When choosing between a pot and a saucier for boiling, a pot offers deeper sides and a larger capacity, making it ideal for boiling large quantities of water or ingredients. A saucier features sloped sides that facilitate easier stirring and prevent ingredients from sticking, which is beneficial for delicate boiling tasks or making sauces. Selecting the right vessel depends on whether volume or ease of stirring during boiling is the priority.
Table of Comparison
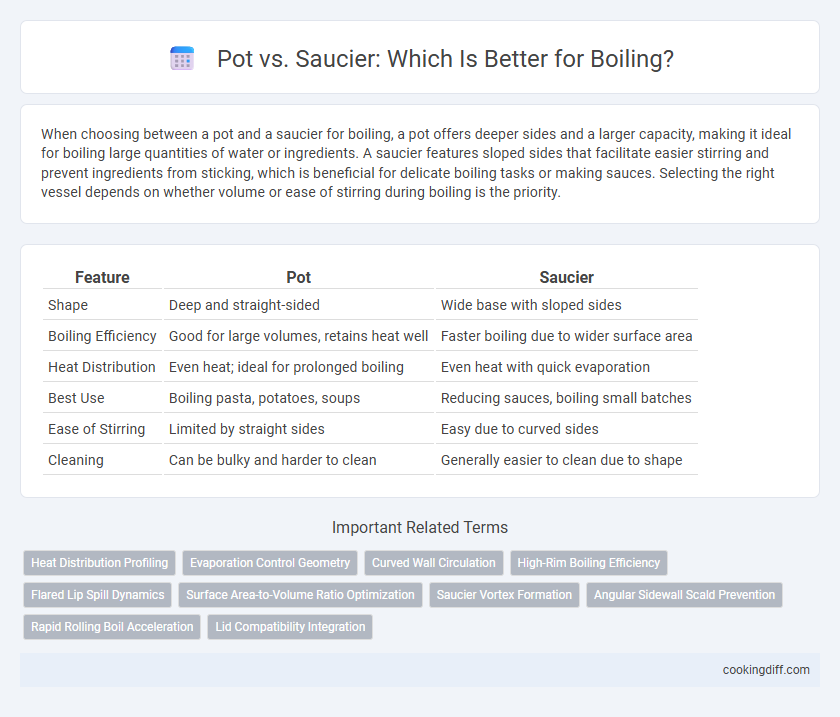
| Feature | Pot | Saucier |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Deep and straight-sided | Wide base with sloped sides |
| Boiling Efficiency | Good for large volumes, retains heat well | Faster boiling due to wider surface area |
| Heat Distribution | Even heat; ideal for prolonged boiling | Even heat with quick evaporation |
| Best Use | Boiling pasta, potatoes, soups | Reducing sauces, boiling small batches |
| Ease of Stirring | Limited by straight sides | Easy due to curved sides |
| Cleaning | Can be bulky and harder to clean | Generally easier to clean due to shape |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Vessel for Boiling
Choosing the right vessel for boiling significantly affects cooking efficiency and food quality. A pot typically features higher sides and a larger capacity, making it ideal for boiling large quantities of water or ingredients.
A saucier, with its rounded bottom and sloped sides, allows for even heat distribution and easier stirring, which is beneficial for delicate sauces and simmering. While a pot excels in holding volume, a saucier provides precision and control during cooking processes that require frequent stirring. Selecting between a pot and a saucier depends on the specific boiling task and the desired cooking outcome.
Pot vs Saucier: Key Design Differences
Pots feature straight, high sides ideal for boiling large volumes of water, while sauciers have rounded sides that facilitate stirring and reduce boiling over. The saucier's sloped profile allows better heat distribution and easier access for whisking compared to the taller, more vertical design of pots.
- Side Profile - Pots have straight, tall sides to retain steam and accommodate large liquid volumes efficiently.
- Shape - Sauciers possess rounded, sloped sides optimized for stirring and preventing food from sticking during boiling.
- Heat Distribution - The curved sides of sauciers promote even heating and reduce hotspots, enhancing boiling control.
Heat Distribution: Pot vs Saucier Performance
When comparing heat distribution for boiling, a pot typically offers even heating ideal for large volumes of water due to its wider base and higher sides. Saucier pans, with their rounded edges and shallower profile, provide more concentrated heat at the center, resulting in faster heat-up times but less uniform temperature across the surface. For boiling tasks requiring consistent heat, pots outperform sauciers by maintaining stable temperatures and minimizing hotspots.
Capacity and Volume Considerations
When boiling, pots typically offer larger capacity options ranging from 6 to 12 quarts, making them ideal for cooking large batches of pasta or stock. Saucier pans generally have smaller volumes, around 3 to 5 quarts, which suit boiling smaller quantities or preparing sauces that require frequent stirring.
