A skillet provides direct, intense heat ideal for evenly toasting pet treats, allowing for quick browning and a crisp texture. Induction griddles offer precise temperature control and energy efficiency, reducing the risk of burning while maintaining consistent heat across the surface. Choosing between a skillet and an induction griddle depends on your preferred level of heat control and cooking speed for perfectly toasted pet snacks.
Table of Comparison
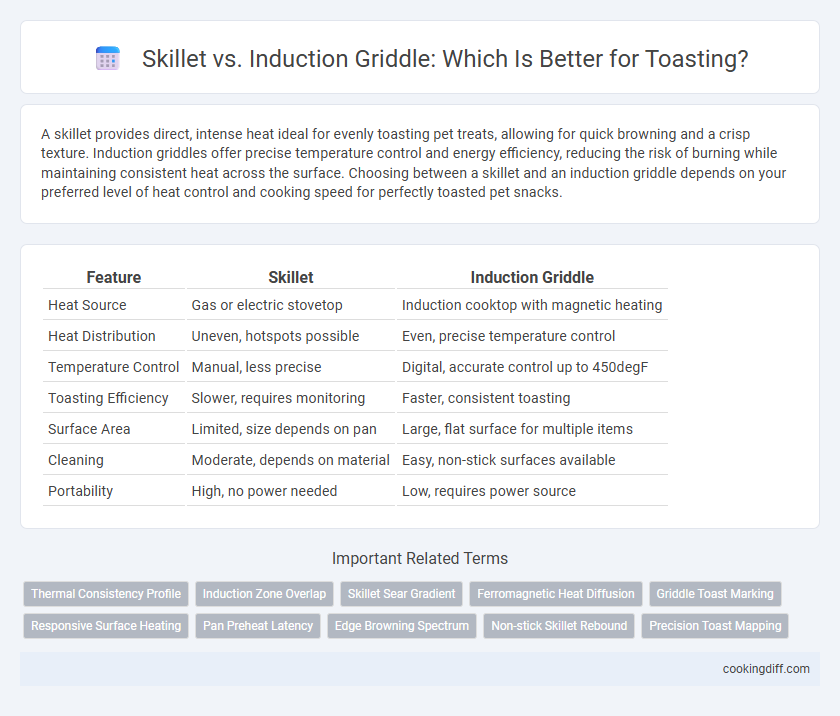
| Feature | Skillet | Induction Griddle |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Gas or electric stovetop | Induction cooktop with magnetic heating |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, hotspots possible | Even, precise temperature control |
| Temperature Control | Manual, less precise | Digital, accurate control up to 450degF |
| Toasting Efficiency | Slower, requires monitoring | Faster, consistent toasting |
| Surface Area | Limited, size depends on pan | Large, flat surface for multiple items |
| Cleaning | Moderate, depends on material | Easy, non-stick surfaces available |
| Portability | High, no power needed | Low, requires power source |
Introduction: Skillet vs Induction Griddle for Toasting
Choosing the right tool for toasting can significantly impact the texture and flavor of your food. Skillets and induction griddles offer distinct heating methods that influence cooking performance.
Skillets provide direct, even heat ideal for achieving a crispy, golden-brown toast crust. Induction griddles heat quickly with precise temperature control, ensuring consistent toasting without hot spots. Both options enhance toasting by distributing heat efficiently, but the choice depends on desired cooking speed and surface area.
Heat Distribution: Skillet and Induction Griddle Compared
Skillets provide direct heat with a slightly uneven distribution that can cause hot spots, making precise toasting challenging. Induction griddles offer consistent, evenly distributed heat due to electromagnetic technology, ensuring uniform toasting across the cooking surface.
Skillets rely on conduction from a single heat source, which may result in temperature fluctuations during toasting. Induction griddles maintain steady heat levels, enhancing control and efficiency for perfectly toasted bread or sandwiches.
Toasting Efficiency: Which Method is Faster?
Induction griddles offer superior toasting efficiency due to rapid and even heat distribution, significantly reducing the time needed to achieve a perfectly toasted surface. Skillets, while versatile, typically require longer preheating and manual heat control, which can slow down the toasting process.
The induction method can toast bread slices evenly in under two minutes, leveraging electromagnetic energy for quick temperature adjustments. In contrast, skillet toasting often demands constant monitoring to avoid uneven browning and can take up to five minutes per batch.
Flavor Profile: How Cooking Surface Affects Taste
Skillet toasting develops a rich, caramelized crust due to direct contact with a seasoned surface, enhancing the Maillard reaction that intensifies flavor complexity. Induction griddles offer even, controlled heat distribution, preserving delicate aromas and preventing burning, which results in a cleaner, more consistent toast flavor. The choice between skillet and induction griddle significantly impacts the taste profile by balancing browning intensity with temperature precision.
Temperature Control: Precision on Skillet vs Induction Griddle
Induction griddles offer superior temperature control through precise electromagnetic heating, ensuring consistent toasting results without hot spots. Skillets rely on stovetop heat sources, making fine-tuning temperature more challenging and prone to uneven heat distribution.
- Induction Griddles Provide Exact Temperature Settings - Users can digitally adjust temperature in small increments for optimal toasting.
