Stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid at low temperatures to tenderize ingredients and develop rich flavors. Stone pot stewing enhances this process by using a heavy, heat-retaining stone vessel that distributes heat evenly and maintains consistent cooking temperatures, resulting in deeper flavor infusion and better texture. This method is especially effective for achieving a hearty, savory stew with intensified aroma and tender ingredients.
Table of Comparison
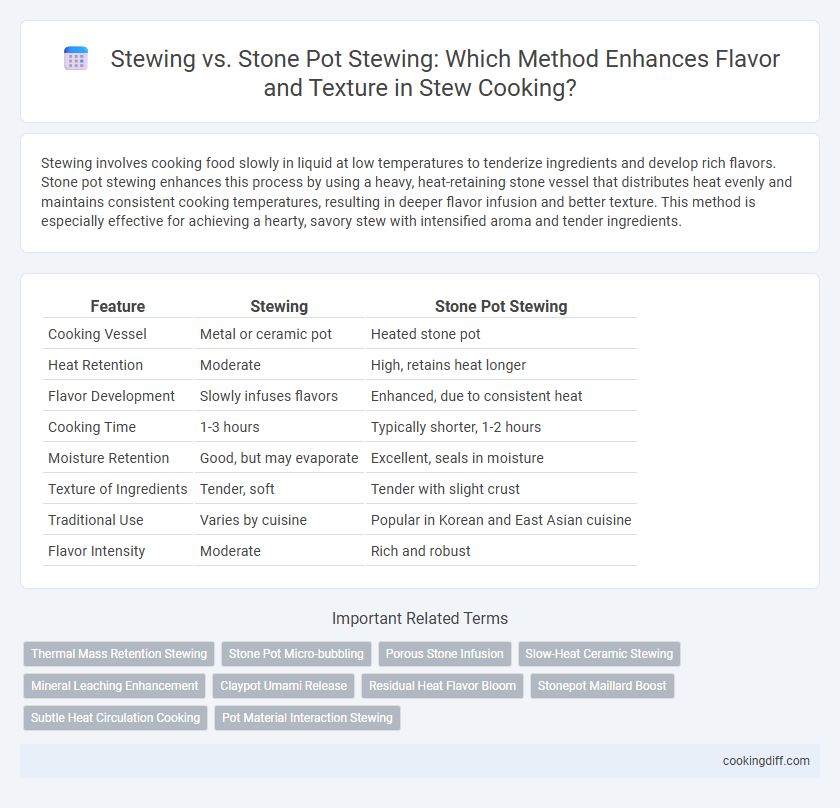
| Feature | Stewing | Stone Pot Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Vessel | Metal or ceramic pot | Heated stone pot |
| Heat Retention | Moderate | High, retains heat longer |
| Flavor Development | Slowly infuses flavors | Enhanced, due to consistent heat |
| Cooking Time | 1-3 hours | Typically shorter, 1-2 hours |
| Moisture Retention | Good, but may evaporate | Excellent, seals in moisture |
| Texture of Ingredients | Tender, soft | Tender with slight crust |
| Traditional Use | Varies by cuisine | Popular in Korean and East Asian cuisine |
| Flavor Intensity | Moderate | Rich and robust |
Introduction to Stewing: Traditional Cooking Techniques
Stewing is a traditional cooking technique that involves slow-cooking ingredients in liquid over low heat to tenderize tougher cuts of meat and develop rich flavors. This method allows the natural juices and seasonings to blend, producing a hearty and comforting dish.
Stone pot stewing uses a heavy stone pot that retains and distributes heat evenly, enhancing the stewing process by maintaining consistent temperature and moisture. This technique is especially popular in Korean cuisine, adding a unique earthy flavor and texture to the stew.
What is Stone Pot Stewing?
Stone pot stewing is a traditional cooking method that uses a thick, heat-retentive stone pot to cook ingredients slowly and evenly. This method enhances flavors and retains moisture better than conventional stewing techniques.
- Material - Stone pots are made from natural volcanic or granite stone, providing excellent heat retention and distribution.
- Cooking Process - The heavy pot traps heat and steam inside, allowing ingredients to simmer gently and develop deep, rich flavors.
- Flavor Profile - Stone pot stewing intensifies the taste and texture of dishes by sealing in juices and nutrients throughout the cooking process.
Core Principles of Classic Stewing
Classic stewing involves slow cooking food in a sealed pot with moderate liquid to allow flavors to meld and meats to tenderize over time. Stone pot stewing enhances heat retention and even cooking, using a porous pot that intensifies flavor concentration and moisture preservation.
- Low and slow cooking - Stewing requires maintaining a low temperature for an extended period to break down tough fibers in ingredients.
- Liquid immersion - Ingredients are submerged in broth or sauce to facilitate even heat distribution and flavor infusion.
- Seal and simmer - A tight seal on the pot locks in moisture and aroma, creating a tender, richly flavored dish.
Unique Benefits of Stone Pot Stewing
Stone pot stewing offers superior heat retention compared to traditional stewing methods, allowing for even cooking and enhanced flavor infusion. The porous nature of the stone pot helps retain moisture, resulting in tender, succulent dishes with richer textures. Unique mineral properties of stone pots also contribute subtle earthy notes, elevating the overall taste profile of stewed ingredients.
