Whipped cream delivers a rich, creamy texture and classic taste, perfect for traditional desserts, while aquafaba offers a vegan-friendly, allergen-free alternative with a light, airy consistency. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, whips up into stiff peaks similar to egg whites, making it ideal for those with dairy restrictions or plant-based diets. Choosing between them depends on dietary needs and flavor preferences, as whipped cream provides indulgence, and aquafaba ensures inclusivity without sacrificing texture.
Table of Comparison
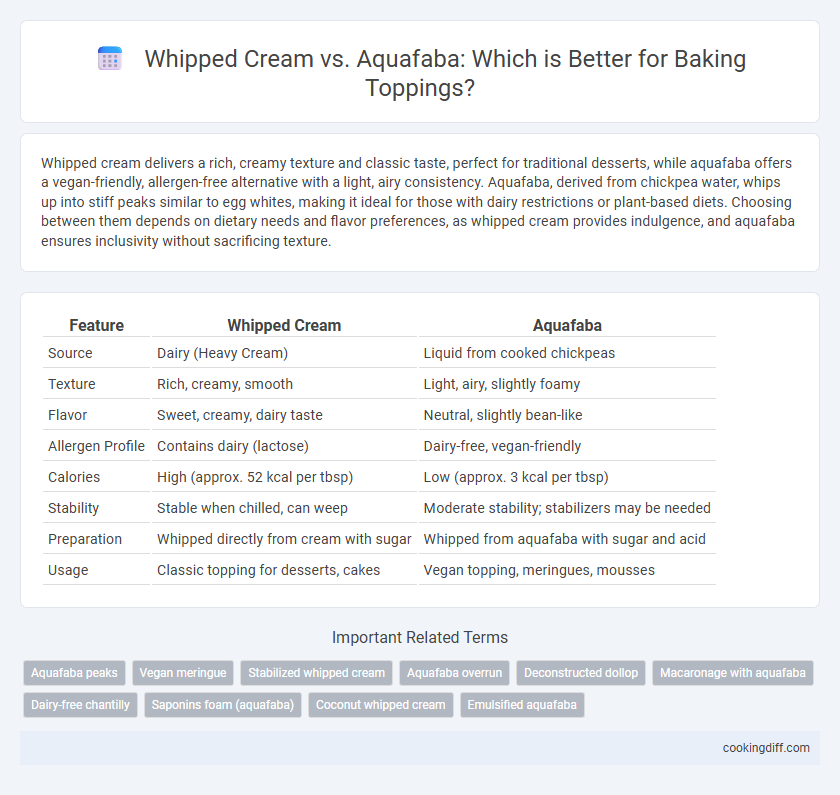
| Feature | Whipped Cream | Aquafaba |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Dairy (Heavy Cream) | Liquid from cooked chickpeas |
| Texture | Rich, creamy, smooth | Light, airy, slightly foamy |
| Flavor | Sweet, creamy, dairy taste | Neutral, slightly bean-like |
| Allergen Profile | Contains dairy (lactose) | Dairy-free, vegan-friendly |
| Calories | High (approx. 52 kcal per tbsp) | Low (approx. 3 kcal per tbsp) |
| Stability | Stable when chilled, can weep | Moderate stability; stabilizers may be needed |
| Preparation | Whipped directly from cream with sugar | Whipped from aquafaba with sugar and acid |
| Usage | Classic topping for desserts, cakes | Vegan topping, meringues, mousses |
Introduction to Dairy and Vegan Toppings
Whipped cream, made from heavy dairy cream, offers a rich and creamy texture favored in traditional baking toppings. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, serves as a popular vegan alternative that mimics whipped cream's fluffiness without dairy.
- Whipped Cream Texture - Provides smooth, velvety peaks ideal for garnishing desserts and beverages.
- Aquafaba Functionality - Acts as a plant-based emulsifier that whips into stable foam suitable for vegan recipes.
- Dietary Preferences - Whipped cream is dairy-based while aquafaba caters to vegans and those with lactose intolerance.
What Is Whipped Cream?
| Whipped Cream Definition | Whipped cream is a dairy product made by beating heavy cream until it becomes light and fluffy, containing at least 30% milk fat. |
| Texture and Flavor | It has a rich, creamy texture and a sweet, mild flavor that enhances desserts and beverages. |
| Common Uses | Widely used as a topping for pies, cakes, hot chocolate, and coffee, providing a smooth, airy finish. |
What Is Aquafaba?
Aquafaba is the viscous water in which legumes such as chickpeas have been cooked, widely used as an egg white substitute in vegan baking and cooking. It mimics the properties of whipped cream by creating a light, airy texture when whipped.
Unlike traditional whipped cream made from dairy, aquafaba is cholesterol-free and lower in fat, making it an appealing choice for health-conscious individuals. It can be flavored and sweetened to suit various desserts while providing similar volume and stability. Aquafaba's versatility extends to creating meringues, mousses, and frostings, offering a plant-based alternative without compromising on texture or taste.
Taste Comparison: Whipped Cream vs Aquafaba
Whipped cream offers a rich, creamy flavor with a slightly sweet and buttery taste that enhances desserts, while aquafaba provides a lighter, more neutral taste with subtle bean-like undertones. The texture of whipped cream is smooth and velvety, making it a classic choice for topping cakes and pies.
Aquafaba's airy and fluffy consistency mimics whipped cream but lacks the creamy richness, making it ideal for those seeking a vegan or low-fat alternative. Its mild taste absorbs surrounding flavors well but may require added sweeteners or flavorings to match the indulgence of traditional whipped cream.
Texture and Consistency Differences
Whipped cream offers a rich, smooth texture with a stable, creamy consistency ideal for traditional desserts. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, provides a lighter, airy texture with a more delicate hold, suitable for vegan toppings.
