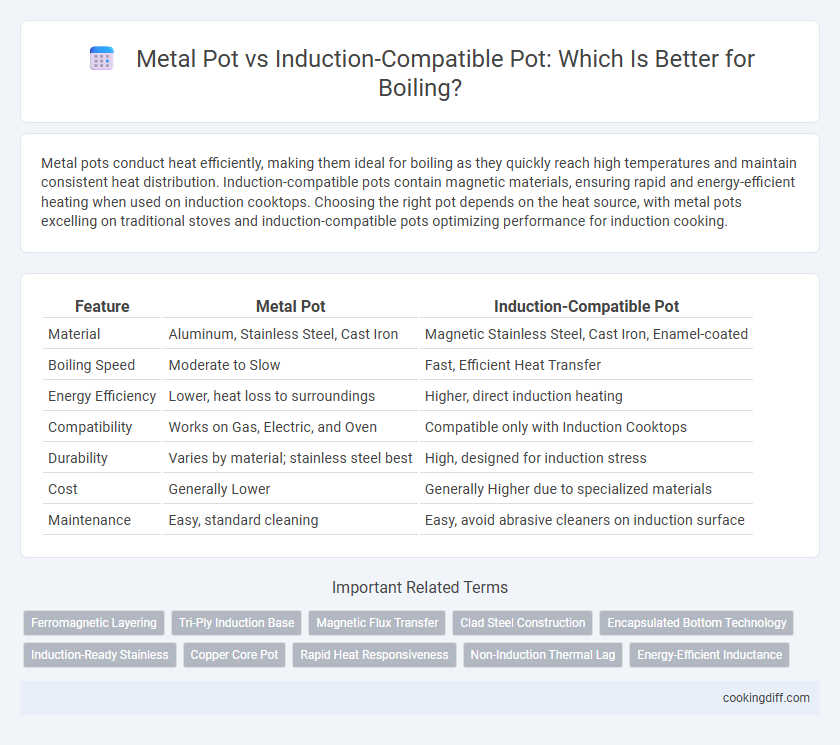
Metal pots conduct heat efficiently, making them ideal for boiling as they quickly reach high temperatures and maintain consistent heat distribution. Induction-compatible pots contain magnetic materials, ensuring rapid and energy-efficient heating when used on induction cooktops. Choosing the right pot depends on the heat source, with metal pots excelling on traditional stoves and induction-compatible pots optimizing performance for induction cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metal Pot | Induction-Compatible Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Cast Iron | Magnetic Stainless Steel, Cast Iron, Enamel-coated |
| Boiling Speed | Moderate to Slow | Fast, Efficient Heat Transfer |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, heat loss to surroundings | Higher, direct induction heating |
| Compatibility | Works on Gas, Electric, and Oven | Compatible only with Induction Cooktops |
| Durability | Varies by material; stainless steel best | High, designed for induction stress |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Generally Higher due to specialized materials |
| Maintenance | Easy, standard cleaning | Easy, avoid abrasive cleaners on induction surface |
Introduction: Boiling Basics and Pot Selection
| Boiling is the process of heating water or other liquids to 100degC (212degF), causing them to vaporize rapidly. Metal pots, such as those made from stainless steel or aluminum, efficiently conduct heat, allowing for quick temperature increases. Induction-compatible pots, typically featuring a ferromagnetic base, are designed to work with induction cooktops, providing precise and energy-efficient boiling by directly heating the pot through electromagnetic fields. |
Understanding Metal Pots: Traditional Boiling Vessels
Metal pots, traditionally made from materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum, have been the go-to vessels for boiling due to their durability and heat conduction properties. These metals efficiently transfer heat, ensuring consistent boiling performance on conventional gas or electric stovetops.
Induction-compatible pots contain magnetic materials like ferrous stainless steel or cast iron, enabling them to work effectively with induction cooktops by generating heat directly in the pot's base. Understanding the difference between standard metal pots and induction-compatible ones helps optimize boiling efficiency and energy use depending on the heat source.
What Are Induction-Compatible Pots?
Induction-compatible pots are specially designed cookware that contain ferromagnetic materials enabling efficient heat transfer on induction cooktops. These pots ensure rapid boiling by directly heating the pot rather than the cooktop surface.
- Magnetic Base - Induction-compatible pots have a magnetic base made from materials like stainless steel or cast iron, essential for activation on induction stovetops.
- Energy Efficiency - These pots convert almost all electromagnetic energy into heat within the pot, resulting in faster boiling and lower energy consumption compared to traditional metal pots.
- Durability - Induction-compatible pots are typically constructed with robust materials that resist warping and maintain consistent heat distribution during prolonged boiling.
Heating Efficiency: Metal Pot vs Induction-Compatible Pot
Metal pots typically have lower heating efficiency on induction cooktops due to poor magnetic conductivity, resulting in slower boil times and higher energy consumption. Induction-compatible pots, often made with ferrous materials like stainless steel or cast iron, maximize energy transfer by directly heating the pot through electromagnetic induction.
Induction-compatible pots heat water more uniformly and quickly compared to traditional metal pots, enhancing boiling efficiency. These pots reduce energy loss by minimizing heat radiation and conduction to the surrounding air. Choosing the right induction-compatible pot can cut boiling times by up to 30%, making cooking faster and more energy-efficient.
Boiling Speed: Which Pot Delivers Faster Results?
