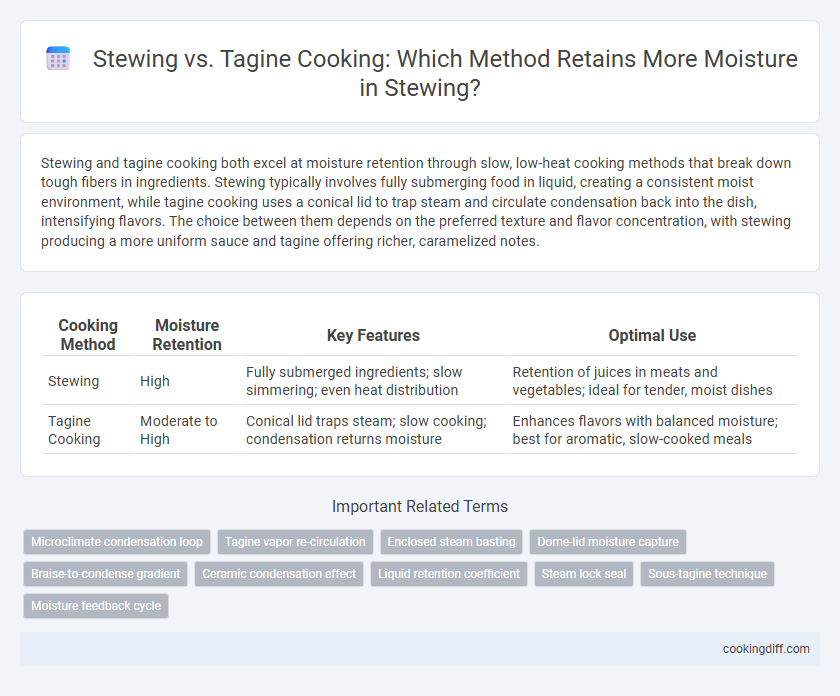
Stewing and tagine cooking both excel at moisture retention through slow, low-heat cooking methods that break down tough fibers in ingredients. Stewing typically involves fully submerging food in liquid, creating a consistent moist environment, while tagine cooking uses a conical lid to trap steam and circulate condensation back into the dish, intensifying flavors. The choice between them depends on the preferred texture and flavor concentration, with stewing producing a more uniform sauce and tagine offering richer, caramelized notes.
Table of Comparison
| Cooking Method | Moisture Retention | Key Features | Optimal Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stewing | High | Fully submerged ingredients; slow simmering; even heat distribution | Retention of juices in meats and vegetables; ideal for tender, moist dishes |
| Tagine Cooking | Moderate to High | Conical lid traps steam; slow cooking; condensation returns moisture | Enhances flavors with balanced moisture; best for aromatic, slow-cooked meals |
Introduction to Stewing and Tagine Cooking
Stewing involves cooking ingredients slowly in a liquid at low temperatures, which helps retain moisture by breaking down connective tissues and releasing gelatin. Tagine cooking, originating from North Africa, uses a conical clay pot designed to circulate steam and condense it back to the dish, enhancing moisture retention naturally. Both methods excel in preserving juiciness, but tagine's unique vessel provides an aromatic infusion alongside superior moisture control.
Defining Moisture Retention in Cooking
Moisture retention in cooking refers to the ability of a method to preserve the natural juices and liquids within food, preventing dryness. Stewing involves submerging ingredients in liquid and slow cooking them, which helps maintain high moisture levels and tenderizes tough cuts. Tagine cooking uses a conical lid that traps steam and condenses it back onto the food, enhancing moisture retention through a self-basting cycle.
How Stewing Retains Moisture
How does stewing retain moisture more effectively compared to tagine cooking? Stewing involves submerging ingredients completely in liquid, which creates a sealed environment that prevents moisture from escaping. This method ensures that juices are locked within the food, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes with enhanced moisture retention.
Tagine: Traditional Methods for Locking in Juices
Tagine cooking utilizes a conical clay pot that promotes steam circulation, effectively locking in moisture and enhancing the flavor profile of the dish. The slow, low-heat method allows ingredients to simmer gently, preserving natural juices more efficiently than typical stewing techniques.
The sealed design of a tagine ensures condensation drips back onto the food, maintaining tenderness and preventing dryness during the cooking process. Traditional Moroccan tagine recipes emphasize this approach for superior moisture retention compared to standard stewing pots.
Differences in Cooking Vessels: Pots vs Tagines
Stewing utilizes heavy pots with tight-fitting lids that ensure even heat distribution and moisture retention through simmering. Tagines feature a conical clay lid designed to trap steam and return condensed liquid back to the dish, enhancing flavor concentration and juiciness.
- Stewing Pots - Typically made of cast iron or stainless steel, these pots provide uniform heat and a sealed environment to prevent moisture loss during long cooking times.
- Tagine Vessels - Crafted from clay or ceramic, the tagine's shape promotes continuous steam circulation, which naturally bastes the food and preserves moisture.
- Moisture Retention Differences - Stewing pots rely on tight lids to contain liquid, while tagines use their unique design to recycle steam, resulting in subtly different textures and flavor profiles.
Heat Distribution and Its Effect on Moisture
Stewing involves simmering ingredients in liquid over low heat, ensuring even heat distribution that promotes consistent moisture retention throughout the dish. Tagine cooking uses a conical clay pot that traps steam, creating a self-basting environment enhancing moisture preservation.
