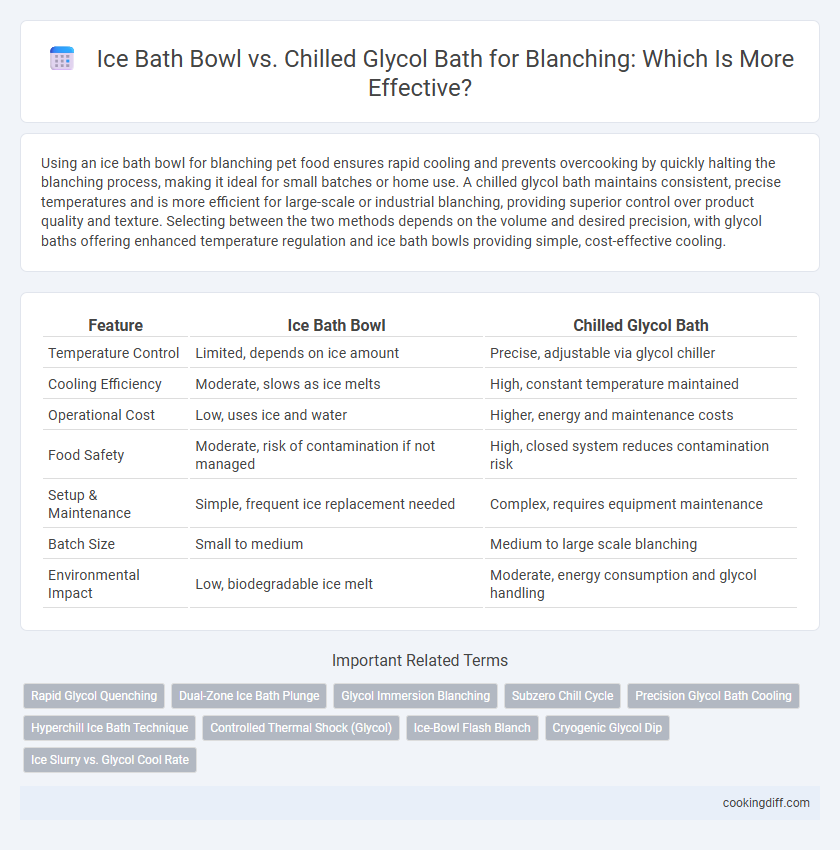
Using an ice bath bowl for blanching pet food ensures rapid cooling and prevents overcooking by quickly halting the blanching process, making it ideal for small batches or home use. A chilled glycol bath maintains consistent, precise temperatures and is more efficient for large-scale or industrial blanching, providing superior control over product quality and texture. Selecting between the two methods depends on the volume and desired precision, with glycol baths offering enhanced temperature regulation and ice bath bowls providing simple, cost-effective cooling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ice Bath Bowl | Chilled Glycol Bath |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Limited, depends on ice amount | Precise, adjustable via glycol chiller |
| Cooling Efficiency | Moderate, slows as ice melts | High, constant temperature maintained |
| Operational Cost | Low, uses ice and water | Higher, energy and maintenance costs |
| Food Safety | Moderate, risk of contamination if not managed | High, closed system reduces contamination risk |
| Setup & Maintenance | Simple, frequent ice replacement needed | Complex, requires equipment maintenance |
| Batch Size | Small to medium | Medium to large scale blanching |
| Environmental Impact | Low, biodegradable ice melt | Moderate, energy consumption and glycol handling |
Introduction: Importance of Rapid Cooling in Blanching
Rapid cooling after blanching is essential to halt enzymatic activity and preserve the texture, color, and nutritional quality of vegetables. Choosing the appropriate cooling method directly impacts product safety and shelf life.
- Ice Bath Bowl - Provides immediate cooling by immersing produce in chilled water with ice, offering simplicity and quick temperature reduction.
- Chilled Glycol Bath - Utilizes refrigerated glycol solutions for precise temperature control and more uniform cooling.
- Cooling Efficiency - Rapid cooling minimizes microbial growth and enzymatic degradation, maintaining food quality and safety.
What is an Ice Bath Bowl?
An Ice Bath Bowl is a container filled with ice and water used to rapidly cool blanching ingredients, halting the cooking process. It maintains temperatures typically around 0degC to 4degC, ensuring effective cooling after hot water or steam blanching.
- Rapid Cooling - The ice bath quickly reduces the temperature of vegetables or fruits to preserve texture and color.
- Simple Setup - It requires only ice and water, making it an accessible option for small-scale blanching.
- Temperature Control - Maintains a consistent cold environment, critical for preventing overcooking and microbial growth.
Understanding Chilled Glycol Bath Technology
| Chilled Glycol Bath Technology | Utilizes a mixture of water and glycol as a refrigerant, achieving precise temperature control between -10degC and 10degC, essential for rapid cooling and minimizing thermal shock during blanching. |
| Ice Bath Bowl | Relies on ice and water to cool blanched products to approximately 0degC, but suffers from inconsistent temperature maintenance and slower cooling rates compared to glycol baths. |
| Performance Efficiency | Chilled glycol baths offer superior heat transfer efficiency and maintain stable low temperatures, improving product texture and shelf life, whereas ice baths are limited by meltwater dilution and temperature fluctuations. |
Temperature Control: Ice Bath vs. Glycol Bath
Ice baths maintain a consistent temperature near 0degC, ideal for quickly halting the cooking process during blanching. This simple method leverages the high heat capacity of ice water for rapid cooling but can fluctuate as ice melts.
