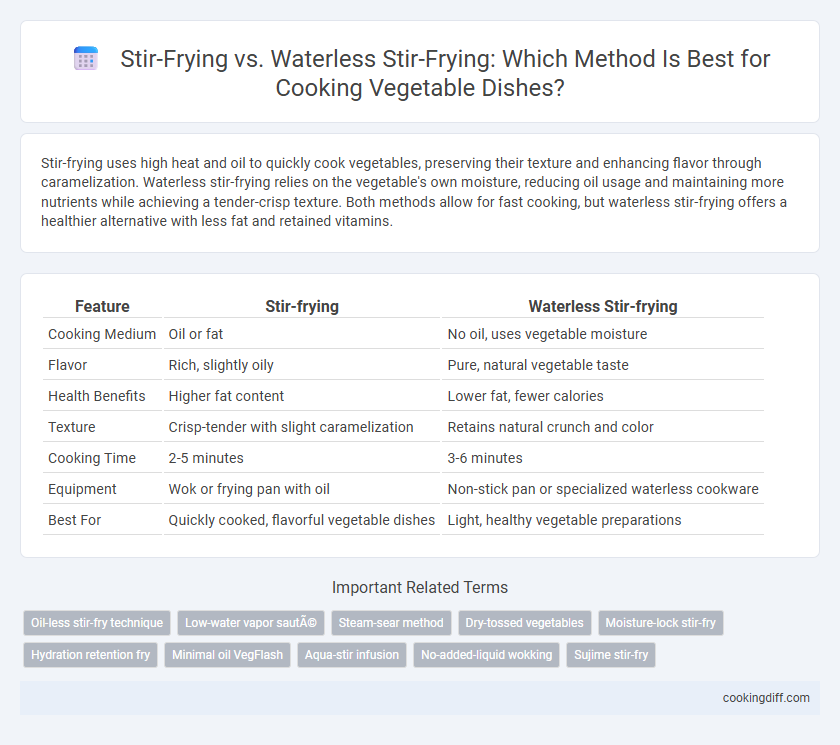
Stir-frying uses high heat and oil to quickly cook vegetables, preserving their texture and enhancing flavor through caramelization. Waterless stir-frying relies on the vegetable's own moisture, reducing oil usage and maintaining more nutrients while achieving a tender-crisp texture. Both methods allow for fast cooking, but waterless stir-frying offers a healthier alternative with less fat and retained vitamins.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stir-frying | Waterless Stir-frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Medium | Oil or fat | No oil, uses vegetable moisture |
| Flavor | Rich, slightly oily | Pure, natural vegetable taste |
| Health Benefits | Higher fat content | Lower fat, fewer calories |
| Texture | Crisp-tender with slight caramelization | Retains natural crunch and color |
| Cooking Time | 2-5 minutes | 3-6 minutes |
| Equipment | Wok or frying pan with oil | Non-stick pan or specialized waterless cookware |
| Best For | Quickly cooked, flavorful vegetable dishes | Light, healthy vegetable preparations |
Introduction to Stir-Frying and Waterless Stir-Frying
Stir-frying is a high-heat cooking method using oil to quickly cook vegetables while preserving their texture and flavor. Waterless stir-frying utilizes the natural moisture of vegetables, eliminating added water or oil for a lighter, nutrient-retentive dish.
- Stir-frying - Requires wok or skillet with oil to achieve fast, even cooking and slight caramelization.
- Waterless stir-frying - Relies on steam generated within the closed cooking vessel from vegetable moisture.
- Health benefits - Waterless stir-frying preserves more vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional methods.
Both techniques enhance vegetable dishes but differ significantly in cooking medium and nutrient retention.
Key Differences: Stir-Frying vs Waterless Stir-Frying
Stir-frying uses high heat and a small amount of oil to quickly cook vegetables, enhancing flavor through caramelization and Maillard reactions. Waterless stir-frying employs steam generated from the vegetables' own moisture, minimizing oil usage and preserving more nutrients and natural colors. Key differences include cooking technique, oil utilization, and nutrient retention, with waterless stir-frying offering a healthier alternative while maintaining texture and taste.
Nutrient Retention in Vegetable Dishes
| Stir-frying | Uses oil and high heat, which can cause some nutrient loss but enhances flavor and texture of vegetables. |
| Waterless Stir-frying | Maintains higher levels of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex by eliminating added water and oil, preserving nutrient retention. |
| Nutrient Retention | Waterless stir-frying retains up to 30% more nutrients compared to traditional stir-frying due to reduced leaching of vitamins and minerals. |
Flavor and Texture Comparison
Stir-frying vegetables in oil enhances their natural flavors through caramelization, creating a rich, slightly crispy texture and a savory taste. Waterless stir-frying preserves the vibrant colors and crispness by using the vegetables' own moisture, resulting in a lighter, fresher flavor profile. Both techniques maintain nutrient integrity, but traditional stir-frying offers a bolder flavor while waterless stir-frying emphasizes natural vegetable freshness and crunch.
Required Equipment for Each Method
Traditional stir-frying requires a wok or a large skillet that can withstand high heat, while waterless stir-frying often uses specialized non-stick pans designed to retain moisture. Each method demands specific tools to optimize cooking results and preserve vegetable texture and nutrients.
- Wok or Large Skillet - Essential for traditional stir-frying to achieve high heat and quick cooking.
