Stainless steel pots offer durability and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for fast, high-heat cooking when stewing pet food. Clay pots provide even heat distribution and retain moisture better, which helps enhance flavor and tenderness during slow cooking. Choosing between the two depends on the cooking time and desired texture in the stewing process.
Table of Comparison
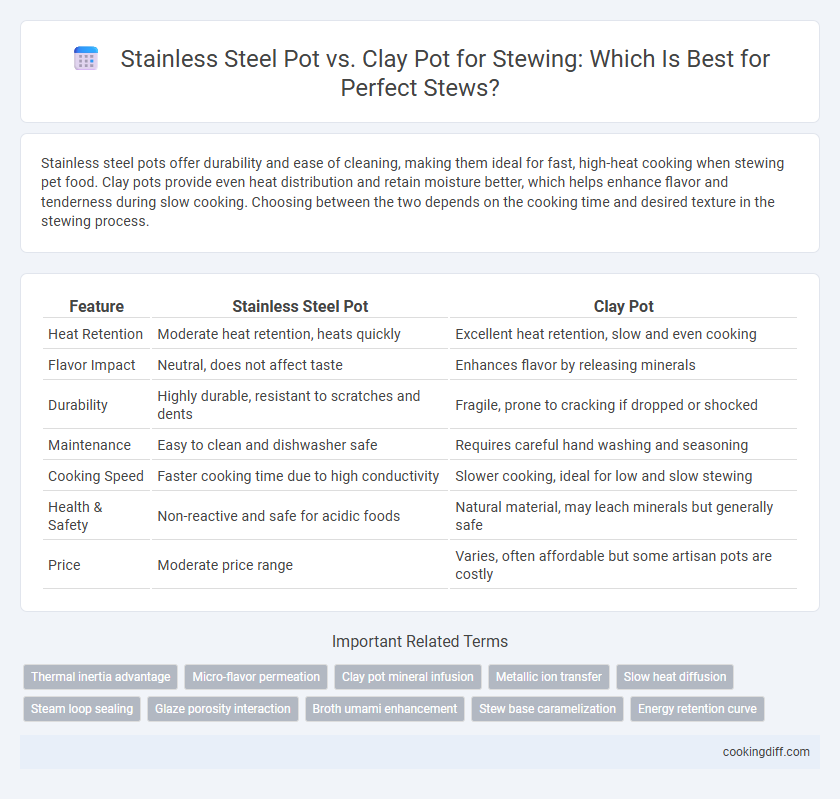
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pot | Clay Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Moderate heat retention, heats quickly | Excellent heat retention, slow and even cooking |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, does not affect taste | Enhances flavor by releasing minerals |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches and dents | Fragile, prone to cracking if dropped or shocked |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and dishwasher safe | Requires careful hand washing and seasoning |
| Cooking Speed | Faster cooking time due to high conductivity | Slower cooking, ideal for low and slow stewing |
| Health & Safety | Non-reactive and safe for acidic foods | Natural material, may leach minerals but generally safe |
| Price | Moderate price range | Varies, often affordable but some artisan pots are costly |
Introduction to Stewing: Stainless Steel vs Clay Pots
Stewing requires pots that evenly distribute heat and retain moisture for tender results. Stainless steel pots offer durability and non-reactive surfaces, making them ideal for acidic ingredients. Clay pots enhance flavor through slow, consistent heat and natural moisture retention, enriching the stew's aroma and texture.
Heat Retention and Distribution in Stewing
Stainless steel pots provide excellent heat distribution due to their conductive metal surface, ensuring even cooking without hot spots. Clay pots excel in heat retention, slowly releasing heat to maintain a consistent temperature ideal for stewing. Choosing between stainless steel and clay depends on whether quick heat response or sustained warmth is prioritized during the stewing process.
Flavor Development in Stainless Steel and Clay Pots
Stainless steel pots maintain consistent heat, which helps in evenly developing rich flavors during stewing without imparting additional taste to the ingredients. Clay pots, on the other hand, absorb moisture and slowly release it, enhancing the depth and complexity of flavors through natural steaming.
The porous nature of clay pots allows for better heat retention and gradual cooking, intensifying the stew's aroma and texture. Stainless steel pots excel in durability and quick temperature adjustment, making them versatile for various stewing recipes. Flavor development in clay pots is often described as more authentic and earthy, while stainless steel emphasizes the natural taste of the ingredients.
Cooking Time Differences: Which Pot is Faster?
Stainless steel pots conduct heat more quickly and evenly, significantly reducing cooking time for stewing compared to clay pots. Their high thermal conductivity allows water and ingredients to reach boiling point faster, accelerating the stewing process.
Clay pots, on the other hand, retain heat longer but take more time to warm up, resulting in slower cooking times. This slow heat absorption promotes deeper flavor development but extends the stewing duration by approximately 20-30% compared to stainless steel alternatives.
Durability and Longevity of Each Pot
| Pot Type | Durability | Longevity |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Pot | Highly resistant to corrosion, dents, and scratches due to alloy composition. | Can last several decades with proper maintenance and no chipping or cracking. |
| Clay Pot | More fragile, prone to cracking, chipping, and breakage from thermal shock or impact. | Typically lasts a few years to a decade, depending on handling and usage frequency. |
Health and Safety: Non-toxic Stewing Choices
Stainless steel pots are preferred for stewing due to their non-reactive nature, which ensures no harmful chemicals leach into food, promoting a safer cooking environment. High-quality stainless steel is durable, resistant to rust, and does not absorb odors, making it ideal for health-conscious stewing.
