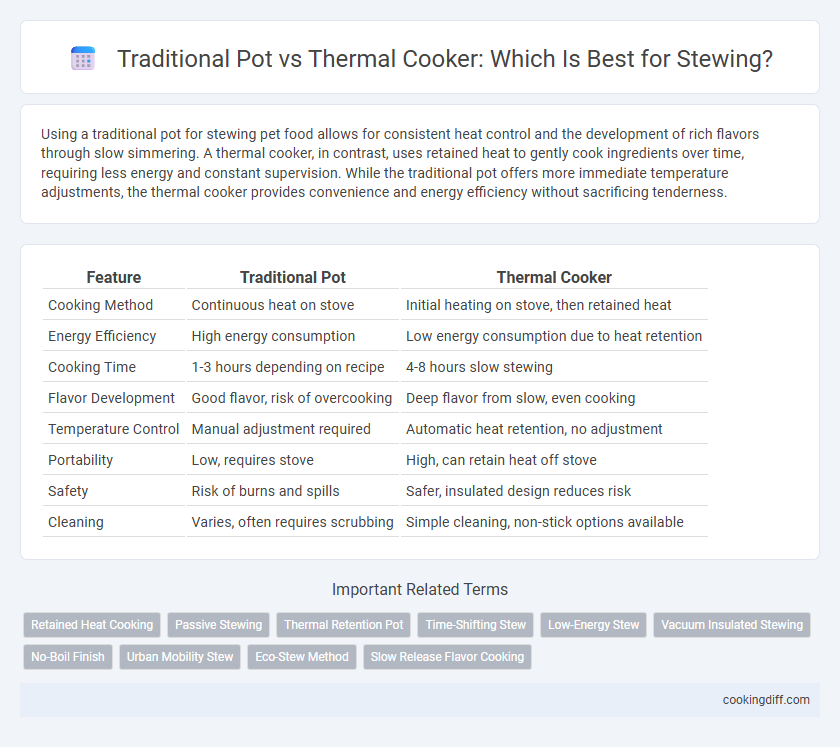
Using a traditional pot for stewing pet food allows for consistent heat control and the development of rich flavors through slow simmering. A thermal cooker, in contrast, uses retained heat to gently cook ingredients over time, requiring less energy and constant supervision. While the traditional pot offers more immediate temperature adjustments, the thermal cooker provides convenience and energy efficiency without sacrificing tenderness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Pot | Thermal Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Continuous heat on stove | Initial heating on stove, then retained heat |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy consumption | Low energy consumption due to heat retention |
| Cooking Time | 1-3 hours depending on recipe | 4-8 hours slow stewing |
| Flavor Development | Good flavor, risk of overcooking | Deep flavor from slow, even cooking |
| Temperature Control | Manual adjustment required | Automatic heat retention, no adjustment |
| Portability | Low, requires stove | High, can retain heat off stove |
| Safety | Risk of burns and spills | Safer, insulated design reduces risk |
| Cleaning | Varies, often requires scrubbing | Simple cleaning, non-stick options available |
Introduction: The Art of Stewing
Stewing is a time-honored cooking technique that slowly breaks down tough cuts of meat and vegetables, enhancing flavors and tenderness over low heat. Traditional pots maintain steady heat, allowing collagen and spices to meld into rich, savory stews.
Thermal cookers use insulated compartments to retain heat without continuous energy, preserving nutrients and infusing ingredients deeply during extended cooking. Both methods showcase the art of stewing by transforming simple ingredients into hearty, flavorful meals.
What is a Traditional Stewing Pot?
A traditional stewing pot is typically made from heavy materials such as cast iron or ceramic that provide even heat distribution essential for slow cooking. It retains moisture and heat, allowing ingredients to simmer gently over long periods to enhance flavors and tenderize meat. These pots often feature thick lids that help trap steam, making them ideal for classic stewing methods.
What is a Thermal Cooker?
What is a thermal cooker and how does it differ from a traditional pot? A thermal cooker uses insulated heat retention technology to slow-cook food without continuous external heat, preserving nutrients and flavors efficiently. Unlike a traditional pot that requires constant stovetop heat, a thermal cooker maintains temperature for hours, reducing energy consumption and preventing overcooking.
Heat Retention: Comparing Traditional Pot and Thermal Cooker
The thermal cooker excels in heat retention by maintaining consistent internal temperatures without continuous external heat, making it energy-efficient for stewing. Traditional pots lose heat quickly once removed from a heat source, requiring ongoing cooking to sustain temperature.
- Thermal Cooker Efficiency - Uses insulated design to keep food hot for hours, reducing energy consumption.
- Traditional Pot Heat Loss - Releases heat rapidly when off the stove, prolonging cooking time.
- Consistent Stewing Temperature - Thermal cookers ensure steady simmering, enhancing flavors and texture.
Energy Efficiency in Stewing Methods
Traditional pots require continuous heat on the stove, leading to higher energy consumption during the stewing process. Thermal cookers use retained heat to cook food gradually without constant energy input, significantly reducing electricity or gas usage. By maintaining temperature with insulation, thermal cookers offer a more energy-efficient alternative for slow-cooked dishes compared to conventional pot methods.