- Whipped cream texture - Dense and velvety, maintaining shape under pressure.
- Aquafaba consistency - Fluffy and lighter, with peaks that hold less firmly over time.
- Stability difference - Whipped cream resists melting faster due to fat content, while aquafaba tends to soften more quickly.
Choosing between whipped cream and aquafaba depends on preference for richness versus a plant-based, airy topping option.
Nutritional Value and Dietary Considerations
Whipped cream is rich in saturated fats and calories, providing essential fat-soluble vitamins like A and D, but it may not suit those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, is low in calories, fat-free, and cholesterol-free, making it a vegan and allergen-friendly alternative.
While whipped cream offers a creamy texture with higher protein content, aquafaba is primarily composed of water and soluble plant proteins, making it a lower-nutrient substitute. Dietary considerations favor aquafaba for individuals following vegan, dairy-free, or low-fat diets, whereas whipped cream suits those seeking richer nutritional profiles and calcium intake.
Preparation and Ease of Use
Whipped cream requires heavy cream and often sugar, needing cold temperatures and vigorous whipping to achieve stiff peaks. Aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, offers a vegan alternative that whips into a foam without refrigeration but typically takes longer to reach the desired consistency.
- Whipped cream demands cold heavy cream - it whips faster and holds shape better when chilled.
- Aquafaba preparation is accessible for vegans - it uses simple canned chickpea liquid but requires extended whipping time.
- Whipped cream's ease varies by equipment - hand whisks make whipping labor-intensive, while electric mixers speed the process.
Stability and Shelf Life of Each Topping
Whipped cream offers a rich texture but tends to lose stability and deflate within a few hours at room temperature, requiring refrigeration to maintain its firmness. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, provides a vegan alternative with moderate stability, lasting longer than whipped cream without immediate collapse. Shelf life of whipped cream is typically a few days when refrigerated, while aquafaba can remain stable for up to 24 hours, making it suitable for short-term use in desserts.
Best Uses for Whipped Cream and Aquafaba in Baking
Whipped cream is ideal for adding rich, creamy texture and flavor to desserts like cakes, pies, and hot beverages, enhancing both appearance and taste. Aquafaba, a vegan alternative derived from chickpea brine, excels in recipes requiring egg white substitutes, such as meringues, mousses, and light frostings. Each topping's unique properties make whipped cream perfect for indulgent recipes, while aquafaba suits allergy-friendly and plant-based baking needs.
Related Important Terms
Aquafaba peaks
Aquafaba peaks, derived from chickpea brine, offer a vegan alternative to whipped cream with stable, glossy, and airy textures ideal for cake and dessert toppings. Its unique protein and starch composition allows it to mimic traditional dairy whipped cream, providing a low-fat, cholesterol-free option that holds firm longer under various temperatures.
Vegan meringue
Whipped cream provides rich, creamy texture but contains dairy, while aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, offers a vegan meringue alternative with a light, airy consistency and strong stabilizing properties ideal for allergy-friendly dessert toppings. Aquafaba's versatility and ability to mimic egg whites make it a popular choice for creating vegan meringues and frostings without sacrificing texture or flavor.
Stabilized whipped cream
Stabilized whipped cream, made by incorporating gelatin, cornstarch, or cream of tartar, offers a rich, creamy texture and holds its shape longer than aquafaba, which is a vegan alternative derived from chickpea water but tends to be lighter and less stable over time. While aquafaba is favored for its allergen-friendly and lower-fat qualities, stabilized whipped cream remains superior for recipes requiring durable, luscious topping consistency.
Aquafaba overrun
Aquafaba, derived from chickpea brine, achieves a remarkable overrun of up to 300%, creating a light, airy topping comparable to traditional whipped cream but entirely plant-based and allergen-free. Its superior foaming capacity and stable structure make aquafaba an excellent vegan alternative for desserts requiring a fluffy, voluminous finish.
Deconstructed dollop
Whipped cream offers a rich, creamy texture with high fat content, creating a stable, luxurious deconstructed dollop ideal for traditional baking toppings. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, provides a low-fat, vegan alternative with airy, light peaks that mimic whipped cream's volume while adding a unique, plant-based twist to deconstructed dollop presentations.
Macaronage with aquafaba
Whipped cream offers a rich, creamy topping with a smooth texture, while aquafaba provides a vegan-friendly alternative made from chickpea water, ideal for delicate recipes like macarons where precise macaronage is critical to achieving the perfect batter consistency. Mastering macaronage with aquafaba ensures a stable, glossy meringue that folds seamlessly, creating light, airy shells with the desired chewy interior.
Dairy-free chantilly
Aquafaba creates a stable, dairy-free Chantilly cream alternative by whipping the viscous liquid from cooked chickpeas until it forms stiff peaks similar to traditional whipped cream. Unlike heavy cream, aquafaba is low-calorie, vegan-friendly, and allergen-free, making it an ideal topping for dairy-free and plant-based baked goods.
Saponins foam (aquafaba)
Aquafaba, derived from chickpea brine, contains saponins that create a stable, airy foam perfect for vegan whipped toppings, rivaling the creaminess of traditional whipped cream. Unlike dairy-based whipped cream, aquafaba's saponin-rich foam offers a cholesterol-free, allergen-friendly alternative that maintains texture and volume in various baking applications.
Coconut whipped cream
Coconut whipped cream offers a rich, creamy texture and natural sweetness with healthy fats, making it ideal for dairy-free baking toppings compared to aquafaba, which is lower in fat and provides a lighter, more airy consistency but less flavor depth. Its stable structure holds well in warm conditions, enhancing desserts like pies and cakes where aquafaba may soften quickly.
Whipped cream vs Aquafaba for topping. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com