- Non-stick Pan - Used in waterless stir-frying to maintain moisture without added liquids.
- High Heat Source - Necessary for conventional stir-frying to sear vegetables rapidly.
Cooking Time and Efficiency
Stir-frying typically requires higher heat and faster cooking times, which helps retain vegetable texture and nutrients while enhancing flavor through caramelization. Traditional stir-frying uses oil to conduct heat evenly, optimizing cooking efficiency for quick meal preparation.
Waterless stir-frying relies on the natural moisture of vegetables, reducing cooking time by steaming rather than frying, which preserves more vitamins. This method increases efficiency by minimizing oil use and promoting healthier, faster cooking with less cleanup.
Oil Usage and Health Considerations
Stir-frying traditionally uses more oil to evenly cook vegetables, which can increase calorie intake. Waterless stir-frying minimizes oil usage by relying on steam and natural vegetable moisture, promoting a healthier preparation method.
- Oil Usage in Stir-frying - Requires a moderate amount of oil to prevent sticking and enhance flavor.
- Oil Usage in Waterless Stir-frying - Uses little to no oil, reducing fat and calorie content.
- Health Considerations - Waterless stir-frying preserves nutrients better and cuts unnecessary fat, supporting heart health.
Best Vegetables for Each Technique
Bell peppers, broccoli, and snap peas excel in traditional stir-frying due to their crisp texture and ability to absorb oil-based sauces, enhancing flavor. Waterless stir-frying suits delicate vegetables like spinach, mushrooms, and zucchini, preserving nutrients and maintaining vibrant color without added oil.
High-heat traditional stir-frying rapidly cooks dense vegetables, creating a desirable sear while locking in moisture. Waterless stir-frying relies on the vegetable's natural water content, ideal for leafy greens or tender produce that can release steam during cooking. Selecting the appropriate technique depends on vegetable density and moisture level, optimizing taste and nutritional retention.
Step-by-Step Guide: Stir-Frying Vegetables
What distinguishes traditional stir-frying from waterless stir-frying when preparing vegetable dishes? Traditional stir-frying uses oil and high heat to quickly cook vegetables, preserving texture and flavor, while waterless stir-frying relies on the vegetables' own moisture to soften them without added fat. Step-by-step, start by heating the pan, add oil for traditional stir-frying or skip it for waterless, then continuously toss vegetables to ensure even cooking and vibrant color retention.
Related Important Terms
Oil-less stir-fry technique
Oil-less stir-fry technique enhances vegetable dishes by preserving natural flavors and nutrients while reducing calorie intake compared to traditional stir-frying with oil. This waterless method uses high heat and moisture from the vegetables themselves to achieve crisp-tender textures without added fats.
Low-water vapor sauté
Low-water vapor saute in stir-frying preserves the natural texture and nutrients of vegetables by minimizing water release compared to traditional stir-frying, which often results in soggier textures due to higher moisture content. Waterless stir-frying enhances flavor concentration and retains vibrant colors by using minimal oil and employing precise heat control to prevent steam formation.
Steam-sear method
Steam-sear methods in waterless stir-frying preserve vegetable nutrients by using moisture released from the ingredients to generate steam for cooking, minimizing oil usage and heat damage. Traditional stir-frying typically relies on higher oil content and intense direct heat, which can lead to nutrient loss and uneven cooking in vegetable dishes.
Dry-tossed vegetables
Stir-frying uses high heat and oil to quickly cook and enhance the texture and flavor of vegetables, while waterless stir-frying relies on the moisture released from the vegetables themselves to gently cook them without added water or oil. Dry-tossed vegetables in waterless stir-frying preserve more nutrients and maintain a crisp texture, resulting in vibrant, nutrient-rich dishes with concentrated natural flavors.
Moisture-lock stir-fry
Moisture-lock stir-fry techniques in both traditional and waterless stir-frying preserve the natural juices and nutrients of vegetables, enhancing flavor and texture without excess oil or water. Waterless stir-frying utilizes high-quality cookware that maintains intense heat, sealing moisture inside the vegetables for a crisp, vibrant dish.
Hydration retention fry
Waterless stir-frying preserves vegetable hydration by cooking without added oil or water, enhancing natural flavors and nutrient retention. Traditional stir-frying uses oil and high heat, which can cause moisture loss and reduce the crispness of vegetables.
Minimal oil VegFlash
Waterless stir-frying for vegetable dishes uses minimal oil by sealing in moisture and cooking at high heat, preserving nutrients and natural flavors better than traditional stir-frying methods. VegFlash technology enhances this process by ensuring rapid, even heating with minimal oil, resulting in healthier, crisp vegetables without compromising texture or taste.
Aqua-stir infusion
Aqua-stir infusion in waterless stir-frying enhances vegetable dishes by preserving nutrients and intensifying natural flavors through the vegetable's own moisture rather than adding water or oil. This method ensures crisp texture and vibrant color while reducing nutrient loss compared to traditional stir-frying techniques that rely on external liquid.
No-added-liquid wokking
Stir-frying involves cooking vegetables quickly at high heat with a small amount of oil, often requiring some liquid like water or broth to prevent sticking and maintain texture. Waterless stir-frying, also known as no-added-liquid wokking, uses the natural moisture released from fresh vegetables, resulting in crisper texture and enhanced nutrient retention without diluting flavors.
Stir-frying vs Waterless stir-frying for vegetable dishes. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com