Chilled glycol baths offer precise temperature control, adjustable between -5degC and 20degC, optimizing blanching for various food products. The glycol solution resists freezing and ensures uniform cooling, enhancing product quality and consistency.
Efficiency in Cooling Speed and Consistency
Chilled glycol baths provide superior cooling speed and temperature consistency compared to traditional ice bath bowls, ensuring rapid and even blanching results. The glycol solution can maintain precise temperatures below freezing without the need for frequent ice replenishment, enhancing operational efficiency. Ice bath bowls, while simpler, often suffer from temperature fluctuations and slower cooling, which can compromise product quality and increase processing time.
Impact on Food Quality and Color Retention
Which cooling method better preserves food quality and color retention after blanching? An ice bath bowl rapidly cools produce, minimizing cooking time and preserving vibrant colors by preventing overcooking. Chilled glycol baths offer precise temperature control for consistent cooling but may result in varying color retention depending on the food type and immersion time.
Safety and Hygiene Considerations
Ice bath bowls offer a straightforward and safe method for blanching, minimizing microbial growth due to frequent water changes and ease of cleaning. Chilled glycol baths, while more complex, maintain consistent low temperatures that reduce bacterial proliferation risk during blanching processes.
Safety in blanching relies heavily on preventing cross-contamination; ice bath bowls require diligent water replacement and sanitation protocols to uphold hygiene standards. Chilled glycol baths provide a closed system with reduced exposure to external contaminants, enhancing overall safety. Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to prevent glycol leaks and ensure food safety compliance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Costs
Ice bath bowls require lower initial investment costs compared to chilled glycol baths, making them a budget-friendly option for small-scale blanching operations. Operating expenses for ice bath systems include ongoing ice procurement and disposal, which can add up over time, whereas chilled glycol baths have higher upfront costs but lower long-term energy and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights that chilled glycol systems offer better cost efficiency in large-scale or continuous blanching applications due to reduced operating labor and consistent temperature control.
Environmental and Maintenance Concerns
Ice bath bowls require frequent water changes to maintain food safety and temperature control, leading to significant water consumption and disposal concerns. This method poses environmental challenges due to high water usage and potential chemical runoff from cleaning agents.
Chilled glycol baths offer a closed-loop cooling system, greatly reducing water waste and minimizing environmental impact. Maintenance involves periodic glycol replacement and system checks, which, while more complex, result in lower overall resource use and eco-friendly operation.
Related Important Terms
Rapid Glycol Quenching
Rapid glycol quenching in blanching offers superior temperature control compared to an ice bath bowl, ensuring consistent and efficient enzyme inactivation for optimal texture and color retention. The chilled glycol bath maintains precise subzero temperatures, accelerating cooling and reducing cell damage in delicate produce during the blanching process.
Dual-Zone Ice Bath Plunge
Dual-Zone Ice Bath Plunge offers precise temperature control for blanching, combining rapid cooling with consistent cold retention, unlike traditional Ice Bath Bowls which often fluctuate in temperature. The chilled glycol bath provides steady cooling and corrosion resistance but lacks the dual-zone capability that optimizes blanching efficiency by simultaneously managing cooling and thawing phases.
Glycol Immersion Blanching
Glycol immersion blanching offers superior temperature control and rapid cooldown rates compared to traditional ice bath bowls, minimizing enzymatic activity and preserving vegetable texture and color more effectively. Its consistent low temperatures and efficient heat transfer reduce blanching time, enhancing overall product quality and processing efficiency in commercial food operations.
Subzero Chill Cycle
An ice bath bowl provides rapid cooling for blanched products using crushed ice and water, achieving temperatures close to 0degC but with limited temperature stability. Chilled glycol baths offer subzero chill cycle capabilities, maintaining consistent temperatures below freezing for optimal enzyme deactivation and texture preservation in high-volume blanching operations.
Precision Glycol Bath Cooling
Chilled glycol baths provide superior precision in temperature control during blanching compared to ice bath bowls, maintaining consistent cooling rates essential for optimizing texture and nutrient retention. This precise temperature stability reduces thermal shock and enhances product quality in industrial food processing settings.
Hyperchill Ice Bath Technique
The Hyperchill Ice Bath Technique utilizes an ice bath bowl to rapidly reduce the temperature of blanched vegetables, preserving texture and color more effectively than a chilled glycol bath due to its superior cooling rate and ease of use. This method leverages precise temperature control and rapid heat extraction, optimizing nutrient retention and minimizing enzymatic activity during the cooling phase.
Controlled Thermal Shock (Glycol)
Chilled glycol baths provide precise temperature control and rapid heat extraction, enabling a consistent and effective controlled thermal shock during blanching, which preserves texture and color better than an ice bath bowl. The glycol solution's ability to maintain stable subzero temperatures enhances enzyme inactivation and microbial reduction, surpassing the limitations of melting ice and temperature variability in ice bath bowls.
Ice-Bowl Flash Blanch
Ice-Bowl Flash Blanch uses an ice bath bowl for rapid cooling, ensuring optimal texture and color retention by quickly halting the blanching process. Compared to a chilled glycol bath, the ice bath bowl offers a simpler, more energy-efficient method with easier maintenance and reduced chemical handling.
Cryogenic Glycol Dip
A cryogenic glycol dip offers precise temperature control and rapid cooling, enhancing the blanching process by preserving texture and color more effectively than an ice bath bowl. Its efficient heat transfer properties reduce thermal shock, resulting in improved product quality and extended shelf life for vegetables.
Ice Bath Bowl vs Chilled Glycol Bath for blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com