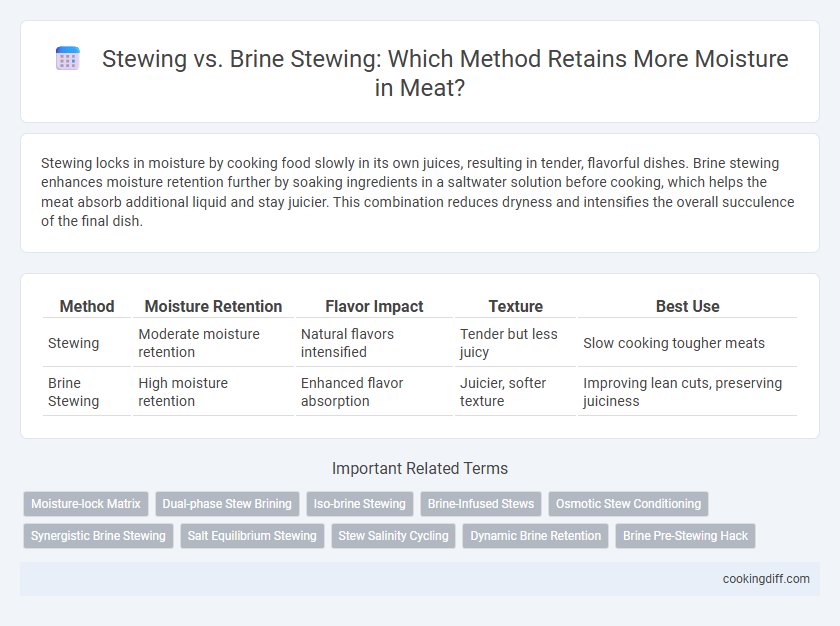
Stewing locks in moisture by cooking food slowly in its own juices, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes. Brine stewing enhances moisture retention further by soaking ingredients in a saltwater solution before cooking, which helps the meat absorb additional liquid and stay juicier. This combination reduces dryness and intensifies the overall succulence of the final dish.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Moisture Retention | Flavor Impact | Texture | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stewing | Moderate moisture retention | Natural flavors intensified | Tender but less juicy | Slow cooking tougher meats |
| Brine Stewing | High moisture retention | Enhanced flavor absorption | Juicier, softer texture | Improving lean cuts, preserving juiciness |
Introduction to Stewing and Brine Stewing
Stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid at low temperatures, which allows flavors to meld and the meat to become tender. This method relies on the natural moisture within the ingredients to maintain juiciness during cooking.
Brine stewing enhances moisture retention by first soaking the meat in a saltwater solution, which helps cells absorb and retain water. This process increases the meat's ability to stay juicy throughout the slow cooking phase. By combining brining with traditional stewing, the final dish achieves a more flavorful and succulent texture compared to stewing alone.
Understanding Moisture Retention in Cooking
Stewing preserves moisture by gently simmering food in liquid, allowing connective tissues to break down slowly and retain juices. Brine stewing enhances this effect by pre-soaking ingredients in a salt solution, which increases water absorption and prevents dryness during cooking.
- Stewing - Uses low heat and liquid to slowly tenderize meat, maintaining natural juices.
- Brine soaking - Infuses salt and water into the meat, increasing its water retention capacity.
- Moisture retention - Directly impacts texture and flavor by reducing moisture loss during cooking.
Combining brine soaking with stewing optimizes moisture retention for juicier, more flavorful dishes.
What Is Traditional Stewing?
Traditional stewing involves cooking food slowly in a closed pot with a moderate amount of liquid, allowing natural juices to infuse the dish and enhance moisture retention. This method relies on low, consistent heat to break down tough fibers in meats and vegetables, resulting in tender, flavorful outcomes. Unlike brine stewing, it does not use a preliminary soaking in saltwater, making the process simpler but sometimes less effective at maximizing internal moisture.
Defining Brine Stewing Methods
Brine stewing involves soaking meat in a saltwater solution before cooking to enhance moisture retention and tenderness. This method contrasts with traditional stewing by integrating a pre-treatment that improves flavor infusion and juiciness.
- Soaking in saline - Meat is immersed in a brine solution, typically containing salt and water, to allow salt ions to penetrate muscle fibers.
- Enhanced water retention - The salt alters protein structures, increasing the meat's capacity to retain moisture during the stewing process.
- Flavor development - Brine stewing facilitates deeper seasoning absorption, resulting in more flavorful and succulent dishes compared to conventional stewing methods.
Science Behind Moisture Retention in Stewing
Stewing retains moisture by cooking food slowly in liquid, allowing muscle fibers to break down and absorb the surrounding juices, which prevents drying out. The heat causes collagen in connective tissues to convert into gelatin, enhancing the dish's overall moisture and tenderness.
