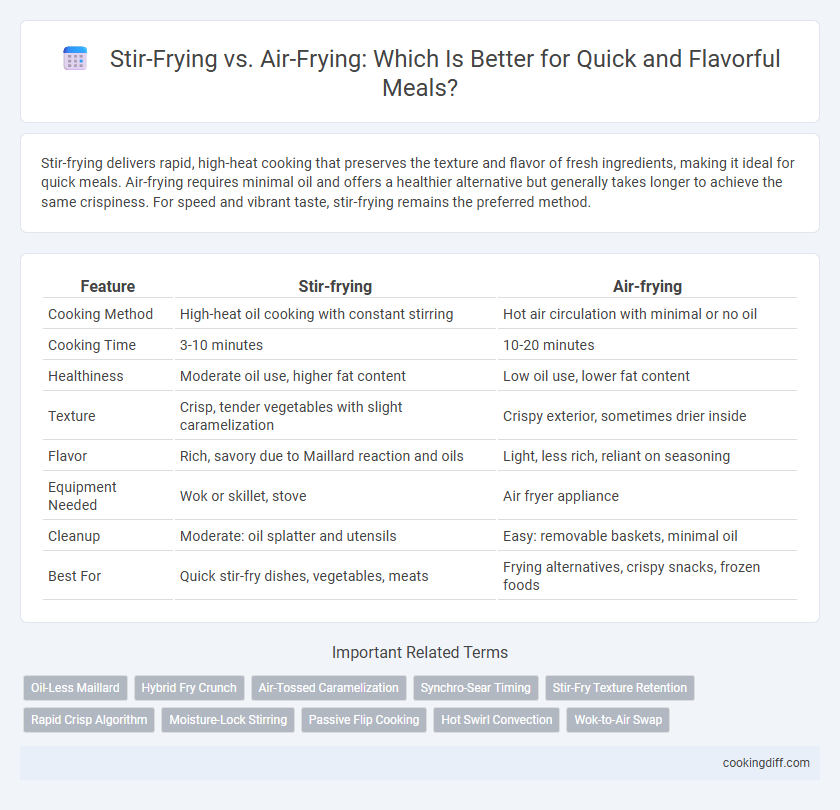
Stir-frying delivers rapid, high-heat cooking that preserves the texture and flavor of fresh ingredients, making it ideal for quick meals. Air-frying requires minimal oil and offers a healthier alternative but generally takes longer to achieve the same crispiness. For speed and vibrant taste, stir-frying remains the preferred method.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stir-frying | Air-frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-heat oil cooking with constant stirring | Hot air circulation with minimal or no oil |
| Cooking Time | 3-10 minutes | 10-20 minutes |
| Healthiness | Moderate oil use, higher fat content | Low oil use, lower fat content |
| Texture | Crisp, tender vegetables with slight caramelization | Crispy exterior, sometimes drier inside |
| Flavor | Rich, savory due to Maillard reaction and oils | Light, less rich, reliant on seasoning |
| Equipment Needed | Wok or skillet, stove | Air fryer appliance |
| Cleanup | Moderate: oil splatter and utensils | Easy: removable baskets, minimal oil |
| Best For | Quick stir-fry dishes, vegetables, meats | Frying alternatives, crispy snacks, frozen foods |
Stir-Frying vs Air-Frying: Which is Better for Quick Meals?
Stir-frying uses high heat and constant stirring to cook food quickly while preserving nutrients and texture, making it ideal for speedy, flavorful meals. Air-frying circulates hot air to cook food with less oil, offering a healthier alternative but often takes longer and may not achieve the same crispiness as stir-frying. For quick meals, stir-frying is generally faster and better at maintaining vibrant flavors and textures.
Nutritional Differences Between Stir-Fried and Air-Fried Dishes
Stir-frying typically retains more nutrients due to shorter cooking times and high heat, preserving vitamins in vegetables. Air-frying reduces fat content by using less oil, which can lower calorie intake but might slightly decrease nutrient retention compared to stir-frying.
