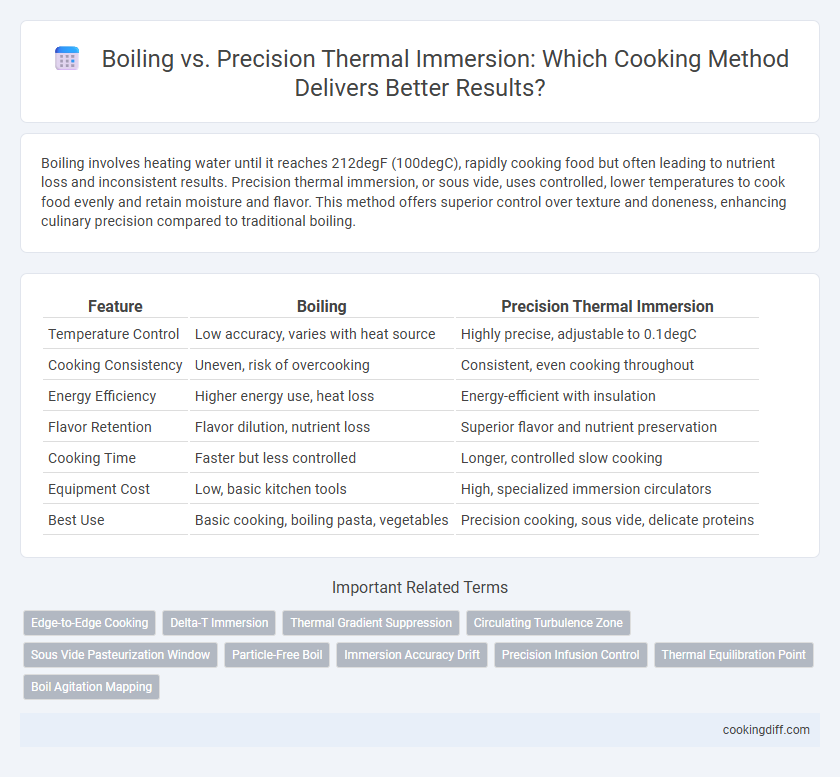
Boiling involves heating water until it reaches 212degF (100degC), rapidly cooking food but often leading to nutrient loss and inconsistent results. Precision thermal immersion, or sous vide, uses controlled, lower temperatures to cook food evenly and retain moisture and flavor. This method offers superior control over texture and doneness, enhancing culinary precision compared to traditional boiling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Boiling | Precision Thermal Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Low accuracy, varies with heat source | Highly precise, adjustable to 0.1degC |
| Cooking Consistency | Uneven, risk of overcooking | Consistent, even cooking throughout |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy use, heat loss | Energy-efficient with insulation |
| Flavor Retention | Flavor dilution, nutrient loss | Superior flavor and nutrient preservation |
| Cooking Time | Faster but less controlled | Longer, controlled slow cooking |
| Equipment Cost | Low, basic kitchen tools | High, specialized immersion circulators |
| Best Use | Basic cooking, boiling pasta, vegetables | Precision cooking, sous vide, delicate proteins |
Understanding Traditional Boiling in Cooking
Boiling is a traditional cooking method where water reaches 100degC (212degF) at sea level, causing vigorous bubbling that cooks food evenly. This high-temperature process is effective for pasta, vegetables, and eggs but can lead to nutrient loss and uneven texture in delicate ingredients.
Precision thermal immersion, or sous vide, uses controlled water temperatures well below boiling, typically between 50degC and 90degC, to cook food evenly over extended periods. This technique preserves moisture, flavor, and nutrients, offering greater consistency and refinement compared to traditional boiling.
What Is Precision Thermal Immersion?
What is precision thermal immersion in cooking? Precision thermal immersion involves using a water bath with exact temperature control to cook food evenly and retain moisture. This method surpasses traditional boiling by minimizing overcooking and enhancing flavor through consistent heat distribution.
Temperature Control: Boiling vs Precision Immersion
Boiling typically maintains a consistent temperature at 100degC (212degF), which can lead to overcooking or uneven results due to lack of precise control. Precision thermal immersion allows chefs to set exact temperatures, ensuring food cooks evenly and retains optimal texture and moisture.
- Boiling temperature fixed at 100degC - Limits control over cooking intensity and can degrade delicate food textures.
- Precision immersion offers adjustable temperatures - Enables cooking at precise degrees for customized doneness levels.
- Thermal immersion maintains steady heat - Prevents temperature fluctuations common in boiling for consistent results.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Boiling requires continuous high heat to maintain water temperature at 100degC, leading to significant energy consumption over time. Precision thermal immersion cookers use a closed system with precise temperature control, minimizing heat loss and reducing overall energy usage.
Energy efficiency in boiling is lower due to constant water evaporation and heat dissipation, whereas thermal immersion devices circulate heated water with insulation to sustain consistent temperatures at lower power. This targeted heating approach in precision thermal immersion results in up to 30% energy savings compared to traditional boiling methods.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor
Boiling cooks food rapidly but can lead to nutrient loss and a softer texture due to high water temperature and agitation. Precision thermal immersion, or sous vide, uses controlled low temperatures to preserve moisture, enhance flavors, and maintain the food's natural texture. This method results in more tender, evenly cooked dishes with intensified aromas and retained nutrients compared to traditional boiling.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Boiling often leads to significant nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and water. Precision thermal immersion cooking, such as sous vide, preserves nutrients by cooking food at lower, controlled temperatures in a sealed environment, minimizing nutrient depletion. Studies show sous vide retains up to 30% more vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional boiling methods.
