Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables to inactivate enzymes that cause spoilage, helping preserve color but can lead to slight nutrient loss. Flash steaming uses high-temperature steam for a short duration, retaining vibrant color more effectively by minimizing water contact and preventing leaching of pigments. Compared to blanching, flash steaming better maintains the natural appearance and nutritional quality of vegetables.
Table of Comparison
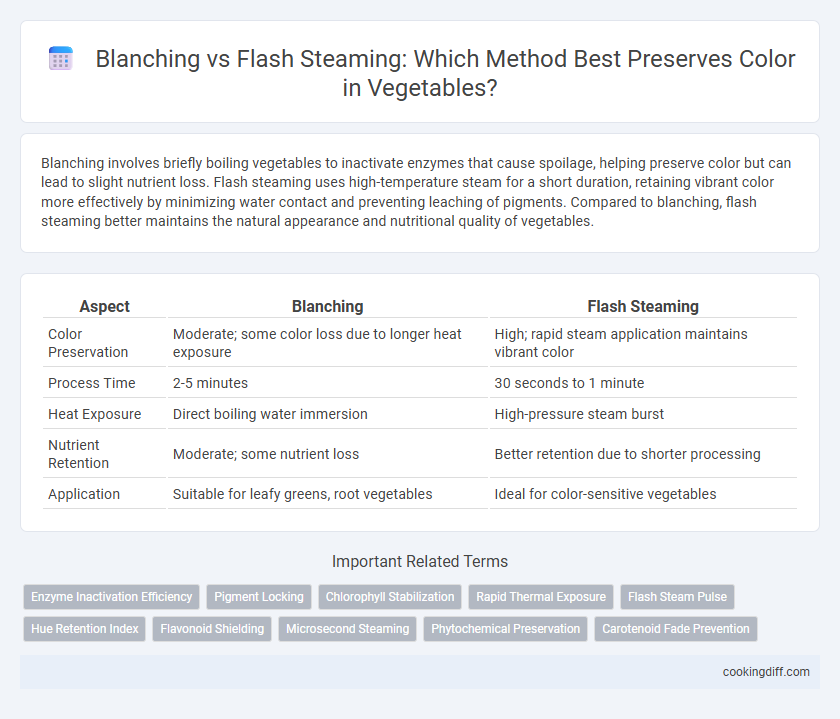
| Aspect | Blanching | Flash Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Color Preservation | Moderate; some color loss due to longer heat exposure | High; rapid steam application maintains vibrant color |
| Process Time | 2-5 minutes | 30 seconds to 1 minute |
| Heat Exposure | Direct boiling water immersion | High-pressure steam burst |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate; some nutrient loss | Better retention due to shorter processing |
| Application | Suitable for leafy greens, root vegetables | Ideal for color-sensitive vegetables |
Understanding Blanching and Flash Steaming
Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables followed by rapid cooling to deactivate enzymes and preserve color, texture, and nutrients effectively. Flash steaming uses high-temperature steam applied for a very short duration, minimizing nutrient loss while enhancing color retention.
Understanding blanching helps optimize temperature and time to prevent overcooking and color degradation. Flash steaming reduces water contact, limiting leaching of water-soluble vitamins and pigments, making it ideal for delicate vegetables. Both methods aim to maintain vibrant color but differ significantly in processing technique and nutrient preservation outcomes.
Science Behind Color Preservation
Blanching and flash steaming both target enzymatic activity to preserve color in vegetables, but flash steaming uses higher temperatures for shorter times, minimizing pigment degradation. The Maillard reaction is less likely during flash steaming, helping maintain chlorophyll and carotenoid integrity.
- Enzyme Inactivation - Flash steaming rapidly deactivates polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase enzymes that cause browning and color loss.
- Heat Exposure - Blanching involves longer heat exposure, which can lead to leaching of water-soluble pigments and duller colors.
- Pigment Stability - Flash steaming preserves chlorophyll structure by preventing acidification and oxidative reactions.
Blanching: Process and Benefits
How does blanching compare to flash steaming in preserving color during vegetable processing? Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables followed by rapid cooling, effectively inactivating enzymes that cause discoloration. This process not only preserves the vibrant color but also enhances texture and extends shelf life more reliably than flash steaming.
Flash Steaming: Process and Benefits
| Flash steaming involves exposing vegetables to high-pressure steam for a very short duration, typically 15-60 seconds, which effectively inactivates enzymes responsible for color degradation. |
| This process ensures superior retention of vibrant colors compared to traditional blanching methods by minimizing leaching of water-soluble pigments and nutrients. |
| Benefits of flash steaming include rapid treatment, enhanced texture preservation, and reduced nutrient loss, making it ideal for maintaining the fresh appearance and quality of green vegetables. |
Color Retention: Blanching vs Flash Steaming
Blanching and flash steaming both aim to preserve the vibrant colors of vegetables during processing, but flash steaming generally offers superior color retention due to faster heat application. This rapid method minimizes pigment degradation, maintaining the fresh, bright appearance of produce better than traditional blanching techniques.
- Flash Steaming - Uses high-temperature steam for a short duration, reducing pigment loss and enzyme activity.
- Blanching - Involves boiling or steaming for longer, which can lead to more color fading and nutrient leaching.