Flavor and Texture Results
Traditional pots allow for slow, consistent heating, resulting in deep flavor development and tender texture as collagen breaks down evenly. Thermal cookers use retained heat to continue cooking without additional energy, preserving moisture and enhancing the stew's natural flavors.
When comparing flavor outcomes, traditional pots often produce richer, more caramelized notes due to direct, sustained heat exposure. Thermal cookers maintain a steadier temperature, which prevents overcooking and helps retain fresh, vibrant ingredients' taste. Both methods yield tender stews, but thermal cookers excel in preserving texture integrity over long cooking periods.
Convenience and Ease of Use
| Traditional Pot | Requires constant monitoring and occasional stirring to prevent burning and ensure even cooking, which can be time-consuming and less convenient for busy individuals. |
| Thermal Cooker | Offers a hands-free cooking experience by maintaining steady temperature without electricity, allowing users to start the stew and leave it to cook slowly, providing greater ease and convenience. |
Safety Considerations for Stewing
Traditional pots require constant heat supervision to prevent boiling over or burning, posing a higher risk of kitchen accidents during stewing. Thermal cookers maintain a safe, insulated environment that significantly reduces the risk of burns and overheating by cooking without continuous external heat.
- Heat control - Traditional pots demand active temperature management to ensure safe cooking conditions.
- Insulated cooking - Thermal cookers provide a stable cooking environment that minimizes direct contact with hot surfaces.
- Risk of burns - Continuous stove use with traditional pots increases the chance of accidental burns compared to thermal cookers.
Cost Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
Traditional pots for stewing typically require continuous heat, leading to higher energy consumption and increased utility costs over time. Thermal cookers use insulated technology to retain heat, significantly reducing energy use and providing cost-effective cooking solutions.
While traditional pots have lower upfront costs, thermal cookers offer superior long-term value due to energy savings and reduced cooking times. Investing in a thermal cooker minimizes fuel expenses and extends cookware lifespan, making it an economical choice for frequent stewing.
Related Important Terms
Retained Heat Cooking
Traditional pots rely on continuous heat from a stove to maintain temperature during stewing, which can lead to higher energy consumption and inconsistent heat distribution. Thermal cookers use insulated layers to retain heat generated from an initial boil, allowing slow, even cooking without constant external heat, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavors efficiently.
Passive Stewing
Traditional pots retain heat slowly, requiring longer cooking times for effective passive stewing, which enhances flavor through gradual heat distribution. Thermal cookers utilize insulated chambers to maintain consistent low temperatures, allowing stewing to continue passively without additional energy input, preserving nutrients and intensifying taste.
Thermal Retention Pot
Thermal retention pots maintain consistent heat for extended periods, enhancing flavor infusion and tenderizing ingredients more efficiently than traditional pots. Their insulated design reduces energy consumption by minimizing the need for continuous heating during stewing.
Time-Shifting Stew
Traditional pots require constant heat and supervision for hours to achieve tender, flavorful stews, while thermal cookers enable time-shifting by retaining heat to cook stews slowly without continuous energy use. This slow, insulated cooking method preserves nutrients and intensifies flavors, making thermal cookers an energy-efficient alternative for busy schedules.
Low-Energy Stew
A traditional pot requires continuous heat for hours, resulting in higher energy consumption during stewing, while a thermal cooker minimizes energy use by trapping heat and allowing slow cooking without constant power. Thermal cookers maintain consistent temperatures, making them ideal for low-energy stews by reducing fuel usage and preserving flavors more efficiently than conventional pots.
Vacuum Insulated Stewing
Vacuum insulated thermal cookers maintain consistent heat retention, enabling slower, even cooking that enhances flavor extraction and nutrient preservation compared to traditional pots. Their airtight design minimizes energy use by eliminating the need for continuous heat, making them ideal for efficient, hands-off stewing.
No-Boil Finish
Traditional pots require constant monitoring and boiling to achieve tender stewing results, while thermal cookers utilize insulated heat retention to finish cooking without boiling, preserving flavors and nutrients. This no-boil finish method in thermal cookers enhances moisture retention and tenderizes meat more efficiently compared to conventional pots.
Urban Mobility Stew
Traditional pots provide even heat distribution essential for Urban Mobility Stew, enhancing the rich flavors through slow simmering, while thermal cookers retain heat efficiently, allowing for energy-saving, hands-off cooking without constant supervision. The thermal cooker's insulated design ensures consistent temperature maintenance, making it ideal for busy urban lifestyles, whereas traditional pots require direct heat and careful monitoring to prevent overcooking.
Eco-Stew Method
The Eco-Stew Method uses a thermal cooker to retain heat efficiently, reducing energy consumption during stewing compared to traditional pots that require constant stovetop heat. Thermal cookers maintain a steady temperature by insulating the pot, enhancing flavor extraction and minimizing carbon footprint for sustainable cooking.
Traditional Pot vs Thermal Cooker for Stewing Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com