Heavy cream provides a rich, dense texture and high-fat content ideal for whipping and creating creamy, decadent baked goods. Oat cream offers a dairy-free, plant-based alternative with a lighter texture and subtle sweetness, making it suitable for vegan recipes or those with lactose intolerance. When substituting, consider oat cream's lower fat content, which may require adjustments to achieve similar consistency and moisture in the final baked product.
Table of Comparison
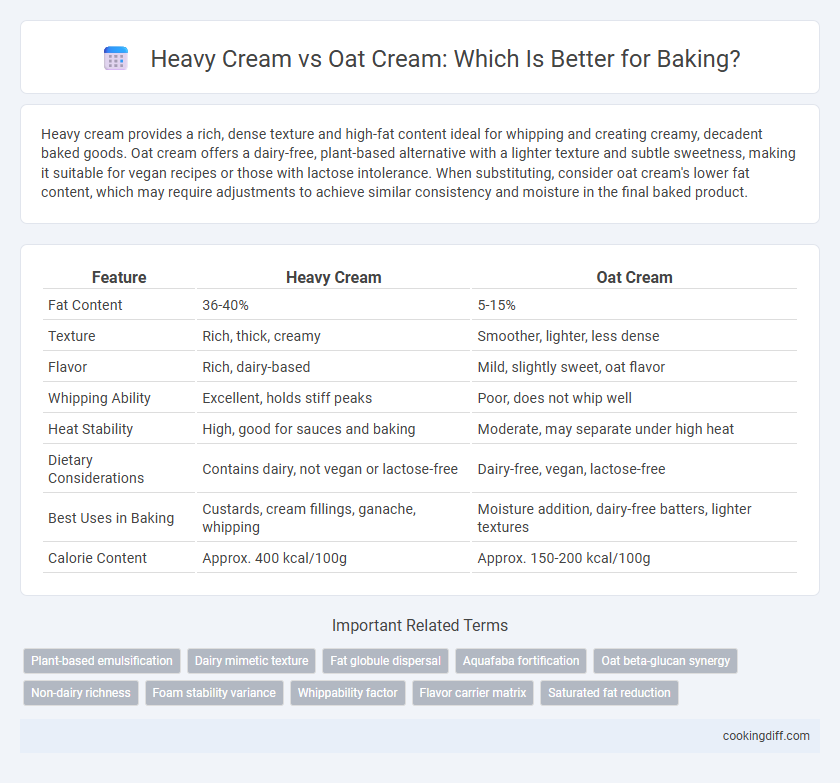
| Feature | Heavy Cream | Oat Cream |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 36-40% | 5-15% |
| Texture | Rich, thick, creamy | Smoother, lighter, less dense |
| Flavor | Rich, dairy-based | Mild, slightly sweet, oat flavor |
| Whipping Ability | Excellent, holds stiff peaks | Poor, does not whip well |
| Heat Stability | High, good for sauces and baking | Moderate, may separate under high heat |
| Dietary Considerations | Contains dairy, not vegan or lactose-free | Dairy-free, vegan, lactose-free |
| Best Uses in Baking | Custards, cream fillings, ganache, whipping | Moisture addition, dairy-free batters, lighter textures |
| Calorie Content | Approx. 400 kcal/100g | Approx. 150-200 kcal/100g |
Introduction to Heavy Cream and Oat Cream
Heavy cream is a rich dairy product with a fat content of around 36-40%, ideal for creating smooth, creamy textures in baked goods. Oat cream, a plant-based alternative made from oats, offers a lower fat content and a naturally sweet, mild flavor suitable for vegan and lactose-free baking. Both creams contribute distinct moisture and richness, influencing the texture and taste of cakes, pastries, and sauces differently.
Nutritional Differences: Heavy Cream vs Oat Cream
Heavy cream contains approximately 36-40% fat, making it rich in calories and essential for creating dense, creamy textures in baked goods. It also provides fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, supporting overall nutrition in traditional baking.