- Skillets Depend on Stove Heat Variation - Heat control varies by burner type and size, affecting uniformity.
- Heat Distribution Benefits Induction Griddles - Even heating minimizes burnt or under-toasted sections on bread.
Versatility: Beyond Toasting on Each Surface
Skillet surfaces offer exceptional versatility for toasting, allowing for uneven heat distribution that creates a unique char and crispness ideal for artisanal breads. Induction griddles provide uniform heating and precise temperature control, making them perfect for evenly toasted sandwiches and delicate items like bagels without burning. Both tools extend beyond basic toasting by accommodating sauteing, searing, and even slow cooking, with induction griddles excelling in consistency and skillets favored for their adaptability over various stovetops.
Cleanup and Maintenance Differences
Induction griddles feature a smooth, non-stick surface that simplifies cleanup after toasting, often requiring only a quick wipe. Skillets may retain crumbs and oils in textured surfaces or crevices, demanding more thorough scrubbing and maintenance to prevent buildup.
- Induction Griddle Non-Stick Surface - This design allows effortless removal of crumbs and resists food sticking, speeding up cleanup.
- Skillet Residue Retention - Textured or cast iron skillets trap oils and bits of food, necessitating deeper cleaning and seasoning maintenance.
- Maintenance Frequency - Induction griddles require less frequent upkeep compared to skillets, which need regular re-seasoning to maintain performance and prevent rust.
Safety Features: Induction vs Traditional Skillet
| Feature | Induction Griddle | Traditional Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Control | Precise temperature regulation minimizes risk of overheating and burning during toasting. | Heat is controlled by stove settings, increasing the chance of uneven toasting and potential hot spots. |
| Surface Temperature | Surface stays cooler except where in contact with cookware, reducing burn hazards. | Entire skillet surface becomes extremely hot, posing higher risk of accidental burns. |
| Auto Shut-off | Built-in safety features often include automatic shut-off when no cookware is detected. | No automatic shut-off; users must monitor skillet manually to prevent fire hazards. |
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Skillets generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to induction griddles, making them more accessible for budget-conscious users. Induction griddles require compatible cookware and higher initial investment but provide consistent heat and energy efficiency.
- Skillet affordability - Skillets are widely available at various price points, often under $30.
- Induction griddle investment - Induction griddles cost between $60 and $150 depending on brand and features.
- Cookware compatibility - Induction griddles necessitate magnetic-bottom pots or pans, limiting accessibility for some users.
Choosing between skillet and induction griddle depends on balancing upfront cost with cooking efficiency and equipment compatibility.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Consistency Profile
Induction griddles offer superior thermal consistency due to their direct electromagnetic heating, ensuring even heat distribution across the surface for perfectly toasted results. Skillets rely on conduction and may develop hot spots, causing uneven toasting and requiring frequent temperature adjustments.
Induction Zone Overlap
Induction griddles offer precise temperature control with minimal heat loss, enhancing consistent toasting by utilizing induction zone overlap for uniform heat distribution. Skillets lack this feature, often resulting in uneven toasting due to isolated heat zones and less efficient energy transfer.
Skillet Sear Gradient
A skillet offers superior sear gradient control for toasting, delivering precise heat distribution and allowing for enhanced browning and texture development compared to a flat induction griddle. Its ability to retain and concentrate heat on specific areas creates a distinct, flavorful crust ideal for artisanal toasting.
Ferromagnetic Heat Diffusion
Skillet toasting relies on ferromagnetic heat diffusion to evenly distribute heat across its iron or steel surface, enhancing browning and flavor development. Induction griddles use electromagnetic fields to directly heat ferromagnetic materials, providing precise temperature control and rapid, uniform heat diffusion ideal for consistent toasting results.
Griddle Toast Marking
Induction griddles provide more consistent heat distribution, resulting in clearer and more uniform toast markings compared to traditional skillets. Skillet toasting often produces uneven browning due to hot spots, while induction griddles offer precise temperature control essential for perfect and visually appealing toast marks.
Responsive Surface Heating
Skillet toasters offer uneven surface heating due to direct contact with burner flames, resulting in hot spots that can char bread edges while leaving centers under-toasted. Induction griddles provide highly responsive surface heating, quickly adjusting temperature for consistent and evenly toasted bread slices without burnt areas.
Pan Preheat Latency
Skillet toasting typically requires longer preheat latency, often several minutes, as the metal must reach a uniform temperature to ensure even toasting. Induction griddles offer rapid preheat times, usually under two minutes, by directly heating the cooking surface with electromagnetic energy, making them more efficient for quick and consistent toasting.
Edge Browning Spectrum
Skillets offer a broader edge browning spectrum due to their direct contact with the heat source, allowing precise control over toasting intensity and texture variations. Induction griddles provide more uniform heat distribution but tend to produce a narrower range of edge browning, making it ideal for consistent, even toasting without pronounced crust development.
Non-stick Skillet Rebound
A non-stick skillet offers superior rebound when toasting, allowing bread slices to lift easily without tearing or sticking, which enhances even browning and consistent texture. In contrast, induction griddles provide rapid, uniform heat but often lack the flexible surface rebound needed for delicate toast handling.
Skillet vs induction griddle for toasting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com