Aluminum pots heat up quickly and offer excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for rapid boiling. Stainless steel insulated pots retain heat longer due to their double-wall construction, reducing energy consumption but requiring more time to reach boiling temperature. Choosing between the two depends on whether speed or heat retention is the priority during boiling tasks.
Table of Comparison
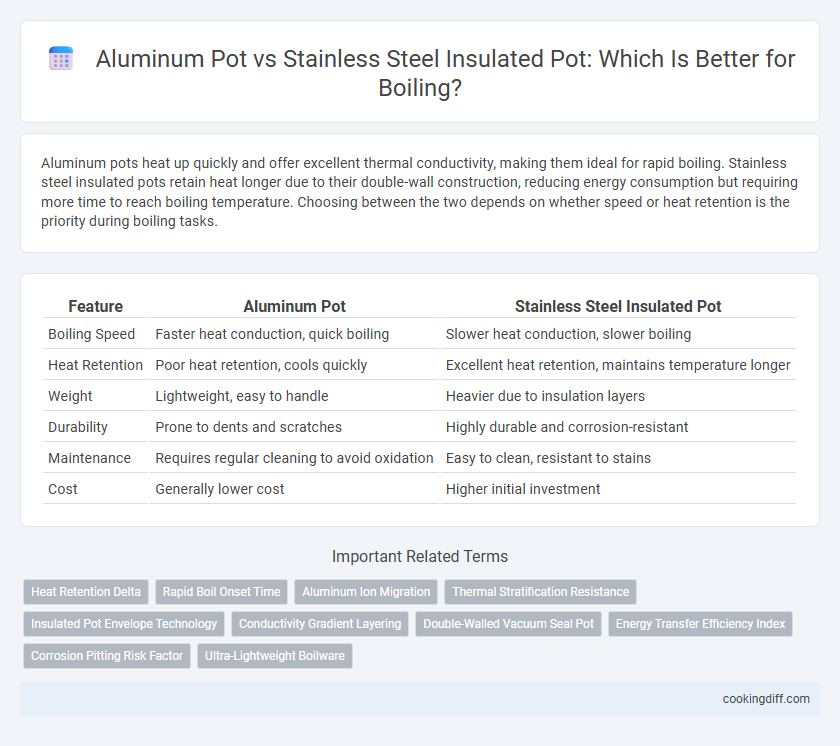
| Feature | Aluminum Pot | Stainless Steel Insulated Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Speed | Faster heat conduction, quick boiling | Slower heat conduction, slower boiling |
| Heat Retention | Poor heat retention, cools quickly | Excellent heat retention, maintains temperature longer |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier due to insulation layers |
| Durability | Prone to dents and scratches | Highly durable and corrosion-resistant |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to avoid oxidation | Easy to clean, resistant to stains |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction: Aluminum Pot vs Stainless Steel Insulated Pot
Aluminum pots heat up quickly due to their high thermal conductivity, making them efficient for boiling water. Stainless steel insulated pots offer superior heat retention and durability, maintaining temperature longer after boiling. Choosing between them depends on whether rapid heating or sustained temperature is the priority in cooking tasks.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Distribution
| Aluminum pots have a high thermal conductivity, approximately 205 W/m*K, which enables rapid heat transfer and uniform temperature distribution for efficient boiling. |
| Stainless steel insulated pots feature lower thermal conductivity, around 16 W/m*K, but their multi-layered design enhances heat retention and prevents heat loss during boiling. |
| While aluminum excels in quick heat distribution, stainless steel insulated pots maintain consistent heat longer, benefitting energy efficiency and controlled boiling processes. |
Boiling Speed and Efficiency
Which pot boils water faster, aluminum or stainless steel insulated? Aluminum pots conduct heat more efficiently due to their high thermal conductivity, resulting in quicker boiling times. Stainless steel insulated pots retain heat longer but generally take more time to reach boiling temperature because of lower thermal conductivity.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Aluminum pots have higher thermal conductivity, allowing them to heat up faster and reduce energy consumption during boiling compared to stainless steel insulated pots. The rapid heat transfer minimizes the time the stove needs to be on, leading to energy savings.
Stainless steel insulated pots retain heat better after boiling, which can lower energy use if the pot remains covered and the contents continue cooking off the heat. However, the initial energy input is higher due to slower heat conduction, resulting in greater total energy consumption during the boiling process.
Durability and Longevity
Aluminum pots offer good heat conductivity but are prone to dents and corrosion, reducing their lifespan when used frequently for boiling. Stainless steel insulated pots provide superior durability and resist rust, ensuring longer-lasting performance under continuous exposure to boiling water.
- Aluminum's susceptibility to corrosion - Prolonged exposure to boiling water can cause aluminum pots to oxidize and degrade faster.
- Stainless steel's rust resistance - High chromium content prevents rust and corrosion, extending pot longevity in humid conditions.
- Insulation benefits - Stainless steel insulated pots retain heat efficiently while protecting the exterior, enhancing durability and energy efficiency.
Safety and Reactivity with Foods
Aluminum pots can react with acidic or alkaline foods, potentially altering flavor and leaching metals, which raises safety concerns during boiling. Stainless steel insulated pots offer superior chemical stability, preventing food contamination and preserving taste.
