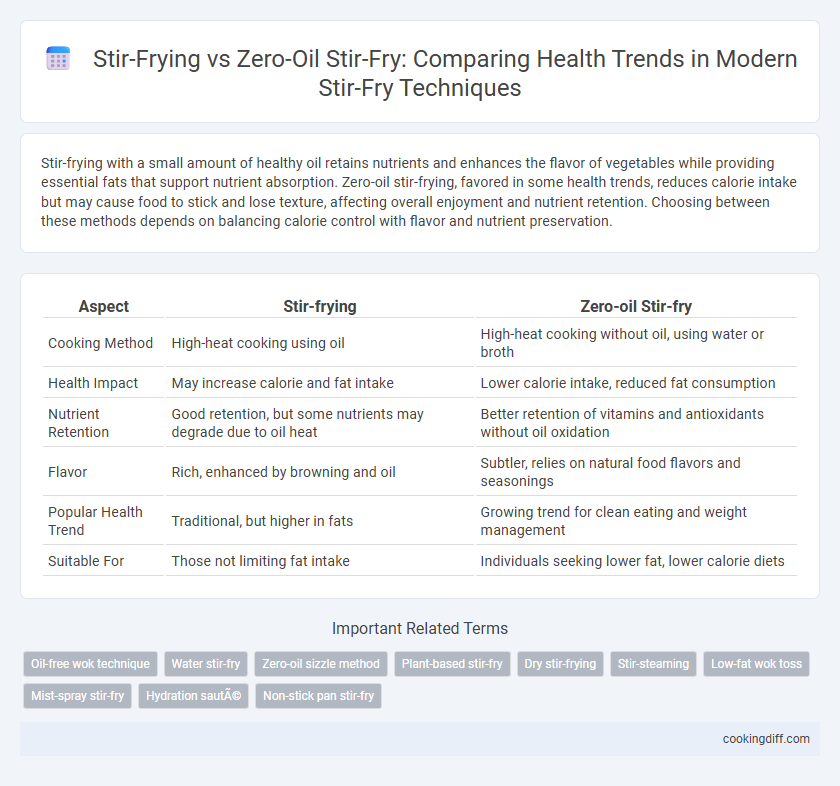
Stir-frying with a small amount of healthy oil retains nutrients and enhances the flavor of vegetables while providing essential fats that support nutrient absorption. Zero-oil stir-frying, favored in some health trends, reduces calorie intake but may cause food to stick and lose texture, affecting overall enjoyment and nutrient retention. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing calorie control with flavor and nutrient preservation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stir-frying | Zero-oil Stir-fry |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-heat cooking using oil | High-heat cooking without oil, using water or broth |
| Health Impact | May increase calorie and fat intake | Lower calorie intake, reduced fat consumption |
| Nutrient Retention | Good retention, but some nutrients may degrade due to oil heat | Better retention of vitamins and antioxidants without oil oxidation |
| Flavor | Rich, enhanced by browning and oil | Subtler, relies on natural food flavors and seasonings |
| Popular Health Trend | Traditional, but higher in fats | Growing trend for clean eating and weight management |
| Suitable For | Those not limiting fat intake | Individuals seeking lower fat, lower calorie diets |
Introduction to Stir-Frying: Traditional Methods
What distinguishes traditional stir-frying methods from zero-oil stir-fry techniques in today's health trends? Traditional stir-frying utilizes high heat and small amounts of oil to quickly cook ingredients, preserving texture and flavor while enhancing nutrient retention. This method contrasts with zero-oil stir-frying, which eliminates oil to reduce calories but may affect taste and cooking efficiency.
Zero-Oil Stir-Fry: Emerging Health Trend
| Zero-oil stir-fry uses water, broth, or steaming techniques to cook vegetables and proteins, significantly reducing calorie intake compared to traditional oil-based methods. This method preserves nutrients, enhances natural flavors, and aligns with trends favoring heart-healthy, low-fat diets. Studies show zero-oil stir-frying supports weight management and cardiovascular health by minimizing unhealthy fat consumption while maintaining food texture and taste. |
Nutrient Retention in Stir-Frying vs Zero-Oil Techniques
Stir-frying with a small amount of oil enhances nutrient absorption by facilitating the release of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Zero-oil stir-frying preserves heat-sensitive vitamins such as vitamin C and certain B vitamins better due to reduced heat transfer through oil.
- Fat-Soluble Vitamin Absorption - Using oil in stir-frying helps dissolve and retain fat-soluble vitamins, boosting their bioavailability.
- Heat-Sensitive Nutrient Preservation - Zero-oil methods limit oil-mediated heat exposure, protecting delicate nutrients from degradation.
- Overall Nutrient Balance - Combining minimal oil with quick cooking times in stir-frying optimizes retention of both fat-soluble and heat-sensitive nutrients.
Flavor Differences: Oil vs Oil-Free Stir-Frying
Stir-frying with oil enhances flavor development through the Maillard reaction, imparting a richer, nuttier taste to vegetables and proteins. Zero-oil stir-frying relies on steam and natural food juices, resulting in lighter, more delicate flavors that highlight the ingredients' freshness.
- Oil in stir-frying - promotes caramelization and deepens savory notes for a more robust flavor profile.
- Zero-oil stir-frying - preserves the pure taste of ingredients by avoiding added fats that can mask subtle flavors.
- Health impact - oil-based stir-frying increases calorie content but enhances palatability, whereas oil-free methods favor lower fat intake with milder taste.
Choosing between oil and oil-free stir-frying depends on balancing desired flavor intensity and health preferences.
Calorie Count Comparison: Which Is Healthier?