Safety Considerations in Boiling vs Thermal Immersion
| Safety Considerations | Boiling | Precision Thermal Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Boiling water reaches 100degC, risking overcooking and burns without precise regulation. | Immersion circulators maintain exact temperatures, reducing burns and improving food safety. |
| Risk of Burns | Open steam and splashing hot water can cause severe burns during traditional boiling. | Closed water bath minimizes steam exposure, lowering burn risk significantly. |
| Food Safety | Boiling kills pathogens but may cause uneven cooking, leading to foodborne illness. | Precision immersion ensures consistent pasteurization, enhancing microbial safety. |
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Boiling requires basic kitchen equipment such as a pot and a heat source, while precision thermal immersion cooking demands specialized devices like an immersion circulator and a water bath container. The complexity and cost of equipment significantly differ between these two cooking techniques.
- Boiling - Involves a standard pot and stovetop or burner, widely available in most kitchens.
- Precision Thermal Immersion - Requires a precision immersion circulator to maintain exact water temperature.
- Water Bath Container - Essential for immersion cooking to hold water and food sealed in bags.
Precision thermal immersion offers more controlled cooking but at the expense of using specialized equipment.
Best Foods for Boiling and for Precision Immersion
Boiling is ideal for cooking starchy vegetables like potatoes and root vegetables, as well as pasta and eggs, where rapid, high-heat water exposure softens and cooks the food evenly. Precision thermal immersion, or sous vide, excels with proteins such as chicken breast, steak, and fish, allowing precise temperature control for perfectly cooked, tender results.
Vegetables like carrots and broccoli retain more nutrients when boiled briefly, while precision immersion maintains flavor and texture in delicate foods by cooking them slowly in a vacuum-sealed bag. Tough cuts of meat benefit from sous vide's ability to break down collagen without overcooking, and custards or eggs achieve consistent texture unattainable by boiling. Both methods have unique advantages, making them suitable for different cooking goals and ingredient types.
Related Important Terms
Edge-to-Edge Cooking
Boiling offers consistent heat transfer through water immersion, ensuring uniform edge-to-edge cooking by surrounding food completely with high-temperature liquid. Precision thermal immersion circulators maintain exact temperatures, preventing overcooking and delivering precise doneness with evenly cooked edges, making it superior for delicate or thick cuts requiring consistent texture throughout.
Delta-T Immersion
Delta-T Immersion technology offers more precise temperature control compared to traditional boiling methods, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing overcooking. This technique maintains a consistent temperature differential (Delta-T), optimizing cooking times and enhancing texture and flavor retention in foods.
Thermal Gradient Suppression
Boiling generates significant thermal gradients due to uneven heat transfer from the water to the food, resulting in inconsistent cooking temperatures and potential overcooking or undercooking in different areas. Precision thermal immersion techniques, like sous vide, maintain uniform temperature distribution by circulating water at a constant temperature, effectively suppressing thermal gradients and ensuring precise, even cooking throughout the food.
Circulating Turbulence Zone
The Circulating Turbulence Zone in precision thermal immersion cooking ensures uniform heat distribution by constantly moving water around food, enhancing cooking consistency and efficiency compared to traditional boiling. Boiling relies on natural convection currents that create uneven temperature zones, often resulting in less precise and inconsistent cooking outcomes.
Sous Vide Pasteurization Window
Boiling rapidly raises water temperature above 100degC, causing uneven cooking and nutrient loss, whereas precision thermal immersion in sous vide maintains a controlled pasteurization window between 54degC to 60degC for extended periods, ensuring even heat distribution and microbial safety. This method preserves texture, flavor, and nutritional value, making sous vide the superior choice for pasteurization and precise temperature control.
Particle-Free Boil
Boiling ensures particle-free cooking by maintaining water at 100degC, effectively removing impurities through vaporization, while precision thermal immersion cookers offer controlled temperature settings without necessarily eliminating particulates. Opting for boiling guarantees a purer cooking medium free of suspended particles, enhancing clarity and food safety compared to immersion methods.
Immersion Accuracy Drift
Precision thermal immersion devices maintain consistent temperature control with minimal accuracy drift, ensuring stable cooking conditions compared to traditional boiling methods. Boiling often involves fluctuating temperatures and uneven heat distribution, which can lead to inconsistent cooking results and lack precise thermal regulation.
Precision Infusion Control
Precision Thermal Immersion offers superior control over temperature stability compared to traditional boiling, enabling consistent cooking results and preventing overcooking. This method uses advanced Precision Infusion Control technology to maintain exact heat levels, enhancing flavor infusion and texture preservation in culinary applications.
Thermal Equilibration Point
The thermal equilibration point during boiling occurs rapidly as water reaches 100degC, causing immediate heat transfer to food, which can lead to uneven cooking. Precision thermal immersion maintains a consistent, lower temperature that precisely controls thermal equilibration, resulting in uniform doneness and better texture retention.
Boiling vs Precision Thermal Immersion for Cooking Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com