Boiling in an Instant Pot involves high heat and rapid bubbling, which is ideal for quickly cooking soups and breaking down ingredients. Simmering uses lower heat with gentle bubbles, preserving delicate flavors and textures without overcooking. Choosing between boiling and simmering depends on the desired soup consistency and cooking time, with simmering often preferred for slow-cooked, flavorful results.
Table of Comparison
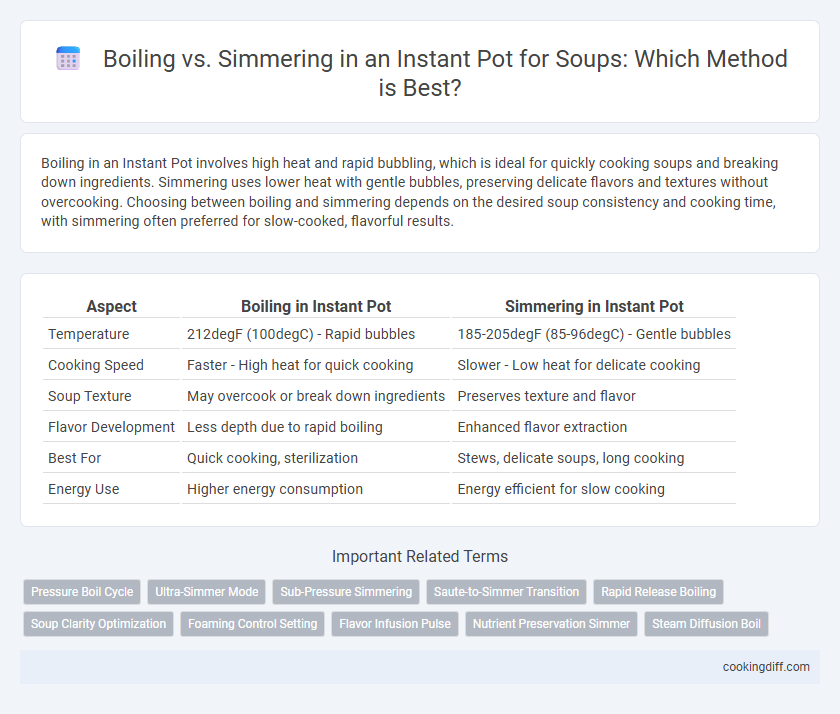
| Aspect | Boiling in Instant Pot | Simmering in Instant Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 212degF (100degC) - Rapid bubbles | 185-205degF (85-96degC) - Gentle bubbles |
| Cooking Speed | Faster - High heat for quick cooking | Slower - Low heat for delicate cooking |
| Soup Texture | May overcook or break down ingredients | Preserves texture and flavor |
| Flavor Development | Less depth due to rapid boiling | Enhanced flavor extraction |
| Best For | Quick cooking, sterilization | Stews, delicate soups, long cooking |
| Energy Use | Higher energy consumption | Energy efficient for slow cooking |
Understanding Boiling and Simmering in the Instant Pot
Boiling in the Instant Pot reaches 212degF (100degC), creating vigorous bubbles that rapidly cook soups, while simmering maintains a lower temperature just below boiling to gently develop flavors. Understanding these temperature differences helps control soup texture and prevents overcooking delicate ingredients.
- Boiling - Produces rapid bubbles and high heat ideal for quick cooking and pasteurization.
- Simmering - Maintains gentle bubbles that allow flavors to meld without breaking down ingredients.
- Instant Pot Settings - Utilize the "Soup" mode for simmering and "Manual" or "Pressure Cook" for boiling phases.
The Science Behind Boiling vs Simmering
| Boiling occurs at 212degF (100degC) where water reaches its highest temperature under standard atmospheric pressure, causing vigorous bubble formation and rapid heat transfer essential for quickly cooking denser soup ingredients. |
| Simmering maintains a lower temperature range between 185degF to 205degF (85degC to 96degC), promoting gentle bubble formation that prevents overcooking while allowing flavors to meld and delicate ingredients to soften without breaking down. |
| The Instant Pot's precise temperature control enables switching between boiling and simmering modes, optimizing soup texture and flavor extraction by balancing heat intensity and cooking duration. |
How the Instant Pot Controls Temperature
The Instant Pot uses precise pressure and temperature sensors to maintain consistent heating, ensuring soup reaches a boil or simmer without overheating. This controlled environment allows the pot to adjust heat levels automatically, preventing boiling over or undercooking during the soup preparation.
When set to boil, the Instant Pot raises the internal temperature to 212degF (100degC) under pressure, rapidly cooking ingredients. Simmering mode lowers the temperature slightly, around 185degF to 205degF (85degC to 96degC), allowing gentle cooking that enhances flavors without breaking down delicate ingredients.
Benefits of Boiling Soups in the Instant Pot
Boiling soups in the Instant Pot rapidly brings ingredients to a high temperature, ensuring efficient cooking and flavor extraction. This method is essential for breaking down tough ingredients and achieving a rich, concentrated broth.
- Faster Cooking Time - Boiling accelerates the cooking process, reducing overall soup preparation time.
- Enhanced Flavor Development - High heat helps release and blend flavors from spices, herbs, and proteins more effectively.
- Improved Nutrient Extraction - Boiling extracts vitamins and minerals from vegetables and bones, enriching the soup's nutritional profile.