Stir-frying typically uses a small amount of oil, adding approximately 40-120 calories per tablespoon depending on the oil type, which increases the overall calorie count of the dish. Zero-oil stir-fry eliminates this added fat, significantly reducing calorie intake while retaining the benefits of quick cooking and nutrient preservation.
Choosing zero-oil stir-frying can be healthier for calorie-conscious individuals as it avoids added fats and maintains the nutritional integrity of vegetables and proteins. However, some oils such as olive or avocado provide heart-healthy fats and fat-soluble vitamins, which can contribute positively to a balanced diet. Ultimately, the health impact depends on ingredient quality and portion control alongside the cooking method.
Impact on Heart Health: Oil vs Zero-Oil Stir-Fry
Stir-frying with moderate amounts of heart-healthy oils like olive or avocado oil provides essential fatty acids that support cardiovascular function. These oils contain unsaturated fats that help reduce LDL cholesterol levels and inflammation, contributing to improved heart health.
Zero-oil stir-frying eliminates added fats, reducing overall calorie intake and saturated fat consumption, which benefits weight management and lowers heart disease risk. However, the absence of healthy oils means missing out on beneficial nutrients that aid in maintaining optimal cholesterol balance.
Texture and Appearance: Does Zero-Oil Affect Quality?
Traditional stir-frying uses oil to create a crispy texture and vibrant appearance, essential for authentic flavor and mouthfeel. Zero-oil stir-frying often results in softer textures and duller colors, which can affect the overall sensory appeal of the dish.
Choosing zero-oil methods may benefit health by reducing fat intake but can compromise the caramelization and glossiness that oil imparts during high-heat cooking. Maintaining texture and visual quality without oil requires precise temperature control and ingredient selection to optimize stir-fry outcomes.
Popular Ingredients for Zero-Oil Stir-Frying
Zero-oil stir-frying uses water or broth to cook ingredients, reducing fat intake while preserving nutrients. Popular ingredients for this method emphasize high water content and robust flavors to maintain taste without added oils.
- Leafy greens - Spinach and bok choy soften quickly and retain vitamins when stir-fried without oil.
- Mushrooms - Shiitake and oyster mushrooms release moisture that enhances texture and umami flavor in oil-free dishes.
- Bell peppers - Their natural sweetness intensifies during zero-oil stir-frying, contributing vibrant color and antioxidants.
Tips for Successful Zero-Oil Stir-Fry at Home
For a successful zero-oil stir-fry at home, use non-stick pans or well-seasoned cast iron skillets to prevent sticking and ensure even cooking. Incorporate moisture-rich ingredients such as mushrooms, tomatoes, or a splash of vegetable broth to facilitate sauteing without oil. Maintain high heat and stir continuously to preserve the crisp texture and vibrant colors typical of traditional stir-frying.
Related Important Terms
Oil-free wok technique
Zero-oil stir-frying using an oil-free wok technique enhances health benefits by significantly reducing calorie intake and minimizing fat consumption while preserving the nutritional integrity and natural flavors of vegetables and proteins. This method leverages high heat and rapid cooking to maintain crisp textures and vibrant colors, aligning with contemporary wellness trends emphasizing low-fat, nutrient-dense meals.
Water stir-fry
Water stir-fry offers a healthier alternative to traditional oil-based stir-frying by significantly reducing calorie intake and avoiding harmful trans fats, aligning with current health trends focusing on low-fat cooking methods. This technique preserves the crispness and nutrients of vegetables while minimizing oil-related health risks such as heart disease and obesity.
Zero-oil sizzle method
Zero-oil sizzle stir-frying eliminates added fats by using high heat and natural food moisture, preserving nutrients and reducing calorie intake compared to traditional stir-frying. This health trend supports weight management and cardiovascular benefits by minimizing oil-induced oxidative compounds while maintaining the dish's texture and flavor.
Plant-based stir-fry
Plant-based stir-fry maximizes nutrient retention by using high heat and minimal oil, while zero-oil stir-fry eliminates added fats to reduce calorie intake and support heart health. Both methods emphasize fresh vegetables and protein alternatives like tofu or tempeh, aligning with modern health trends prioritizing plant-based, low-fat diets.
Dry stir-frying
Dry stir-frying, a zero-oil cooking method, retains the nutritional integrity of vegetables by minimizing fat intake and preserving heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and folate. This health-conscious trend aligns with dietary recommendations for reduced oil consumption, promoting lower calorie dishes while maintaining the characteristic crisp texture and vibrant flavor of traditional stir-frying.
Stir-steaming
Stir-steaming combines rapid cooking and vapor retention to preserve nutrients while offering a healthier alternative to traditional stir-frying methods that often use oil. This technique aligns with current health trends by reducing fat intake without sacrificing texture or flavor in vegetables and lean proteins.
Low-fat wok toss
Low-fat wok toss methods enhance stir-frying by minimizing oil use, preserving nutrients while reducing calorie intake. Zero-oil stir-fry techniques align with health trends by promoting fresh vegetables and lean proteins, offering a heart-healthy alternative to traditional oil-heavy cooking.
Mist-spray stir-fry
Mist-spray stir-fry uses a fine vapor of oil to achieve the high heat and quick cooking of traditional stir-frying while significantly reducing oil consumption, aligning with current health trends favoring lower fat intake. This method retains the texture and flavor benefits of conventional stir-frying but offers a healthier alternative by minimizing calorie intake without sacrificing taste.
Hydration sauté
Hydration saute enhances stir-frying by incorporating water or broth instead of oil, reducing calorie intake and promoting heart health through lower fat consumption. This zero-oil stir-fry method preserves nutrient retention and keeps vegetables crisp while supporting modern health trends focused on hydration and clean eating.
Stir-frying vs Zero-oil stir-fry for health trends Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com