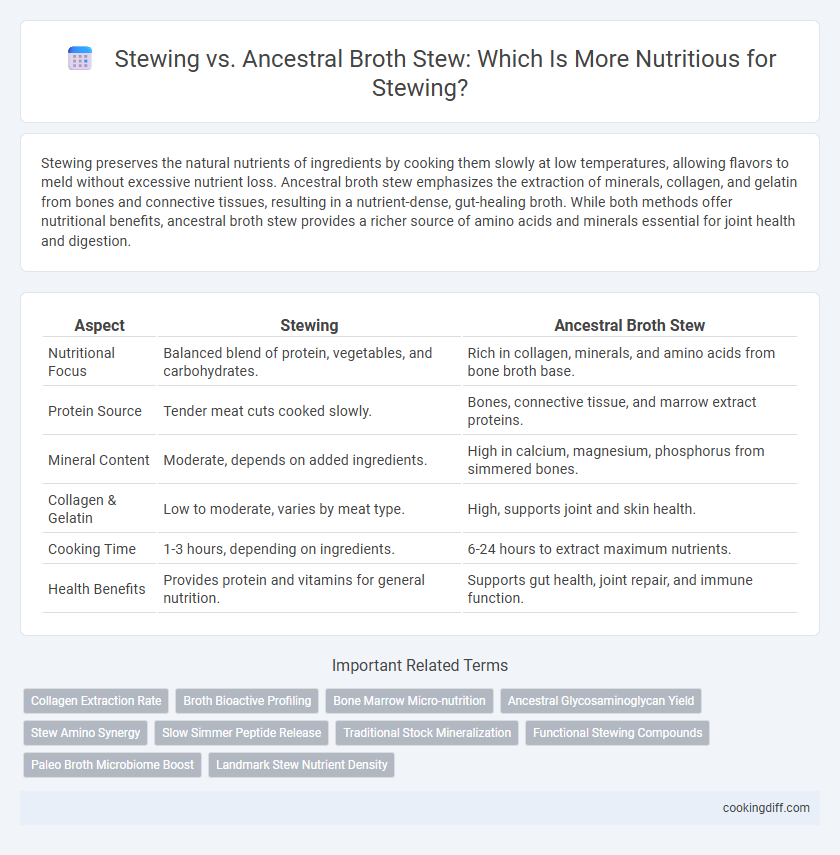
Stewing preserves the natural nutrients of ingredients by cooking them slowly at low temperatures, allowing flavors to meld without excessive nutrient loss. Ancestral broth stew emphasizes the extraction of minerals, collagen, and gelatin from bones and connective tissues, resulting in a nutrient-dense, gut-healing broth. While both methods offer nutritional benefits, ancestral broth stew provides a richer source of amino acids and minerals essential for joint health and digestion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stewing | Ancestral Broth Stew |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Focus | Balanced blend of protein, vegetables, and carbohydrates. | Rich in collagen, minerals, and amino acids from bone broth base. |
| Protein Source | Tender meat cuts cooked slowly. | Bones, connective tissue, and marrow extract proteins. |
| Mineral Content | Moderate, depends on added ingredients. | High in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus from simmered bones. |
| Collagen & Gelatin | Low to moderate, varies by meat type. | High, supports joint and skin health. |
| Cooking Time | 1-3 hours, depending on ingredients. | 6-24 hours to extract maximum nutrients. |
| Health Benefits | Provides protein and vitamins for general nutrition. | Supports gut health, joint repair, and immune function. |
Understanding Stewing: Classic Cooking Technique Explained
Stewing is a slow-cooking method that immerses ingredients in liquid to break down fibers and extract rich flavors while preserving nutrients. Unlike ancestral broth stews, which rely heavily on bone marrow and connective tissue for mineral content, classic stewing emphasizes tender meat and vegetable integration.
- Stewing Technique - Involves simmering meat and vegetables at low temperatures for several hours, ensuring nutrient retention.