Clay pots offer natural heat retention and enhance flavor but may contain trace minerals and sometimes lead if not properly manufactured, posing potential health risks. Opting for certified, lead-free clay pots is crucial to ensure a non-toxic stewing experience while enjoying traditional cooking benefits.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Stainless Steel vs Clay
Stainless steel pots are easier to clean and maintain, resisting stains and odors from stewing. Clay pots require careful hand washing and seasoning to prevent cracking and retain their porous quality.
- Durability - Stainless steel withstands abrasive cleaning and dishwasher use without damage.
- Porosity - Clay pots absorb flavors and moisture, necessitating gentle cleaning to avoid residue buildup.
- Maintenance - Stainless steel needs minimal upkeep while clay pots require seasoning and thorough drying to extend lifespan.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Value
Stainless steel pots generally require a higher initial investment compared to clay pots but offer greater long-term durability and versatility. Clay pots, while more affordable upfront, may require more frequent replacement due to their fragile nature.
- Stainless steel pot cost - The average price ranges from $40 to $150 depending on size and brand.
- Clay pot cost - Typically priced between $15 and $50, making it an economical choice for budget-conscious cooks.
- Value over time - Stainless steel pots provide better value due to their resistance to breaking and ease of maintenance.
Choosing between these pots depends on balancing initial budget constraints with long-term usage needs.
Best Dishes for Each Pot Type
Stainless steel pots excel at quick, high-heat stewing, preserving the texture of meats and vegetables. Clay pots are ideal for slow, even cooking that enhances flavors and tenderness over extended periods.
- Beef stews and braises - Benefit from stainless steel's heat control for a rich, caramelized crust.
- Traditional tagines and herbal soups - Thrive in clay pots due to their moisture-retaining properties and steady heat distribution.
- Vegetable stews and grains - Cook evenly in clay pots, maintaining natural flavors and nutrients.
Related Important Terms
Thermal inertia advantage
Stainless steel pots boast high thermal conductivity but lower thermal inertia, leading to quicker temperature fluctuations during stewing; in contrast, clay pots offer superior thermal inertia, maintaining consistent heat over extended periods for even cooking and enhanced flavor development. This thermal retention in clay pots prevents sudden temperature drops, making them ideal for slow and gentle stewing processes.
Micro-flavor permeation
Stainless steel pots offer rapid heat conduction but lack the porous structure that facilitates micro-flavor permeation, resulting in a more uniform but less infused taste. Clay pots, with their porous composition, enable gradual heat distribution and allow micro-flavors to penetrate deeply into ingredients, enhancing the complexity and depth of stewed dishes.
Clay pot mineral infusion
Clay pots enhance stewing by releasing beneficial minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and iron into the food, enriching flavor and nutritional value. Unlike stainless steel pots, clay pots provide natural heat retention and slow, even cooking that deepens taste while promoting mineral infusion.
Metallic ion transfer
Stainless steel pots resist metallic ion transfer, ensuring no alteration in flavor or potential toxicity during stewing, while clay pots may release trace amounts of metallic ions that can subtly influence the taste and nutritional content of the dish. The inert nature of stainless steel makes it ideal for slow cooking without chemical interaction, whereas porous clay pots can absorb and leach ions, affecting the stew's overall quality.
Slow heat diffusion
Stainless steel pots provide rapid heat conduction with slow diffusion, allowing precise temperature control during stewing, while clay pots offer slow, even heat diffusion that enhances flavor absorption and tenderizes ingredients over long cooking times. The choice between stainless steel and clay pots affects the consistency and depth of stewed dishes, with stainless steel granting quicker heat response and clay pots promoting gentle, uniform cooking.
Steam loop sealing
Stainless steel pots provide a tighter steam loop sealing due to their rigid construction and precision-fitted lids, which helps retain moisture and intensify flavors during stewing. Clay pots, while offering porous properties that allow slight steam escape and gradual moisture circulation, often result in less efficient steam loop sealing, affecting the stew's consistency and depth.
Glaze porosity interaction
Stainless steel pots offer a non-porous, smooth surface that prevents flavor absorption and ensures even heat distribution for consistent stewing results. In contrast, clay pots feature a porous, glazed surface that interacts with moisture and enhances flavor infusion but may absorb oils and liquids over time, affecting taste complexity and pot durability.
Broth umami enhancement
Stainless steel pots maintain a neutral flavor profile, allowing the natural umami of ingredients to shine without interference, while clay pots absorb and release moisture slowly, enriching the broth with deeper, more complex umami nuances. The porous nature of clay facilitates prolonged heat retention and gradual flavor melding, resulting in a richer, more savory stew compared to the cleaner, more straightforward broth from stainless steel.
Stew base caramelization
Stainless steel pots excel at stew base caramelization due to their high heat conductivity and non-porous surface, allowing for even browning and flavor development without absorbing odor. Clay pots retain moisture well but offer slower caramelization because their porous material distributes heat unevenly, resulting in a milder, less intense stew base.
Stainless steel pot vs Clay pot for stewing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com