Oat cream, a plant-based alternative, typically contains 10-15% fat and offers fiber along with beta-glucans that promote heart health. It is lower in saturated fat and cholesterol-free, making it a suitable choice for vegan and lactose-intolerant bakers seeking a lighter nutritional profile.
Flavor Profiles in Baking
Heavy cream delivers a rich, buttery flavor that enhances the depth and texture of baked goods, making it ideal for creamy fillings and decadent desserts. Oat cream provides a subtle, slightly sweet, and nutty taste that complements baked items with lighter, plant-based profiles. Choosing between heavy cream and oat cream depends on the desired richness and flavor complexity in recipes like cakes, pastries, and custards.
Texture and Consistency Comparison
How do heavy cream and oat cream differ in texture and consistency for baking? Heavy cream provides a rich, dense texture with high fat content that enhances moisture and creates a smooth, creamy consistency in baked goods. Oat cream, being plant-based, offers a lighter, slightly thinner texture with a mild oat flavor, making it suitable for dairy-free recipes but less effective at creating dense, rich textures.
Performance in Cakes, Muffins, and Breads
Heavy cream provides a rich, stable fat content ideal for creating moist, tender cakes and muffins with a smooth crumb. Oat cream, while lower in fat and protein, adds moisture and a subtle sweetness but may result in a denser texture and less rise in baked goods.
- Moisture retention - Heavy cream helps maintain moisture in cakes and muffins, enhancing softness and shelf life.
- Texture impact - Oat cream can cause slightly drier or denser baked products due to its lower fat and protein content.
- Flavor profile - Heavy cream contributes a rich dairy flavor, whereas oat cream imparts a mild, naturally sweet taste suitable for vegan baking.
Selecting heavy cream optimizes traditional cake softness and rise, while oat cream suits dairy-free recipes prioritizing moisture and subtle flavor.
How Heavy Cream and Oat Cream Affect Moisture Levels
Heavy cream contains around 36-40% fat, which helps retain moisture in baked goods, resulting in a rich and tender texture. Oat cream, typically lower in fat (around 10-15%) and higher in water content, can increase moisture but may create a lighter, less creamy consistency.
Using heavy cream in baking enhances moisture retention by forming a stable fat network that traps steam during baking, ensuring softness and richness. Oat cream's plant-based composition introduces more water and less fat, making it suitable for dairy-free recipes but potentially producing drier or less cohesive baked products. Adjusting liquid ratios is essential when substituting oat cream to maintain optimal moisture balance and texture in the final bake.
Vegan and Dairy-Free Baking Substitutes
Heavy cream provides rich fat content essential for traditional baking textures, while oat cream offers a plant-based, dairy-free alternative suitable for vegan recipes. Oat cream's lower fat content and natural sweetness create a lighter, slightly different flavor profile in baked goods.
- Heavy Cream in Baking - Heavy cream adds moisture and richness, enhancing the texture and flavor of cakes, frostings, and custards.
- Oat Cream Benefits - Oat cream serves as an allergen-friendly substitute, free from dairy and soy, ideal for vegan and lactose-intolerant bakers.
- Texture and Flavor Differences - Heavy cream yields denser, creamier results, while oat cream produces lighter, subtly sweet baked goods with a mild oat flavor.
Impact on Whipping and Frosting
Heavy cream contains higher fat content, making it ideal for whipping into stable peaks and smooth frostings. Oat cream has lower fat and more water, resulting in softer, less stable whipped textures that may affect frosting consistency.
- Heavy Cream Whipping - Achieves firm, long-lasting peaks perfect for decorating and piping.
- Oat Cream Whipping - Produces lighter, less stable foam that can collapse quickly.
- Frosting Stability - Heavy cream-based frostings hold shape better under heat and moisture compared to oat cream counterparts.
