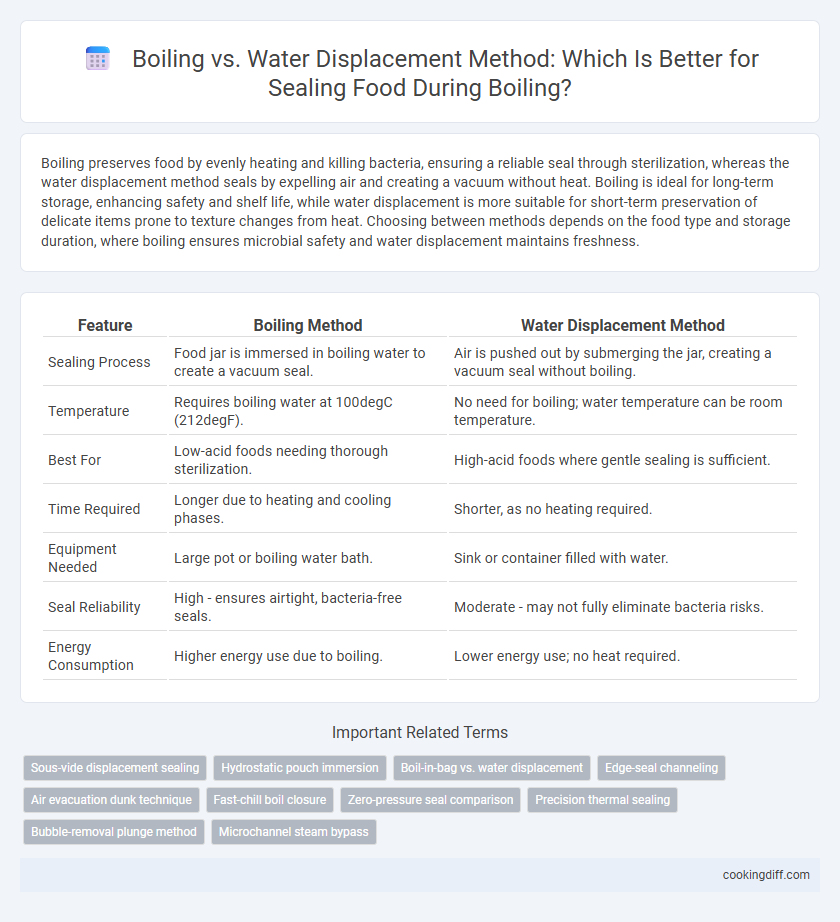
Boiling preserves food by evenly heating and killing bacteria, ensuring a reliable seal through sterilization, whereas the water displacement method seals by expelling air and creating a vacuum without heat. Boiling is ideal for long-term storage, enhancing safety and shelf life, while water displacement is more suitable for short-term preservation of delicate items prone to texture changes from heat. Choosing between methods depends on the food type and storage duration, where boiling ensures microbial safety and water displacement maintains freshness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Boiling Method | Water Displacement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Process | Food jar is immersed in boiling water to create a vacuum seal. | Air is pushed out by submerging the jar, creating a vacuum seal without boiling. |
| Temperature | Requires boiling water at 100degC (212degF). | No need for boiling; water temperature can be room temperature. |
| Best For | Low-acid foods needing thorough sterilization. | High-acid foods where gentle sealing is sufficient. |
| Time Required | Longer due to heating and cooling phases. | Shorter, as no heating required. |
| Equipment Needed | Large pot or boiling water bath. | Sink or container filled with water. |
| Seal Reliability | High - ensures airtight, bacteria-free seals. | Moderate - may not fully eliminate bacteria risks. |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to boiling. | Lower energy use; no heat required. |
Introduction to Sealing Food: Boiling vs Water Displacement
What are the key differences between boiling and water displacement methods for sealing food? Boiling uses heat to create a vacuum seal by expanding air inside the jar, while water displacement relies on the food's natural juices to push air out during sealing. Choosing the right method depends on the food type and the desired preservation time.
Understanding the Boiling Method for Food Sealing
Boiling is a popular method for sealing food by heating jars in boiling water to create a vacuum seal that preserves freshness and prevents contamination. This technique is preferred over the water displacement method because it ensures a more uniform heat distribution, reducing the risk of spoilage.
- Heat Penetration - Boiling allows consistent heat to reach all parts of the jar evenly, enhancing the seal quality.
- Vacuum Formation - The method relies on boiling to expel air inside the jar, creating a strong vacuum seal as it cools.
- Preservation Efficacy - Proper boiling time and temperature effectively kill bacteria and enzymes, extending food shelf life.
Exploring the Water Displacement Method
The water displacement method involves submerging filled jars in water to force out air before sealing, ensuring a tight vacuum without heat exposure. This technique preserves the food's texture and nutrients better compared to boiling, which uses high temperatures to kill bacteria but can alter flavor and consistency.
Unlike boiling, the water displacement method reduces the risk of overcooking sensitive ingredients, making it ideal for delicate preserves and fresh foods. It also requires less energy and equipment, providing a gentle yet effective sealing process that extends shelf life efficiently.
Benefits of Boiling for Sealing Food
| Boiling ensures a more uniform heat distribution, effectively killing bacteria and enzymes that cause spoilage, which significantly extends the shelf life of sealed food. The high temperature of boiling water creates a strong vacuum seal by shrinking the food and jar contents, reducing the likelihood of contamination. Compared to the water displacement method, boiling provides a more reliable sterilization process, making it ideal for preserving low-acid foods. |
Advantages of Water Displacement in Food Preservation
Water displacement method offers superior preservation by minimizing air exposure, which reduces oxidation and extends shelf life. This technique maintains food texture and flavor better than boiling, making it ideal for delicate items.