Boiling in the Instant Pot is ideal for soups that require robust flavor and quick preparation.
Advantages of Simmering Soups for Flavor Development
Simmering soups in an Instant Pot allows for gradual extraction of flavors from ingredients, enhancing the overall taste complexity. This gentle heat prevents the breakdown of delicate vegetables and proteins, preserving their texture and nutritional value. The controlled temperature also reduces the risk of overcooking, resulting in a richer, more balanced soup flavor profile.
Texture Differences: Boiling vs Simmering Soups
How does boiling versus simmering affect the texture of soups in an Instant Pot? Boiling can cause proteins and vegetables to break down quickly, leading to a softer, sometimes mushy texture. Simmering maintains a gentle heat that preserves ingredient integrity, resulting in a more tender and distinct texture.
Nutrient Retention during Boiling and Simmering
Boiling in an Instant Pot reaches higher temperatures that can cause greater nutrient loss in soup ingredients, especially water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Simmering at lower temperatures helps preserve these nutrients by minimizing the breakdown of heat-sensitive compounds.
Simmering also reduces nutrient leaching into the cooking liquid, retaining more minerals and antioxidants within the soup. Using the Instant Pot's simmer function ensures a gentle cooking process that balances flavor development with nutrient retention.
Best Instant Pot Settings for Boiling and Simmering Soups
The best Instant Pot settings for boiling soups include using the "Saute" function on high to reach a rapid boil, while simmering is achieved by lowering the temperature using the "Keep Warm" or "Low Saute" mode. Controlling pressure release can also impact simmering, allowing gentle cooking without reaching a full boil.
- High Saute for Boiling - This setting rapidly brings soups to a boil, ideal for cooking ingredients quickly and evenly.
- Low Saute or Keep Warm for Simmering - These settings maintain a gentle heat that prevents boiling, perfect for slowly melding flavors without overcooking.
- Natural Pressure Release - Used to sustain a simmer inside the sealed pot, preserving delicate soup textures and flavors.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Boiling or Simmering
Common mistakes when boiling or simmering soups in an Instant Pot include setting the temperature too high, which can cause overcooking or burning. Maintaining a consistent simmer instead of a rolling boil prevents soup ingredients from breaking down and losing texture. Avoid opening the lid frequently, as sudden temperature changes can disrupt cooking and extend the overall time required.
Related Important Terms
Pressure Boil Cycle
The Pressure Boil cycle in an Instant Pot rapidly raises the temperature to achieve a vigorous boil, ideal for breaking down tough ingredients and extracting deep flavors in soups. Simmering, by contrast, uses lower heat and gentle bubbling to maintain delicate textures and prevent overcooking, preserving the integrity of herbs and vegetables.
Ultra-Simmer Mode
Ultra-Simmer Mode in Instant Pots maintains a precise temperature just below boiling point, ideal for soups that require gentle cooking and clear broth without the agitation of boiling. This mode prevents overcooking ingredients and preserves delicate flavors, unlike standard boiling which can cause cloudiness and tougher textures.
Sub-Pressure Simmering
Sub-pressure simmering in an Instant Pot maintains a gentle, consistent temperature below boiling, ideal for extracting flavors without breaking down delicate ingredients in soups. Unlike full boiling, this method prevents over-agitation, preserving texture while enhancing nutrient retention during the cooking process.
Saute-to-Simmer Transition
The Instant Pot's saute function rapidly heats liquids to a boil, facilitating quick browning or flavor extraction, while transitioning to simmer mode maintains a gentle, consistent temperature optimal for soups to develop complex flavors without overcooking ingredients. This precise control between saute-to-simmer transition prevents boiling over and ensures delicate textures are preserved in slow-cooked soups.
Rapid Release Boiling
Rapid release boiling in an Instant Pot quickly expels pressure, causing soup liquids to reach high temperatures rapidly for faster cooking. Unlike simmering, which maintains a gentle, steady temperature, rapid release boiling can break down ingredients more aggressively and intensify flavors in a short time.
Soup Clarity Optimization
Boiling in an Instant Pot achieves rapid temperature increase that agitates soup ingredients, often resulting in cloudier broth due to protein coagulation and food particles dispersing. Simmering maintains a gentle, steady heat that preserves soup clarity by allowing impurities to rise slowly and be skimmed off, crucial for clear, refined broth textures.
Foaming Control Setting
The Instant Pot's Foaming Control Setting effectively regulates the vigorous boiling often seen in soups, preventing overflow and maintaining safe cooking pressure during both boiling and simmering phases. This feature ensures consistent temperature management while minimizing foaming and sputtering, essential for clear, well-textured soups.
Flavor Infusion Pulse
Boiling in an Instant Pot rapidly heats soup to 212degF, causing vigorous bubbling that can dilute flavors and break down delicate ingredients, whereas simmering maintains a gentle heat around 185-205degF, promoting deeper flavor infusion and preventing overcooked textures. Using the simmer function optimizes Pulse flavor infusion by allowing spices and herbs to release aromatic oils gradually, enhancing the overall taste profile without overpowering the soup.
Nutrient Preservation Simmer
Simmering in an Instant Pot for soups preserves more nutrients than boiling by maintaining lower temperatures and gentle bubbles, reducing nutrient degradation from heat exposure. This method helps retain vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex, which are sensitive to high heat, ensuring a more nutritious soup.
Boiling vs Simmering in Instant Pot for Soups. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com