- Nutritional Focus - Classic stewing prioritizes balanced protein and vitamin release from fresh ingredients rather than mineral extraction.
- Ancestral Broth Stew - Uses long-simmered bones to enrich the broth with collagen, calcium, and trace minerals, differing from standard stewing approaches.
What is Ancestral Broth Stew?
What distinguishes Ancestral Broth Stew from traditional stewing methods? Ancestral Broth Stew prioritizes nutrient-dense bone broth made by simmering bones and connective tissues for extended periods, extracting collagen, minerals, and amino acids. This method enhances gut health and joint support, offering superior nutritional benefits compared to conventional stews that primarily use meat and vegetables.
Nutritional Breakdown: Stewing Versus Broth Stews
Stewing incorporates whole pieces of meat and vegetables simmered for an extended period, preserving a broader spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Ancestral broth stews concentrate on extracting collagen, gelatin, and trace minerals from bones through slow cooking, resulting in a nutrient-dense liquid rich in amino acids and minerals like calcium and magnesium.
The nutritional profile of stewing offers higher protein and fiber content due to the inclusion of solid ingredients, supporting muscle repair and digestive health. In contrast, broth stews provide concentrated electrolytes and compounds beneficial for joint health and gut lining, often lacking in fiber but superior in bioavailable minerals.
Essential Nutrients Preserved in Stewing
Stewing retains a higher concentration of essential nutrients such as collagen, amino acids, and minerals compared to Ancestral Broth Stew, which often involves longer cooking times leading to nutrient degradation. The controlled heat and moisture in stewing help preserve vitamins like B-complex and minerals including calcium, magnesium, and potassium, essential for metabolic and immune functions. This nutrient-rich environment supports optimal absorption, making stewing a superior method for maintaining the bioavailability of key nutrients critical for overall health.
Bone Broth Stew: Key Nutritional Highlights
Bone Broth Stew is rich in collagen, gelatin, and essential amino acids that support joint health and skin elasticity. The slow simmering process extracts minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, enhancing bone strength and immune function. Compared to Ancestral Broth Stew, bone broth offers higher bioavailable nutrients crucial for gut healing and inflammation reduction.
Protein Quality: Stewing vs Broth-Based Stews
Stewing preserves the protein integrity of whole meats and vegetables by slow cooking them together, resulting in a nutrient-rich dish with high-quality amino acids. Ancestral broth stews, primarily made from bones and connective tissues, offer gelatin and collagen but often contain less complete protein compared to traditional stews.
The protein quality in stewing is superior due to the retention of muscle fibers and essential amino acids, which are less prevalent in broth-based stews. Broth-based stews excel in providing joint-supporting nutrients like collagen, but their overall protein profile lacks the complete spectrum found in stews with meat. For optimal nutritional intake, combining both methods can balance high-quality protein and beneficial collagen compounds.
Mineral Absorption: Broth Stew Advantages
Stewing extracts minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium effectively, enhancing nutrient bioavailability in broth stews compared to traditional stewing methods. The prolonged simmering process in broth stew breaks down bones and connective tissues, releasing essential minerals into the liquid.
Mineral absorption is further improved due to the gelatin and collagen content in broth stews, which aid digestion and nutrient uptake. This results in a nutrient-dense meal that supports bone health and overall mineral balance.
Collagen and Gelatin Content in Ancestral Stews
| Cooking Method | Collagen Content | Gelatin Presence | Nutritional Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stewing | Moderate | Partial | Provides basic protein and minerals |
| Ancestral Broth Stew | High | Rich and abundant | Enhanced joint and skin support due to superior collagen and gelatin extraction |
Micronutrient Retention: Comparing Cooking Methods
Stewing typically involves prolonged cooking times at lower temperatures, which can reduce the retention of heat-sensitive micronutrients in vegetables and meat. Ancestral broth stew methods, often simmered gently for extended periods, may enhance mineral extraction from bones while sacrificing some vitamins.