The tagine's unique shape allows heat to circulate gently, concentrating steam and preventing evaporation, which maintains the food's tenderness and juiciness. Stewing's uniform heat ensures that all ingredients absorb flavors evenly but may lose moisture faster due to direct liquid contact and occasional stirring. Consequently, tagine cooking excels in moisture retention by combining low heat with steam recirculation, while stewing relies on consistent simmering to keep ingredients moist.
Flavor Development: Stew vs Tagine
| Flavor Development: Stewing vs Tagine |
| Stewing involves slow cooking ingredients in a sealed pot, promoting even moisture retention and deep flavor absorption through prolonged simmering. Tagine cooking uses a conical clay pot that traps steam and concentrates flavors, enhancing aromatic spices and tenderizing meat with minimal evaporation. The unique design of the tagine intensifies flavor layering, while stewing offers consistent, hearty taste integration over extended cooking times. |
Ingredient Preparation and Liquid Ratios
Stewing involves submerging ingredients fully in liquid, typically using a ratio of 1:2 ingredients to liquid, which ensures thorough moisture retention by slow simmering. Ingredient preparation in stewing often includes uniform chopping to promote even cooking and absorption of flavors throughout the dish.
Tagine cooking uses less liquid, often relying on the moisture released from ingredients combined with a tightly sealed conical lid to circulate steam effectively and retain moisture. Ingredients are usually layered and sometimes partially cooked beforehand to optimize the balance between liquid evaporation and retention within the tagine vessel.
Best Recipes for Moisture Retention in Each Method
Stewing and tagine cooking both excel in moisture retention by slow-cooking ingredients in sealed environments, but they differ in vessel design and heat distribution. Each method benefits from specific recipes that maximize tenderness and juiciness of the meat and vegetables.
- Classic Beef Stew - Uses a heavy pot with a tight lid to trap steam, ensuring the beef becomes tender while retaining its natural juices.
- Moroccan Chicken Tagine - Combines preserved lemons and olives in a conical lid pot that circulates moisture back into the dish, preserving succulent chicken flavors.
- Lamb and Vegetable Tagine - Slow-cooks lamb with root vegetables in a ceramic tagine, maintaining a moist environment that enhances spice absorption and tenderness.
Selecting recipes that complement each cooking method's moisture retention strengths guarantees rich, flavorful results.
Related Important Terms
Microclimate condensation loop
Stewing creates a sealed environment where heat and liquid circulate, promoting a microclimate condensation loop that efficiently retains moisture in the food. Tagine cooking enhances this effect through its conical lid, which condenses steam and allows it to drip back onto the ingredients, intensifying flavors while preserving juiciness.
Tagine vapor re-circulation
Stewing relies on fully submerging ingredients in liquid, while Tagine cooking utilizes a conical lid that condenses steam and recirculates moisture back onto the food, enhancing flavor retention and tenderness. This vapor re-circulation system in Tagine minimizes moisture loss, creating a self-basting environment that preserves juiciness better than traditional stewing methods.
Enclosed steam basting
Stewing and tagine cooking both utilize enclosed steam basting to enhance moisture retention, but tagines, with their conical lids, allow steam to condense and drip back onto the food more efficiently, preserving juiciness and tenderness. This unique steam circulation in tagine vessels minimizes evaporation compared to traditional stewing pots, resulting in richer flavors and moist textures.
Dome-lid moisture capture
Stewing typically relies on a sealed pot to retain moisture by trapping steam, but tagine cooking excels with its distinctive dome-lid design that captures condensation and directs it back into the dish, enhancing flavor concentration and moisture retention. The moisture captured on the dome lid continuously drips back onto the ingredients, ensuring a tender, succulent texture that conventional stewing pots often cannot replicate.
Braise-to-condense gradient
Stewing utilizes a braise-to-condense gradient where ingredients slowly simmer in liquid, enhancing moisture retention through continuous liquid contact and evaporation control. In contrast, tagine cooking relies on a conical lid to condense steam and redirect moisture back into the dish, creating a unique self-basting environment that preserves juiciness more efficiently than traditional stewing methods.
Ceramic condensation effect
Stewing retains moisture by submerging ingredients in liquid, while tagine cooking leverages the ceramic lid's condensation effect that continuously recycles steam, enhancing flavor concentration and moisture retention. The ceramic condensation in tagines creates a self-basting environment, reducing moisture loss compared to traditional stewing methods.
Liquid retention coefficient
Stewing typically has a higher liquid retention coefficient compared to tagine cooking, as the fully covered pot minimizes evaporation and preserves moisture within the dish. Tagines use a conical lid that encourages condensation and moisture recirculation but allow slightly more steam to escape, resulting in moderate liquid retention.
Steam lock seal
Stewing relies on a steam lock seal, which traps moisture inside the cooking vessel, preventing evaporation and ensuring tender, juicy results. Tagine cooking also retains moisture through its conical lid design, but the steam lock in stewing provides a more consistent, airtight environment crucial for slow-cooked moisture retention.
Sous-tagine technique
Sous-tagine cooking enhances moisture retention by using a tightly sealed tagine lid that circulates steam and intensifies flavors, outperforming traditional stewing methods that often lose moisture through evaporation. This technique combines slow cooking with a humid environment, preserving juices and creating tender, succulent dishes.
Stewing vs Tagine cooking for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com