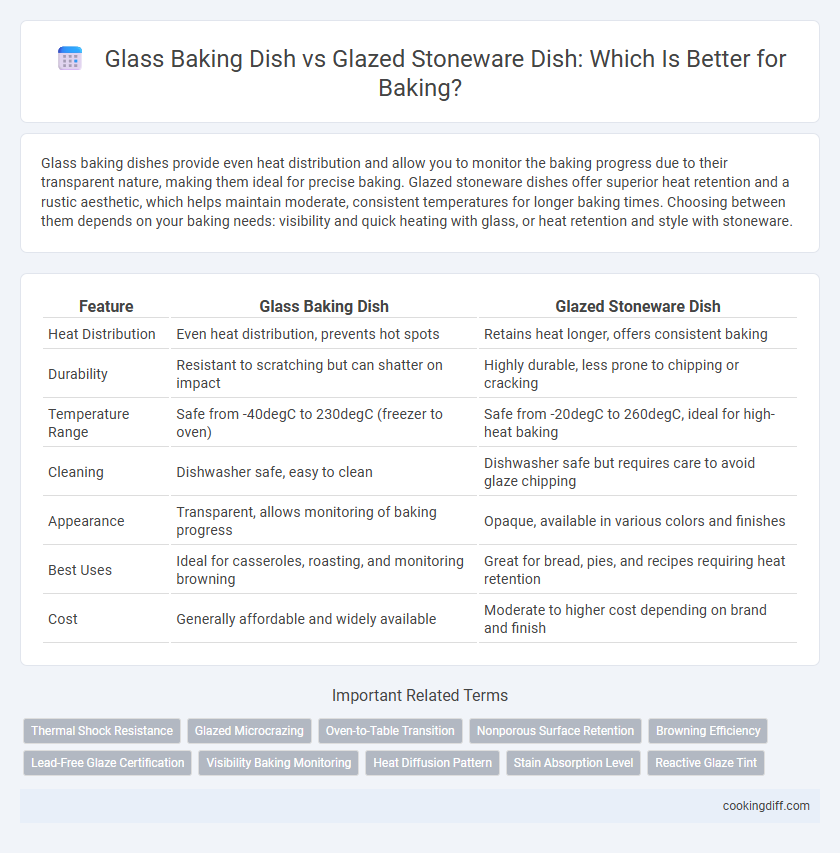
Glass baking dishes provide even heat distribution and allow you to monitor the baking progress due to their transparent nature, making them ideal for precise baking. Glazed stoneware dishes offer superior heat retention and a rustic aesthetic, which helps maintain moderate, consistent temperatures for longer baking times. Choosing between them depends on your baking needs: visibility and quick heating with glass, or heat retention and style with stoneware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Baking Dish | Glazed Stoneware Dish |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Even heat distribution, prevents hot spots | Retains heat longer, offers consistent baking |
| Durability | Resistant to scratching but can shatter on impact | Highly durable, less prone to chipping or cracking |
| Temperature Range | Safe from -40degC to 230degC (freezer to oven) | Safe from -20degC to 260degC, ideal for high-heat baking |
| Cleaning | Dishwasher safe, easy to clean | Dishwasher safe but requires care to avoid glaze chipping |
| Appearance | Transparent, allows monitoring of baking progress | Opaque, available in various colors and finishes |
| Best Uses | Ideal for casseroles, roasting, and monitoring browning | Great for bread, pies, and recipes requiring heat retention |
| Cost | Generally affordable and widely available | Moderate to higher cost depending on brand and finish |
Introduction: Glass vs Glazed Stoneware Baking Dishes
Glass baking dishes offer excellent heat retention and allow even cooking with clear visibility of the food inside, making them ideal for recipes requiring precise monitoring. Glazed stoneware dishes provide superior heat distribution and a naturally non-stick surface, which enhances browning and creates a crispy texture. Choosing between glass and glazed stoneware depends on the desired cooking performance and the specific baking task.
Heat Conductivity: Glass vs Stoneware Performance
How does the heat conductivity of glass baking dishes compare to that of glazed stoneware dishes? Glass baking dishes generally offer faster and more even heat distribution, resulting in quicker baking times and consistent browning. Glazed stoneware dishes retain heat longer, providing more gradual and steady cooking, which is ideal for slow-baked recipes and maintaining warmth after baking.
Baking Results: Texture and Browning Comparison
| Glass Baking Dish | Glazed Stoneware Dish |
|---|---|
| Glass dishes distribute heat evenly, promoting consistent baking and preventing hotspots, resulting in well-cooked interior textures with moderate crust browning. | Glazed stoneware retains heat longer, creating a slower baking environment that enhances crust crispness and deeper browning, ideal for breads and casseroles. |
| Produces moister baked goods due to less heat retention after oven removal, preserving soft textures in cakes and custards. | Promotes firmer, crunchier textures by maintaining elevated temperatures after baking, which enhances caramelization on surfaces. |
| Best for recipes requiring gentle, uniform heat for tender crumb development. | Preferred for dishes benefiting from intense bottom heat and stronger Maillard reactions for crispier crusts. |
Durability and Longevity of Each Dish Type
Glass baking dishes are prone to thermal shock but resist staining and odors, offering moderate durability. Glazed stoneware dishes provide excellent durability with resistance to chipping and retain heat longer, contributing to longevity.
- Glass dishes can break under sudden temperature changes - Careful handling and gradual temperature adjustments are essential for durability.
- Glazed stoneware is highly resistant to chips and scratches - The dense, glazed surface enhances longevity in everyday use.
- Stoneware retains heat better than glass - This heat retention improves baking consistency over time.