- Micronutrient Retention - Stewing can cause vitamin loss but increases mineral availability through slow cooking.
- Bone-Derived Nutrients - Ancestral broth stews extract calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus effectively from bones.
- Vitamin Preservation - Shorter cooking or lower heat improves retention of water-soluble vitamins compared to extended stewing.
Balancing cooking time and temperature is key to maximizing micronutrient retention in both stewing and ancestral broth stews.
Related Important Terms
Collagen Extraction Rate
Stewing achieves moderate collagen extraction as prolonged simmering breaks down connective tissues, but ancestral broth stew excels by using long, slow cooking with bones and connective tissues, maximizing collagen release for superior nutritional benefits. The higher collagen extraction rate in ancestral broth stew supports joint health, skin elasticity, and gut repair more effectively than traditional stewing methods.
Broth Bioactive Profiling
Stewing extracts bioactive compounds such as collagen, amino acids, and minerals through prolonged simmering, while Ancestral Broth Stew emphasizes enhanced broth bioactive profiling by incorporating bones, connective tissues, and aromatic herbs rich in gelatin, glucosamine, and antioxidants. Nutritional focus on broth bioactive profiling reveals higher concentrations of peptides, electrolytes, and anti-inflammatory nutrients in Ancestral Broth Stew compared to basic stewing methods.
Bone Marrow Micro-nutrition
Stewing extracts minerals, collagen, and nutrients from bone marrow, enhancing bioavailable micro-nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus vital for bone health. Ancestral Broth Stew, simmered for extended hours, maximizes marrow's micro-nutrition by breaking down connective tissues, releasing concentrated vitamins and fatty acids essential for cellular regeneration and immune support.
Ancestral Glycosaminoglycan Yield
Stewing typically involves prolonged simmering that extracts collagen and nutrients, but Ancestral Broth Stew maximizes glycosaminoglycan yield by utilizing traditional slow-cooking techniques and specific bone selections rich in cartilage. This method enhances joint-supporting compounds like chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid, offering superior nutritional benefits compared to standard stewing.
Stew Amino Synergy
Stewing enhances nutrient extraction by breaking down proteins and collagen, promoting optimal amino acid synergy vital for muscle repair and immune support. Compared to ancestral broth stew, stewing preserves a balanced amino acid profile, maximizing nutrient bioavailability and supporting overall metabolic health.
Slow Simmer Peptide Release
Stewing utilizes slow simmering to break down collagen and connective tissues, enhancing peptide release for improved protein bioavailability and nutrient absorption. Ancestral broth stew, often simmered for extended hours, maximizes amino acid and mineral extraction, supporting gut health and providing a rich source of bioactive peptides crucial for cellular repair.
Traditional Stock Mineralization
Stewing enhances nutrient absorption by slow-cooking ingredients in their natural juices, promoting the release of minerals and collagen. Ancestral broth stew, rooted in traditional stock mineralization techniques, maximizes mineral content through prolonged simmering of bones and connective tissue, resulting in a highly bioavailable source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus.
Functional Stewing Compounds
Stewing concentrates functional compounds like gelatin, collagen, and amino acids, enhancing nutrient bioavailability and gut health compared to ancestral broth stew, which primarily emphasizes mineral extraction from bones. The higher presence of Maillard reaction products and slow-cooked vegetables in stewing promotes anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects absent or minimal in traditional ancestral broth preparation.
Paleo Broth Microbiome Boost
Stewing enhances nutrient extraction by slowly breaking down collagen and minerals, supporting gut health through gelatin-rich Paleo broth that nurtures the microbiome. Ancestral broth stew prioritizes traditional simmering techniques to maximize amino acids and minerals, optimizing digestive benefits crucial for a balanced microbiome and improved nutrient absorption.
Stewing vs Ancestral Broth Stew for nutritional focus. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com