Brine stewing introduces a saline solution before cooking, which increases the meat's ability to hold water through protein denaturation and osmosis. This process augments moisture retention, resulting in juicier and more flavorful stewed dishes compared to traditional stewing alone.
How Brine Stewing Affects Juiciness
Brine stewing enhances meat juiciness by allowing salt and water to penetrate muscle fibers, increasing moisture retention. This method prevents drying out during cooking compared to traditional stewing techniques.
- Salt Penetration - Brining causes proteins to relax and absorb water, making the meat more tender and juicy.
- Moisture Retention - The salt solution reduces moisture loss during heat application in the stewing process.
- Improved Texture - Brine stewing results in a softer, more succulent texture due to better water distribution in the meat fibers.
Key Ingredient Differences: Water vs. Brine
How do key ingredient differences between stewing and brine stewing affect moisture retention? Stewing primarily uses water, which allows natural flavors to infuse but may result in moderate moisture retention. Brine stewing incorporates a saltwater solution, enhancing moisture retention by improving the meat's ability to hold water during cooking.
Texture and Flavor Outcomes Compared
| Stewing | Brine Stewing |
|---|---|
| Maintains natural texture by slow cooking in liquid, tenderizing meat through heat and moisture. Flavor develops from cooking ingredients and seasoning without altering the meat's intrinsic taste. | Enhances moisture retention by pre-soaking meat in saltwater solution, resulting in juicier and more succulent texture. Infuses subtle saltiness and additional depth to flavor profiles, improving overall taste complexity. |
Pros and Cons: Stewing vs. Brine Stewing
Stewing preserves moisture by cooking food slowly in its own juices, enhancing natural flavors without added salt, making it ideal for tender cuts of meat. Brine stewing involves soaking ingredients in a saltwater solution before cooking, which increases moisture retention and improves texture but can result in a slightly saltier taste. While stewing is simpler and retains original flavors, brine stewing offers better juiciness and tenderness at the risk of over-salting.
Related Important Terms
Moisture-lock Matrix
Stewing creates a moisture-lock matrix by slowly cooking food in liquid, allowing natural fibers to absorb and retain moisture effectively. Brine stewing enhances this process by soaking ingredients in a saltwater solution beforehand, which increases their water-holding capacity and improves overall juiciness during cooking.
Dual-phase Stew Brining
Dual-phase stew brining significantly enhances moisture retention by combining initial brining with subsequent stewing, allowing meat fibers to absorb and lock in water more effectively than traditional stewing alone. This method optimizes juiciness and tenderness through controlled salt diffusion and gradual cooking, resulting in superior texture and flavor.
Iso-brine Stewing
Iso-brine stewing enhances meat moisture retention by maintaining an equilibrium salt concentration that prevents protein denaturation and water loss. Compared to traditional stewing, iso-brine stewing optimizes texture and juiciness through controlled osmotic balance.
Brine-Infused Stews
Brine-infused stews enhance moisture retention by allowing the meat to absorb a saltwater solution before cooking, which helps retain juiciness and tenderness during the stewing process. Compared to traditional stewing, this method reduces moisture loss and results in a richer, more flavorful dish.
Osmotic Stew Conditioning
Osmotic stew conditioning enhances moisture retention by using a brine solution to create an osmotic gradient that draws water into the meat fibers, preventing dehydration during cooking. Unlike traditional stewing, this method improves tenderness and juiciness by maintaining higher internal moisture levels throughout the process.
Synergistic Brine Stewing
Synergistic brine stewing enhances moisture retention by combining salt-induced protein swelling with gentle cooking, resulting in juicier, more tender meats compared to traditional stewing. The brine solution facilitates deeper flavor penetration while preserving cellular moisture, optimizing texture and succulence in the final dish.
Salt Equilibrium Stewing
Salt Equilibrium Stewing enhances moisture retention by balancing salt concentration inside and outside the meat, preventing excessive water loss during cooking. Compared to traditional brine stewing, this method ensures uniform salt diffusion, resulting in juicier, tender stewed dishes with optimal hydration.
Stew Salinity Cycling
Stew salinity cycling enhances moisture retention by alternating between low and high salt concentrations, promoting cell structure regulation and water absorption. Traditional stewing lacks this dynamic salinity adjustment, often resulting in less effective moisture preservation during cooking.
Dynamic Brine Retention
Dynamic brine retention enhances moisture retention in stewing by enabling continuous absorption and redistribution of brine within the meat fibers, leading to juicier and more tender results compared to traditional stewing. This process optimizes water-binding capacity through osmotic pressure and ionic interactions, significantly reducing moisture loss during prolonged cooking.
Stewing vs Brine Stewing for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com