Shelf Life and Storage Tips
| Type | Shelf Life | Storage Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Cream | Typically lasts 1-2 weeks in the refrigerator unopened; once opened, consume within 5-7 days. | Store in the coldest part of the fridge below 40degF (4degC) and keep tightly sealed to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage. |
| Oat Cream | Generally has a shelf life of 7-10 days refrigerated after opening, sometimes shorter due to plant-based nature. | Refrigerate immediately after opening, keep in an airtight container, and shake well before use to maintain consistency for baking. |
Related Important Terms
Plant-based emulsification
Heavy cream provides rich fat content and natural emulsifiers essential for stable emulsification in baking, whereas oat cream offers a plant-based alternative with lower fat but contains beta-glucans and starches that act as natural emulsifiers, supporting moisture retention and texture. Oat cream's plant-based emulsification properties make it suitable for vegan baking, but it may require additional stabilizers for the same creamy consistency achieved by heavy cream.
Dairy mimetic texture
Heavy cream provides a rich, smooth texture with high fat content essential for stable whipped toppings and creamy baked goods, while oat cream offers a dairy-free alternative that mimics the creaminess with a slightly lighter, plant-based consistency but may lack the same stability in heat-sensitive recipes. Oat cream's emulsifiers and added fats help approximate heavy cream's mouthfeel, making it suitable for vegan baking where dairy's dense texture is desired.
Fat globule dispersal
Heavy cream contains larger fat globules that create a rich, stable emulsion ideal for whipping and adding moisture to baked goods, while oat cream's smaller fat globules offer a lighter dispersion, resulting in a less stable texture but suitable for dairy-free baking. The difference in fat globule size influences the cream's ability to retain air and moisture, affecting the final crumb and tenderness of cakes and pastries.
Aquafaba fortification
Heavy cream provides rich fat content essential for stable emulsions and creamy textures in baking, while oat cream offers a plant-based alternative with lower fat and a mild flavor. Aquafaba fortification enhances oat cream's whipping and binding properties, closely mimicking heavy cream's performance in recipes requiring aeration and moisture retention.
Oat beta-glucan synergy
Oat cream enhances baking recipes by providing a natural source of beta-glucan, which improves moisture retention and crumb structure, resulting in softer and more tender baked goods compared to heavy cream. The beta-glucan in oat cream works synergistically with other ingredients to create a stable texture and contribute to increased dietary fiber content in the final product.
Non-dairy richness
Oat cream offers a rich, non-dairy alternative to heavy cream in baking, providing a creamy texture and mild flavor ideal for vegan and lactose-free recipes. Its natural sweetness and ability to whip moderately make it suitable for cakes, desserts, and sauces without the saturated fat content found in heavy cream.
Foam stability variance
Heavy cream contains about 36-40% fat, providing superior foam stability and rich texture in baking applications, while oat cream typically has a lower fat content around 10-15%, resulting in less stable foams and a lighter, less dense consistency. The higher fat content in heavy cream supports the formation of firm, long-lasting peaks, essential for recipes like mousses and whipped toppings, whereas oat cream foams tend to collapse faster due to its plant-based emulsifiers and lower fat profile.
Whippability factor
Heavy cream contains 36-40% fat, providing excellent whippability and stable peaks ideal for recipes requiring fluffy textures, while oat cream, with a lower fat content around 10-15%, offers limited whipping ability and often requires additives to achieve similar volume and stability. Choosing heavy cream ensures consistent aeration and structure in baked goods, whereas oat cream suits dairy-free diets but may result in softer, less stable whipped toppings.
Flavor carrier matrix
Heavy cream contains around 36-40% fat, creating a rich, creamy matrix that effectively carries and enhances butterfat-soluble flavors in baked goods. Oat cream, typically lower in fat (around 10-15%) and higher in carbohydrates, provides a milder, slightly sweet flavor but a less robust fat matrix, resulting in a subtler flavor carrier and different texture in baked recipes.
Heavy Cream vs Oat Cream for Baking Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com