- Vitamin retention - Stir-frying preserves water-soluble vitamins better by cooking food quickly at high heat.
- Fat content - Air-frying uses minimal oil, resulting in lower overall fat and calorie levels in meals.
- Antioxidant levels - Stir-fried dishes often maintain higher antioxidant compounds due to rapid cooking methods.
Cooking Speed: Stir-Frying and Air-Frying Compared
Stir-frying typically cooks food faster than air-frying due to direct contact with a hot pan and continuous stirring. Air-frying uses hot air circulation which takes longer but offers a hands-off cooking approach.
- Stir-frying speed advantage - Stir-frying heats food quickly at high temperatures, often completing meals in under 10 minutes.
- Air-frying convenience - Air-frying requires preheating and longer cooking times, usually between 15 to 25 minutes for similar dishes.
- Cooking method impact - Stir-frying demands attention and stirring for even cooking, whereas air-frying allows meal preparation without constant monitoring.
Flavor and Texture: What to Expect from Each Method
Stir-frying preserves the vibrant flavors and crisp texture of vegetables through high heat and constant stirring, creating a savory, caramelized finish. Air-frying offers a healthier alternative by circulating hot air for a crispy exterior but may produce a drier texture compared to the moist, tender results from stir-frying.
Stir-frying enhances aroma and depth of flavor by quickly sealing in juices and allowing ingredients to brown evenly. Air-frying delivers a crunch similar to deep-frying without excessive oil, but it can lack the complex, layered taste achieved in stir-frying. Choosing between these methods depends on whether you prioritize bold flavors and moisture or a healthier, crispy texture in your quick meals.
Equipment Essentials: Wok vs Air Fryer
Stir-frying requires a wok, a versatile round-bottomed pan that allows high-heat cooking with rapid tossing to evenly cook ingredients and retain their texture. An air fryer uses circulating hot air to crisp food with minimal oil, ideal for a healthier alternative but lacks the direct flame and quick searing capability of a wok. Choosing between a wok and an air fryer depends on whether you prioritize traditional high-heat cooking for quick, flavorful meals or prefer a countertop appliance for convenient, oil-reduced frying.
Versatility: What Can You Cook with Stir-Frying vs Air-Frying?
Stir-frying offers exceptional versatility by allowing quick cooking of a wide range of ingredients, from vegetables and meats to seafood and tofu, while maintaining vibrant textures and flavors. Its high heat and constant stirring make it ideal for preparing diverse quick meals such as stir-fried noodles, fried rice, and vegetable medleys.
Air-frying excels at producing crispy textures using little to no oil, suitable for items like frozen snacks, chicken wings, and roasted vegetables, but it is less adaptable to sauces and liquid-based dishes. While air-frying is convenient for reheating and crisping, stir-frying provides broader adaptability for complex, sauce-infused meals in a fraction of the time.
Oil Usage: Saving Calories with Stir-Frying or Air-Frying
Stir-frying uses a small amount of oil to quickly cook ingredients, preserving nutrients and flavors while controlling calorie intake. Air-frying eliminates the need for oil by circulating hot air, significantly reducing fat content in meals.
- Stir-frying requires minimal oil - typically 1-2 tablespoons, which helps reduce overall calorie consumption compared to deep-frying.
- Air-frying uses little to no added oil - making it ideal for those seeking low-fat cooking methods without sacrificing texture.
- Both methods support healthy eating - by cutting down excess oil, they provide flavorful meals with fewer calories than traditional frying.
Choosing between stir-frying and air-frying depends on desired flavor, texture, and oil usage preferences for quick, calorie-conscious meals.