Metal pots, especially those made of copper or aluminum, conduct heat rapidly, resulting in faster boiling times compared to many induction-compatible pots. Induction-compatible pots, typically made from stainless steel with a magnetic base, often offer more efficient energy transfer but may heat slightly slower depending on the thickness of the pot's base.
The boiling speed depends heavily on the pot's material composition and compatibility with the heat source. Induction pots designed with a high-quality magnetic base can match or exceed traditional metal pots in boiling speed by optimizing electromagnetic energy transfer.
Energy Consumption During Boiling
Induction-compatible pots generally consume less energy during boiling compared to traditional metal pots due to faster heat transfer efficiencies. Metal pots tend to lose more heat to the environment, resulting in higher overall energy consumption.
- Induction-compatible pots heat faster - Magnetic induction generates heat directly in the pot, reducing energy loss during boiling.
- Metal pots have lower energy efficiency - Heat conduction through the pot material causes higher energy dissipation.
- Induction cooking reduces boiling time - Faster boiling decreases electricity or gas usage, saving energy.
Safety and Ease of Use on Different Cooktops
Metal pots, especially those made of stainless steel or aluminum, offer excellent durability and can be safely used on most cooktops, but they may not be compatible with induction surfaces unless specifically designed. Induction-compatible pots feature magnetic bases that allow for rapid heating and precise temperature control, enhancing safety by reducing the risk of overheating or spills. Ease of use varies as metal pots can be heavier and less responsive on induction cooktops, while induction-compatible pots provide efficient energy transfer and stable heat distribution for safer boiling.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Metal pots, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, offer superior durability and resist dents and scratches under regular use. Induction-compatible pots, often composed of layered materials with magnetic bases, require careful maintenance to preserve their induction functionality.
- Durability of Metal Pots - Metal pots are highly resistant to physical damage and can withstand high temperatures without warping.
- Maintenance of Metal Pots - These pots are generally easy to clean and do not demand special care beyond standard washing.
- Maintenance of Induction-Compatible Pots - Induction-compatible pots need to be checked for magnetic base integrity to ensure continued compatibility with induction cooktops.
The choice between metal and induction-compatible pots impacts both the longevity and the upkeep required for efficient boiling performance.
Cost Considerations: Upfront and Long-Term
Which option offers better cost efficiency when boiling: a metal pot or an induction-compatible pot? Metal pots generally have lower upfront costs, making them an economical choice for initial purchase. Induction-compatible pots, while more expensive initially, provide long-term savings through faster heating and energy efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Ferromagnetic Layering
Metal pots without ferromagnetic layering are incompatible with induction cooktops, resulting in inefficient or failed boiling processes. Induction-compatible pots feature a ferromagnetic base layer that enables rapid heat generation and uniform boiling by efficiently interacting with the cooktop's electromagnetic field.
Tri-Ply Induction Base
A metal pot with a tri-ply induction base offers superior heat distribution and energy efficiency compared to standard pots, ensuring faster and more even boiling. Its layered construction, combining stainless steel and aluminum, optimizes magnetic compatibility with induction cooktops, reducing hot spots and enhancing cooking performance.
Magnetic Flux Transfer
Metal pots without induction-compatible bases lack the magnetic flux transfer needed for efficient heating on induction cooktops, resulting in slower boiling times. Induction-compatible pots contain ferromagnetic materials that enhance magnetic flux transfer, enabling rapid and energy-efficient boiling performance.
Clad Steel Construction
Clad steel construction in metal pots provides superior heat distribution and durability compared to standard induction-compatible pots, ensuring rapid and even boiling. This multi-layer design typically combines stainless steel with an aluminum or copper core, enhancing thermal conductivity crucial for efficient induction cooking.
Encapsulated Bottom Technology
Encapsulated bottom technology in metal pots enhances heat distribution and retention, making it highly efficient for boiling compared to standard induction-compatible pots that rely solely on magnetic bases. This technology combines layers of aluminum or copper with stainless steel, ensuring faster boiling times and energy savings by maximizing surface contact with induction cooktops.
Induction-Ready Stainless
Induction-ready stainless steel pots offer superior energy efficiency and rapid heat transfer compared to traditional metal pots, ensuring faster boiling times and consistent temperature control. Their magnetic stainless steel construction enhances compatibility with induction cooktops, reducing energy waste and providing optimal cooking performance.
Copper Core Pot
Copper core pots provide superior heat conductivity and even distribution, reducing boiling times compared to standard metal pots. Their compatibility with induction cooktops ensures efficient energy transfer and consistent temperature control during boiling processes.
Rapid Heat Responsiveness
Metal pots, particularly those made from copper or aluminum, offer rapid heat responsiveness due to their high thermal conductivity, allowing water to reach boiling point quickly. Induction-compatible pots, typically constructed with a magnetic stainless steel base, provide efficient and precise heat control, resulting in faster boiling times on induction cooktops compared to traditional ones.
Non-Induction Thermal Lag
Metal pots such as stainless steel or aluminum heat rapidly on traditional gas or electric stovetops, minimizing thermal lag during boiling, whereas induction-compatible pots made of ferromagnetic materials exhibit reduced thermal lag due to direct electromagnetic heating. Non-induction cookware experiences slower heat transfer and longer boiling times on induction cooktops because they rely on surface conduction rather than magnetic induction.
Metal Pot vs Induction-Compatible Pot for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com