- Minimized oxidation - Water displacement limits air contact, preventing spoilage and nutrient loss.
- Preserved texture - This method avoids heat damage common in boiling, maintaining food's original consistency.
- Enhanced flavor retention - By reducing exposure to oxygen and heat, flavors stay more vibrant and fresh.
Water displacement is a practical, energy-efficient approach to sealing food while preserving quality and nutrition.
Comparing Safety: Boiling vs Water Displacement
Boiling food in sealed jars ensures temperatures above 100degC, effectively killing harmful bacteria and providing a reliable sterilization method. Water displacement relies on air being pushed out during vacuum formation but may not consistently reach the temperatures needed to destroy all pathogens.
Boiling offers a higher level of microbial safety compared to the water displacement method, reducing risks of contamination and spoilage. This method maintains a uniform heat distribution essential for long-term food preservation, while water displacement can leave air pockets that foster bacterial growth. Therefore, boiling remains the preferred choice in home canning for ensuring food safety and effective sealing.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor
Boiling as a sealing method can alter food texture by softening it due to prolonged heat exposure, which may enhance flavor absorption but risks overcooking. In contrast, the water displacement method preserves texture by minimizing direct heat contact, maintaining the original flavor profile more effectively.
- Boiling softens food texture - Prolonged boiling causes cell walls to break down, resulting in a softer, sometimes mushy texture.
- Flavor absorption is enhanced during boiling - Heat facilitates the infusion of spices and marinades into the food.
- Water displacement preserves texture - Lack of direct heat prevents overcooking, keeping food firmer and flavors intact.
Efficiency and Time Requirements
Boiling food for sealing is highly efficient as it uses consistent high temperatures to destroy bacteria, ensuring airtight preservation. The water displacement method requires less time overall since it involves submerging jars to expel air without prolonged heating. Efficiency-wise, boiling provides better sterilization, but the water displacement method saves time and energy by avoiding extended boil periods.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Boiling requires a pot large enough to submerge the food containers fully and a reliable heat source to maintain a consistent boiling temperature of 100degC (212degF). A lid for the pot and tongs or jar lifters are essential to safely handle hot jars during the process.
The water displacement method necessitates a large container filled with water to cover the food containers partially, often performed in a sink or specialized container. Unlike boiling, this method requires less heat control but still benefits from a thermometer to monitor water temperature and ensure effective sealing.
Related Important Terms
Sous-vide displacement sealing
Sous-vide displacement sealing utilizes water displacement to effectively remove air and create an airtight seal, preserving food flavor and texture better than boiling methods that risk nutrient loss through high temperatures. This technique ensures precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution, enhancing food safety and quality during cooking.
Hydrostatic pouch immersion
Hydrostatic pouch immersion during boiling ensures uniform heat transfer by fully submerging the pouch, creating a consistent hydrostatic pressure that prevents air pockets and improves seal integrity. This method offers superior sealing reliability compared to the water displacement technique, which may leave residual air and result in inconsistent vacuum levels.
Boil-in-bag vs. water displacement
Boil-in-bag sealing offers a convenient method for preserving food flavor and nutrients through direct heat application without removing air, whereas the water displacement method submerges bags in water to expel air, reducing oxidation but requiring precise control to prevent water ingress. Compared to water displacement, boil-in-bag ensures airtight sealing by heat shrinking the bag, making it ideal for sous-vide cooking and long-term storage.
Edge-seal channeling
Boiling effectively prevents edge-seal channeling by maintaining a consistent temperature that ensures airtight sealing, unlike the water displacement method which may allow air pockets to form along the edges. The precise heat application during boiling enhances vacuum integrity, reducing the risk of contamination and spoilage.
Air evacuation dunk technique
The boiling method ensures thorough sterilization by using high heat to evacuate air and create a vacuum seal, whereas the water displacement method relies on submerging jars to expel air through liquid pressure without heat. The air evacuation dunk technique during boiling maximizes oxygen removal, preventing food spoilage and enhancing preservation by creating an airtight environment.
Fast-chill boil closure
Fast-chill boil closure outperforms traditional water displacement methods by creating a stronger, airtight seal through rapid cooling immediately after boiling, which locks in freshness and preserves flavor more effectively. This technique reduces the risk of contamination and spoilage by ensuring a vacuum seal that maintains optimal food quality during storage.
Zero-pressure seal comparison
Boiling creates a zero-pressure seal by using steam expansion to evacuate air from containers, preventing contamination and preserving food freshness. In contrast, the water displacement method relies on submerging containers to push air out without heat, which may not achieve a consistent zero-pressure seal as effectively as boiling.
Precision thermal sealing
Boiling achieves precision thermal sealing by uniformly applying high heat, ensuring airtight seals that preserve food freshness and prevent contamination. The water displacement method relies on pressure differences but lacks the consistent temperature control necessary for optimal seal integrity and long-term preservation.
Bubble-removal plunge method
The bubble-removal plunge method effectively seals food by immersing containers in boiling water, allowing trapped air bubbles to escape and ensuring a tight seal. Compared to the water displacement method, this technique enhances vacuum formation by using boiling water's heat to expel air more efficiently, reducing spoilage risks.
Boiling vs Water displacement method for sealing food. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com