Flavor Development: Stewing vs Stone Pot Stewing
| Flavor Development in Stewing | Stewing involves slow cooking ingredients in liquid, allowing flavors to meld as heat breaks down fibers and fats, producing rich, tender meals. |
| Flavor Development in Stone Pot Stewing | Stone pot stewing enhances flavor by retaining heat evenly and distributing it gradually, intensifying the aroma and depth of spices through the pot's porous surface. |
| Comparison | Stone pot stewing achieves more concentrated and layered flavors due to consistent heat retention and natural mineral infusion, while traditional stewing relies largely on slow simmering in metal cookware. |
Texture Differences: Pottery vs Conventional Cookware
Stewing in stone pots enhances texture by retaining heat evenly and allowing slow, uniform cooking. Conventional cookware often leads to quicker heat fluctuations, affecting the final softness of ingredients.
- Heat Retention - Stone pots maintain consistent heat, promoting tender and moist textures in stews.
- Surface Porosity - Pottery's porous surface absorbs and redistributes moisture, enriching the stew's mouthfeel.
- Material Density - Conventional cookware's metal density causes rapid temperature changes, sometimes resulting in unevenly cooked textures.
Stone pot stewing delivers a richer, more complex texture that conventional cookware cannot easily replicate.
Temperature Control in Stewing Methods
Stewing typically requires moderate, steady heat to ensure ingredients cook evenly while retaining moisture, with temperatures usually maintained between 180degF and 205degF. Stone pot stewing offers superior temperature control due to the pot's thick walls, which distribute heat gradually and maintain consistent warmth for prolonged periods.
Precise temperature control in stone pot stewing enhances flavor development by preventing overheating and reducing the risk of ingredient overcooking or burning. This method creates a stable cooking environment, ideal for recipes requiring long, slow simmering to tenderize tougher cuts of meat and infuse rich flavors.
Nutrient Retention: Comparing Cooking Outcomes
Stewing preserves nutrients by slowly cooking ingredients in a sealed pot, allowing vitamins and minerals to remain within the dish. Stone pot stewing enhances nutrient retention further by providing even heat distribution and retaining moisture, reducing nutrient loss through evaporation. Studies show stone pot stewing can retain up to 15% more vitamins compared to conventional stewing methods.
Best Dishes for Each Stewing Technique
Traditional stewing is ideal for dishes like beef bourguignon and coq au vin, where slow cooking tenderizes tougher cuts of meat and blends rich flavors. Stone pot stewing excels with Korean dishes such as kimchi jjigae or sundubu jjigae, as the pot retains heat evenly, enhancing the depth and spiciness of the broth.
Beef bourguignon benefits from the long, slow cooking process of traditional stewing, allowing the wine and herbs to infuse deeply. Stone pot stewing is perfect for seafood stews and tofu-based dishes, which require steady, high heat to develop complex, layered flavors. Both methods highlight unique textures and intensities, making them suitable for specific types of cuisine and ingredient combinations.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Mass Retention Stewing
Stewing in traditional pots offers less thermal mass retention compared to stone pot stewing, which excels in maintaining consistent heat for longer periods due to the stone's dense material. This enhanced thermal mass retention in stone pots allows for more even cooking, deeper flavor development, and improved tenderness of stewed ingredients.
Stone Pot Micro-bubbling
Stone pot stewing enhances flavor and tenderness through its unique micro-bubbling effect, which evenly distributes heat and retains moisture better than traditional stewing methods. This slow, consistent simmering in a stone pot results in richer aromas and more succulent textures, making it ideal for long-cooked dishes.
Porous Stone Infusion
Porous stone infusion in stone pot stewing enhances flavor absorption by allowing slow, even heat distribution and gradual release of minerals, which enriches the stew's taste and texture compared to traditional stewing methods. This natural porosity also helps retain moisture and nutrients, creating a more aromatic and nourishing dish.
Slow-Heat Ceramic Stewing
Slow-heat ceramic stewing enhances flavor retention and nutrient preservation by evenly distributing heat at low temperatures, unlike traditional stewing methods that often use quicker, uneven heating. Stone pot stewing offers high heat retention but can cause localized overcooking, whereas slow-heat ceramic pots provide a gentle, consistent simmer ideal for tenderizing tough ingredients and developing rich, complex flavors.
Mineral Leaching Enhancement
Stone pot stewing enhances mineral leaching by utilizing the pot's porous structure to slowly release essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron into the food. Traditional stewing methods typically lack this mineral infusion, resulting in a less nutrient-rich broth.
Claypot Umami Release
Stewing in a traditional claypot enhances the umami flavor by allowing slow, even heat distribution that helps break down ingredients and meld savory tastes deeply. Stone pot stewing, while also retaining heat well, tends to trap moisture more effectively, intensifying the umami release through gentle simmering and minimal evaporation.
Residual Heat Flavor Bloom
Stewing in a traditional pot allows for even heat distribution but often loses residual heat quickly, which can diminish flavor bloom compared to stone pot stewing. Stone pot stewing retains residual heat longer due to its dense material, enhancing the extraction and melding of flavors for a richer, more aromatic dish.
Stonepot Maillard Boost
Stone pot stewing enhances the Maillard reaction by maintaining higher, more consistent heat compared to traditional stewing methods, resulting in deeper caramelization and richer flavor development in slow-cooked dishes. This heat retention characteristic of stone pots promotes intensified browning and savory complexity, making stone pot stewing a superior technique for maximizing taste and texture.
Subtle Heat Circulation Cooking
Stewing uses consistent, low-temperature heat to slowly break down fibers and infuse flavors, while stone pot stewing enhances this process through subtle heat circulation within the porous stone, ensuring even cooking and moisture retention. The stone pot's thermal properties promote gradual, uniform heat distribution that deepens flavors and maintains tenderness more effectively than traditional stewing methods.
Stewing vs Stone Pot Stewing for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com