- Color Retention - Flash steaming preserves chlorophyll and carotenoids more effectively by limiting heat exposure time.
Choosing flash steaming over blanching enhances color retention in processed vegetables, improving visual appeal and marketability.
Nutrient Loss Comparison
Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables to deactivate enzymes, which can cause significant nutrient loss, particularly of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex vitamins. Flash steaming uses high-temperature steam for a short duration, preserving more nutrients by minimizing contact with water and reducing leaching. Studies show flash steaming retains higher levels of antioxidants and vitamins compared to traditional blanching methods.
Best Practices for Vibrant Results
Blanching and flash steaming are critical techniques in preserving the vibrant color of vegetables during processing. Employing best practices for each method ensures maximum color retention and overall product quality.
- Blanching Time and Temperature - Precise control of blanching time and temperature minimizes pigment degradation and enzymatic browning.
- Flash Steaming Efficiency - Rapid exposure to steam deactivates enzymes quickly, reducing color loss and preserving freshness.
- Immediate Cooling - Submerging products in chilled water or using air cooling immediately after treatment locks in color and texture.
Suitable Vegetables for Each Method
Blanching is ideal for dense vegetables like green beans, broccoli, and carrots, as it effectively slows enzyme activity and preserves vibrant color. This method involves immersing vegetables in boiling water for a precise duration, ensuring consistent color retention.
Flash steaming suits delicate vegetables such as spinach, asparagus, and peas, where rapid steam exposure gently halts oxidation and maintains bright hues. This technique minimizes nutrient loss and prevents color fading by using high-temperature steam in short bursts.
Equipment and Preparation Tips
Blanching equipment typically includes large steamers or boiling water tanks designed for consistent temperature control, essential for optimal color preservation in vegetables. Preparation tips emphasize the importance of sizing food uniformly and using precise timing to prevent nutrient loss and color dulling.
Flash steaming uses high-pressure steam chambers that rapidly heat produce, retaining vibrant colors by minimizing cooking time and preventing water absorption. Proper preheating of equipment and immediate cooling post-steaming are critical preparation steps to ensure maximum color retention and texture quality.
Related Important Terms
Enzyme Inactivation Efficiency
Blanching typically achieves higher enzyme inactivation efficiency compared to flash steaming, effectively preserving the vibrant color of vegetables by halting enzymatic browning reactions. Flash steaming, while faster, may result in partial enzyme inactivation, potentially compromising color retention during subsequent processing or storage.
Pigment Locking
Blanching effectively locks pigments in vegetables by rapidly heating them to deactivate enzymes responsible for color degradation, resulting in vibrant color retention. Flash steaming offers a quicker alternative that minimizes pigment leaching and preserves chlorophyll and carotenoids, enhancing overall color stability during processing.
Chlorophyll Stabilization
Blanching involves brief exposure to boiling water or steam, effectively inactivating enzymes that degrade chlorophyll, thereby enhancing color preservation in vegetables. Flash steaming offers a quicker method that better stabilizes chlorophyll by minimizing heat exposure and reducing pigment leaching, resulting in superior retention of vibrant green hues.
Rapid Thermal Exposure
Blanching involves rapid thermal exposure through brief boiling or steaming, effectively inactivating enzymes responsible for color degradation, while flash steaming uses even shorter steam treatments to preserve vibrant color by minimizing nutrient and pigment loss. Rapid thermal exposure in both methods halts enzymatic activity swiftly, but flash steaming offers superior color retention due to reduced heat exposure time and moisture contact.
Flash Steam Pulse
Flash Steam Pulse technology outperforms traditional blanching by rapidly heating produce with high-pressure steam, effectively preserving vibrant color and nutrient retention. This method minimizes thermal degradation and oxidative stress, resulting in superior color preservation compared to conventional water blanching.
Hue Retention Index
Blanching involves briefly exposing vegetables to boiling water or steam, helping to deactivate enzymes that cause color degradation, whereas flash steaming uses high-pressure steam for a shorter time, which more effectively preserves the Hue Retention Index by minimizing pigment loss. Studies show that flash steaming maintains a higher Hue Retention Index compared to traditional blanching, resulting in brighter, more vibrant colors in processed vegetables.
Flavonoid Shielding
Blanching effectively stabilizes color by inactivating enzymes but can cause leaching of flavonoids, whereas flash steaming better preserves flavonoid content, maintaining stronger natural pigmentation due to minimal nutrient loss. Flavonoid shielding during flash steaming enhances antioxidant retention, resulting in superior color stability compared to traditional blanching methods.
Microsecond Steaming
Microsecond steaming achieves superior color preservation compared to traditional blanching by minimizing thermal exposure and preventing chlorophyll degradation. This rapid heat treatment method maintains vibrant green hues in vegetables while enhancing nutrient retention and reducing processing time.
Phytochemical Preservation
Blanching and flash steaming both aim to preserve phytochemicals, but flash steaming retains higher levels of antioxidants and vitamins such as vitamin C and polyphenols due to shorter exposure to heat and minimal water contact. Studies reveal flash steaming reduces leaching and degradation of bioactive compounds, enhancing the nutritional and color quality of vegetables compared to traditional blanching methods.
Blanching vs Flash Steaming for color preservation Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com