Oven Safety and Temperature Limits
Glass baking dishes typically withstand oven temperatures up to 450degF, offering reliable oven safety as they distribute heat evenly. Glazed stoneware dishes, however, can often tolerate higher temperatures, sometimes up to 500degF, but require careful handling to prevent thermal shock.
Oven safety for glass dishes involves avoiding sudden temperature changes to prevent cracking, while glazed stoneware's dense composition offers excellent heat retention but may be prone to chipping if dropped. Temperature limits for glass baking dishes are generally lower, making them ideal for moderate baking tasks, whereas glazed stoneware suits recipes requiring higher heat. Understanding these temperature tolerances enhances baking results and prolongs dish longevity.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Glass baking dishes are typically smooth and non-porous, making them easier to clean and resistant to staining. Glazed stoneware dishes often have a textured surface that may require more careful scrubbing to avoid residue buildup and maintain the glaze's integrity.
- Non-porous Surface - Glass dishes resist absorbing oils and odors, allowing for straightforward cleaning.
- Textured Glaze - Stoneware's glazed finish can trap food particles, necessitating gentle but thorough cleaning.
- Durability in Cleaning - Glass can withstand dishwasher use more reliably than some glazed stoneware, which may chip or dull over time.
Choosing between these materials depends on your preference for ease of cleaning versus aesthetic and heat retention qualities.
Versatility in Cooking and Serving
Glass baking dishes offer exceptional versatility by allowing direct transition from oven to table with minimal heat retention, making them ideal for serving. Glazed stoneware dishes provide superior heat distribution and a rustic aesthetic, enhancing both cooking performance and presentation.
- Glass Baking Dish - Enables easy monitoring of baking progress through transparent sides and suits a variety of oven-based recipes.
- Glazed Stoneware Dish - Retains heat longer for extended serving warmth and provides an attractive, durable surface for both cooking and presentation.
- Versatility - Both materials accommodate oven, microwave, and dishwasher use, catering to seamless cooking and serving experiences.
Aesthetic Appeal and Presentation
Glass baking dishes offer a clear view of the baking process and provide a sleek, modern aesthetic that enhances presentation by showcasing the food's color and texture. Their glossy finish reflects light, adding an elegant touch to the table setting.
Glazed stoneware dishes bring a rustic, artisanal charm with their varied colors and matte textures, perfect for cozy, home-style presentations. These dishes retain heat well, keeping food warm longer while contributing to a visually appealing, handmade look.
Cost Comparison: Glass vs Stoneware
Glass baking dishes typically cost less upfront, with prices ranging from $10 to $30, making them an affordable choice for everyday use. They provide even heat distribution but may be prone to scratching or breaking over time compared to stoneware.
Glazed stoneware dishes usually range from $25 to $60, reflecting their durability and superior heat retention for consistent baking results. Although more expensive, stoneware offers long-term value due to its resistance to chipping and excellent moisture retention properties.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Shock Resistance
Glass baking dishes offer good thermal shock resistance but can crack when exposed to sudden temperature changes, whereas glazed stoneware dishes provide superior thermal shock resistance, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without damage. This makes glazed stoneware ideal for baking recipes that require moving from oven to countertop or vice versa.
Glazed Microcrazing
Glazed stoneware dishes often develop microcrazing, a network of fine cracks on the surface glaze that can harbor bacteria and affect the dish's longevity, whereas glass baking dishes typically resist such microscopic fractures due to their non-porous, smooth surface. Microcrazing in glazed stoneware can compromise food safety over time, making glass bakeware a more hygienic choice for repeated baking tasks.
Oven-to-Table Transition
Glass baking dishes offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for recipes that benefit from consistent temperatures; their clear design allows easy monitoring of browning during baking. Glazed stoneware dishes provide superior oven-to-table transition with their stylish appearance and ability to maintain warmth longer, enhancing presentation while serving directly from oven to dining table.
Nonporous Surface Retention
Glass baking dishes feature a nonporous surface that resists staining and odor absorption, ensuring consistent food flavor and easy cleaning over time. Glazed stoneware dishes also provide a sealed, nonporous finish but may require more careful handling to maintain their glaze and prevent microscopic cracks that could harbor bacteria.
Browning Efficiency
Glass baking dishes conduct heat evenly but tend to brown edges more quickly due to their transparency and heat retention, enhancing crust development in baked goods. Glazed stoneware dishes provide consistent heat distribution and moderate browning, ideal for slower, more even cooking without burning edges.
Lead-Free Glaze Certification
Glass baking dishes offer the advantage of being naturally non-reactive and free from harmful chemicals, often certified with lead-free glaze to ensure food safety during high-temperature baking. Glazed stoneware dishes, while providing excellent heat retention and even cooking, must be carefully selected for lead-free glaze certification to prevent potential lead contamination, especially in older or imported products.
Visibility Baking Monitoring
Glass baking dishes offer superior visibility during baking, allowing for easy monitoring of browning and doneness without opening the oven. Glazed stoneware dishes, while excellent for heat retention and even cooking, limit visual inspection due to their opaque surfaces.
Heat Diffusion Pattern
Glass baking dishes provide steady and even heat diffusion, allowing for uniform cooking and browning without hot spots, while glazed stoneware dishes retain heat longer and distribute it more gradually, resulting in slower, consistent baking that enhances moisture retention in baked goods. Choosing between glass and glazed stoneware depends on the desired baking outcome, with glass offering quicker heat transfer and stoneware promoting thorough, gentle cooking.
Stain Absorption Level
Glass baking dishes exhibit low stain absorption levels due to their non-porous surface, ensuring easy cleaning and maintaining a clear appearance over time. In contrast, glazed stoneware dishes have a slightly higher stain absorption level because microscopic pores in the glaze can trap food particles, which may lead to discoloration with prolonged use.
Glass Baking Dish vs Glazed Stoneware Dish for baking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com