional value of the meal. Both methods offer benefits, but stewing provides a more nutrient-rich liquid component that can be consumed alongside the solids.
Flavor Development: Stewing vs Waterless Techniques
Stewing enhances flavor development by slowly breaking down ingredients in a moisture-rich environment, allowing complex, melded tastes to emerge. Waterless cooking preserves natural juices but may result in less depth of flavor compared to stewing.
- Maillard Reaction - Stewing often includes initial browning which promotes Maillard reactions critical for deep, savory flavors.
- Moisture Retention - Waterless cooking retains inherent moisture, preventing dilution but limiting flavor blending from added liquids.
- Flavor Layering - Stewing's prolonged simmering time encourages layering of spices and aromatics, enhancing overall taste complexity.
Texture and Juiciness: Comparing Final Results
| Cooking Method | Texture | Juiciness |
|---|---|---|
| Stewing | Produces tender, well-cooked meat with a soft, melt-in-mouth texture due to slow cooking in liquid. | High moisture retention as ingredients are simmered in broth or sauce, preserving natural juices. |
| Waterless Cooking | Maintains firmer texture by cooking ingredients in sealed cookware using their own moisture. | Encourages intense flavor retention but can sometimes result in slightly drier texture compared to stewing. |
Ideal Foods for Stewing and Waterless Cooking
Stewing is ideal for tougher cuts of meat like beef chuck, pork shoulder, and lamb shanks, which benefit from slow cooking in liquid to break down connective tissues and retain moisture. Waterless cooking suits vegetables with high water content such as zucchini, tomatoes, and mushrooms, preserving their natural juices and nutrients by cooking in their own steam. Both methods optimize moisture retention but differ in their suitability based on food texture and water content.
Equipment Needs: Traditional Stewpot vs Waterless Cookware
Traditional stewpots require a heavy, often enameled cast iron or stainless steel pot with a tight-fitting lid to ensure moisture retention during slow cooking. Stewpots rely on liquid to create steam and maintain a moist environment for breaking down tough ingredients.
Waterless cookware is designed with a specially engineered lid that locks in steam and nutrients without adding extra water. This equipment allows cooking at lower temperatures by using natural food moisture, reducing nutrient loss and preserving flavors more effectively than traditional pots.
Related Important Terms
Closed-lid micro-stewing
Closed-lid micro-stewing enhances moisture retention by creating a sealed environment that traps steam and natural juices within the food, preventing evaporation and preserving texture and flavor. Compared to traditional waterless cooking, this method offers precise temperature control and minimal liquid loss, resulting in tender, succulent dishes with intensified taste profiles.
Vapor-seal cooking
Stewing relies on vapor-seal cooking, which traps steam within the pot to retain moisture and intensify flavors, whereas waterless cooking uses minimal or no added water, preserving nutrients but often resulting in less tender dishes. Vapor-seal stewing ensures that the natural juices of ingredients are maintained, enhancing texture and richness compared to the drier environment of waterless methods.
Liquid-lock moisture method
Stewing uses ample liquid to envelop ingredients, effectively locking in moisture and enhancing flavor through slow, even cooking. In contrast, waterless cooking relies on the natural moisture of the food itself, but stewing's liquid-lock method ensures superior retention of juices and tenderness.
Waterless braising
Waterless braising enhances moisture retention by cooking food in its natural juices without adding water, preserving nutrients and intensifying flavors compared to traditional stewing. This method uses sealed cookware and low heat to trap steam, resulting in tender, succulent dishes with minimal nutrient loss.
Self-basting evaporation
Stewing relies on self-basting evaporation where moisture from the ingredients continuously circulates within the pot, enhancing flavor and tenderness by preventing dryness. Waterless cooking also preserves moisture but lacks the vigorous evaporation cycle that stewing utilizes to naturally baste the food during the cooking process.
Condensation cycling
Stewing utilizes condensation cycling to continuously circulate moisture within the cooking vessel, resulting in superior moisture retention compared to waterless cooking methods that rely on sealed environments without active vapor movement. This repeated evaporation and condensation process in stewing enhances flavor infusion while preserving the natural juiciness of ingredients.
Low-dilution stewing
Low-dilution stewing enhances moisture retention by minimizing the amount of added liquid, allowing food to cook in its own juices and concentrated flavors. This technique contrasts with waterless cooking, which relies on steaming with minimal or no added liquid but may result in less flavor concentration due to the different cooking environment.
Moisture-migration control
Stewing effectively controls moisture migration by submerging ingredients in flavorful liquid, preserving juiciness and preventing dryness through slow, uniform heat transfer. In contrast, waterless cooking relies on steam generated from the natural moisture of food, which may result in less consistent moisture retention in dense or fibrous ingredients.
Aroma-trap simmering
Stewing employs aroma-trap simmering to retain moisture by cooking food slowly in its own juices, enhancing flavor concentration and preventing dehydration. Waterless cooking also preserves moisture but typically requires sealed vessels at higher temperatures, which can diminish the delicate aromas that stewing captures.
Stewing vs Waterless Cooking for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com