Cleaning Up: Ease of Maintenance for Each Method
| Stir-frying | Involves using a wok or frying pan that often requires thorough hand-washing to remove oil and food residue, which can be time-consuming. Non-stick skillets simplify cleaning but still need careful maintenance to preserve the coating. Residual grease and splatter increase cleaning effort after each use. |
| Air-frying | Features a non-stick basket and trays that are usually dishwasher-safe, reducing cleaning time significantly. Minimal oil usage results in less greasy residue, making wipe-down quicker and easier. Regular maintenance involves simply rinsing or placing components in the dishwasher for efficient cleanup. |
Best Ingredients for Stir-Frying and Air-Frying
Stir-frying is ideal for fresh vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, and snap peas, as well as thinly sliced meats and tofu, which cook quickly and retain their texture and nutrients. High heat and constant stirring ensure even cooking and vibrant flavors, making it perfect for ingredients that require fast, intense heat exposure.
Air-frying works best with ingredients that benefit from a crispy exterior, such as potatoes, chicken wings, and breaded vegetables, using hot air circulation to achieve a fried texture without oil. Pre-cut, uniform pieces promote even cooking, while marinated proteins can develop a flavorful crust during the air-frying process.
Related Important Terms
Oil-Less Maillard
Stir-frying uses direct high heat and continuous stirring to achieve the Maillard reaction quickly with minimal oil, creating a flavorful, crispy texture while retaining nutrient density. Air-frying replicates this oil-less Maillard effect through rapid hot air circulation, offering a healthier alternative that reduces fat content without sacrificing the characteristic browning and crunch.
Hybrid Fry Crunch
Hybrid Fry Crunch combines the rapid high-heat cooking of stir-frying with the healthier oil-free technique of air-frying, delivering quick meals with crispy textures and enhanced flavor. This method preserves nutrients while reducing fat content, making it ideal for fast, nutritious dishes.
Air-Tossed Caramelization
Stir-frying achieves air-tossed caramelization by rapidly cooking ingredients in a hot wok, which preserves texture and enhances flavor through intense, direct heat and continuous movement. In contrast, air-frying offers a healthier alternative by using hot air circulation to caramelize food evenly with less oil, delivering a crisp exterior without the need for constant stirring.
Synchro-Sear Timing
Stir-frying achieves optimal flavor through Synchro-Sear Timing by rapidly searing ingredients in high heat, locking in moisture and nutrients within minutes. Air-frying, while healthier with less oil, often lacks the precise timing control necessary for the perfect sear, resulting in a different texture and flavor profile for quick meals.
Stir-Fry Texture Retention
Stir-frying preserves the natural crispness and vibrant texture of vegetables and proteins by cooking them quickly over high heat with continuous stirring, preventing sogginess and ensuring even heat distribution. This method retains moisture and enhances the mouthfeel, offering a superior texture compared to air-frying, which can sometimes result in drier or less uniform texture in quick meals.
Rapid Crisp Algorithm
Stir-frying leverages high heat and constant motion to rapidly sear ingredients, preserving texture and nutrients within minutes, while air-frying uses Rapid Crisp Algorithm technology to evenly circulate hot air, creating a crispy exterior with less oil and slower cook times. For quick meals, the Rapid Crisp Algorithm ensures air-fried dishes achieve crispness comparable to stir-frying but with enhanced convenience and reduced fat content.
Moisture-Lock Stirring
Stir-frying preserves moisture by rapidly cooking ingredients in high heat with constant stirring, maintaining a tender texture and vibrant flavor. Air-frying uses hot air circulation to cook with less oil, but may dry out foods faster, lacking the moisture-locking benefit of continuous stirring.
Passive Flip Cooking
Passive flip cooking in stir-frying enhances rapid heat distribution by continuously tossing ingredients in a hot wok, preserving texture and flavor with minimal oil. In contrast, air-frying relies on circulating hot air for even cooking but lacks the dynamic ingredient agitation that intensifies flavor development in stir-fried dishes.
Hot Swirl Convection
Stir-frying utilizes Hot Swirl Convection to rapidly circulate high-heat air and oil, ensuring even cooking and preserving food texture while locking in nutrients. In contrast, air-frying relies on similar convection principles without oil, offering a healthier option but typically producing a different crispness and flavor profile compared to stir-fried dishes.
Stir-frying vs Air-frying for quick meals Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com