Stainless steel's non-reactive surface makes it safer for boiling a wide range of ingredients, including acidic tomatoes or vinegar-based sauces. The insulated design maintains consistent heat without harmful reactions, enhancing safety by reducing hot spots. Aluminum pots require anodization or coating to improve safety, whereas stainless steel provides inherent reactivity resistance.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Aluminum pots are lightweight and have a smooth surface, making them easier to clean but prone to scratches and discoloration over time. Stainless steel insulated pots offer superior durability and resistance to stains and corrosion, reducing long-term maintenance efforts. The insulated design also prevents food from sticking, further simplifying the cleaning process compared to aluminum pots.
Weight and Portability Factors
Aluminum pots are significantly lighter than stainless steel insulated pots, making them more suitable for travel and outdoor activities. The portability of aluminum pots is enhanced by their lightweight design, whereas stainless steel insulated pots prioritize durability and heat retention over weight.
- Weight Advantage - Aluminum pots typically weigh 30-50% less than stainless steel insulated pots of similar size.
- Portability - Lightweight aluminum pots are easier to carry in backpacks, ideal for camping and hiking.
- Durability Trade-off - Stainless steel insulated pots offer better insulation but increase the overall weight, reducing ease of transport.
Cost Comparison and Value
Aluminum pots generally cost less than stainless steel insulated pots, making them a more budget-friendly option for boiling purposes. Their lower price point often comes with reduced durability and heat retention efficiency compared to stainless steel models.
Stainless steel insulated pots offer better value over time due to their superior thermal insulation and long-lasting build, which can reduce energy consumption during boiling. Despite higher initial costs, these pots provide enhanced performance and durability, justifying the investment for regular use.
Related Important Terms
Heat Retention Delta
Aluminum pots heat up quickly but have a lower heat retention delta compared to stainless steel insulated pots, which maintain boiling temperatures longer due to their superior thermal insulation properties. The enhanced heat retention of stainless steel insulated pots reduces energy consumption and ensures more consistent cooking results by minimizing temperature fluctuations during boiling.
Rapid Boil Onset Time
Aluminum pots offer faster boil onset times due to aluminum's superior thermal conductivity of approximately 205 W/m*K, enabling rapid heat transfer and quicker water heating. Stainless steel insulated pots, while durable and energy-efficient, have lower thermal conductivity around 16 W/m*K, resulting in slower boil onset but better heat retention once boiling is achieved.
Aluminum Ion Migration
Aluminum pots efficiently conduct heat but pose a risk of aluminum ion migration into food, especially when boiling acidic substances, potentially affecting taste and health. Stainless steel insulated pots resist ion migration due to their non-reactive surface, maintaining food safety and purity during boiling.
Thermal Stratification Resistance
Aluminum pots exhibit lower thermal stratification resistance due to their high thermal conductivity, allowing rapid and even heat distribution during boiling. Stainless steel insulated pots offer superior thermal stratification resistance by maintaining temperature gradients longer, which enhances heat retention and energy efficiency in boiling applications.
Insulated Pot Envelope Technology
Insulated pot envelope technology in stainless steel pots enhances heat retention by creating a vacuum or foam layer that minimizes thermal conductivity, resulting in faster boiling and sustained temperature compared to aluminum pots. While aluminum pots offer rapid heat conduction due to their high thermal conductivity, they lack the insulating layers that reduce heat loss, making stainless steel insulated pots more energy-efficient for boiling.
Conductivity Gradient Layering
Aluminum pots exhibit superior thermal conductivity, allowing rapid and even heat distribution crucial for efficient boiling, while stainless steel insulated pots rely on conductivity gradient layering to compensate for their lower thermal conductivity by combining multiple layers that enhance heat retention and prevent hotspots. The conductive aluminum core in layered stainless steel pots improves boiling performance by maintaining consistent temperature control, reducing energy consumption and ensuring faster boiling times.
Double-Walled Vacuum Seal Pot
Double-walled vacuum seal pots, whether made of aluminum or stainless steel, significantly improve boiling efficiency by minimizing heat loss and maintaining internal temperature longer. Aluminum pots offer faster heat conduction ideal for rapid boiling, while stainless steel insulated pots provide superior durability and corrosion resistance, making them preferable for long-term use and consistent heat retention.
Energy Transfer Efficiency Index
Aluminum pots exhibit a higher Energy Transfer Efficiency Index compared to stainless steel insulated pots due to aluminum's superior thermal conductivity, allowing faster and more uniform heat distribution during boiling. Stainless steel insulated pots retain heat longer due to their insulation, but their lower thermal conductivity results in slower initial energy transfer, impacting boiling speed and energy consumption.
Corrosion Pitting Risk Factor
Aluminum pots have a higher corrosion pitting risk factor due to their reactive surface when exposed to acidic or salty boiling liquids, which can degrade the material over time. Stainless steel insulated pots offer superior corrosion resistance with an inert surface that prevents pitting, ensuring durability and maintaining water purity during boiling processes.
Aluminum pot vs Stainless steel insulated pot for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com