Pot designs with high sides help reduce evaporation during long boiling processes, maintaining liquid volume efficiently. Saucier pans feature sloped sides that provide greater surface area but may lead to quicker liquid reduction, affecting volume retention during boiling.
Ease of Stirring and Access
A saucier's rounded bottom and sloping sides enhance ease of stirring by preventing ingredients from sticking in corners, making it ideal for boiling tasks that require frequent stirring. In contrast, a pot's straight sides provide more depth but limit access and maneuverability when stirring dense or thick mixtures.
- Saucier's curved design - Facilitates continuous stirring and reduces food buildup along edges.
- Pot's straight sides - Offer greater volume but restrict hand movement and stirring comfort.
- Access to contents - Improved in sauciers due to wide opening and shape, aiding in quicker ingredient incorporation.
Versatility in the Kitchen
| Pot | Designed with high sides and a large capacity, making it ideal for boiling large quantities of water or liquids. Its versatility extends to cooking pasta, soups, and stews due to even heat distribution and ample space. |
| Saucier | Features rounded bottoms and sloped sides, perfect for boiling smaller quantities and tasks requiring frequent stirring. Its shape facilitates efficient heat circulation and makes it suitable for sauces and delicate reductions. |
| Kitchen Versatility | Pots are essential for bulk boiling and multi-purpose cooking, while sauciers offer precision and ease for boiling smaller portions or sauces, adding diversity to kitchen technique and functionality. |
Cleaning and Maintenance
Pots typically have straight sides and a flat bottom, making them easier to clean with standard scrubbers due to fewer crevices where food particles can get trapped. Saucier pans feature rounded sides which require more attention during cleaning to prevent residue buildup in the curves.
Stainless steel pots generally resist staining and corrosion, simplifying maintenance over time. Saucier pans, often made from similar materials, demand careful drying to avoid water spots and preserve their non-stick or polished finish.
Boiling Speed and Efficiency
When boiling, a pot typically offers faster heating due to its wider base and larger surface area, allowing more direct contact with the heat source. A saucier, with its sloped sides, provides better evaporation control but may result in slower boiling times. For efficiency in rapid boiling, a pot is generally preferred over a saucier.
Best Uses for Pots and Sauciers
Which is better for boiling: a pot or a saucier? Pots are ideal for boiling large quantities of water or cooking pasta and vegetables due to their tall, straight sides and ample capacity. Sauciers, with their rounded bottoms and sloped sides, excel at simmering and reducing sauces but are less efficient for rapid boiling tasks.
Related Important Terms
Heat Distribution Profiling
A pot typically features thicker, more uniform walls and a heavier base that promote even heat distribution, making it ideal for sustained boiling and preventing hotspots. In contrast, a saucier's rounded bottom and thinner walls cause faster heat transfer but less uniform heat distribution, which suits rapid reductions or delicate sauces rather than consistent boiling.
Evaporation Control Geometry
A saucier's rounded sides and broader surface area enhance evaporation control by promoting consistent heat distribution and reducing liquid loss during boiling, whereas a pot's straight, vertical sides typically result in faster evaporation due to increased surface exposure. This geometric distinction allows sauciers to maintain moisture levels more effectively, making them ideal for simmering and delicate sauces.
Curved Wall Circulation
Sauciers feature gently curved walls that promote superior liquid circulation and prevent ingredients from getting stuck in corners, enhancing the boiling process. In contrast, pots with straight sides often create stagnant zones, leading to uneven heat distribution and less efficient boiling.
High-Rim Boiling Efficiency
A pot with high rims provides superior boiling efficiency by minimizing water evaporation and heat loss, allowing liquids to reach and maintain boiling temperatures more effectively. In contrast, sauciers with lower walls promote faster evaporation, making them less efficient for prolonged boiling tasks.
Flared Lip Spill Dynamics
A saucier's flared lip design effectively redirects boiling water vapor and minimizes spillover by allowing steam to escape more smoothly compared to the straight sides of a pot, which can cause turbulent boil-over. This feature enhances control during rapid boiling, reducing splashes and maintaining a cleaner cooking surface.
Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio Optimization
A saucier's rounded bottom increases the surface area-to-volume ratio compared to a traditional pot, promoting faster, more even boiling and heat distribution. This design reduces hotspots and improves energy efficiency, making sauciers ideal for delicate reductions and sauces requiring precise temperature control.
Saucier Vortex Formation
Saucier pans enhance boiling efficiency through vortex formation, which promotes rapid heat distribution and uniform temperature throughout the liquid. This swirling motion reduces hotspots and accelerates evaporation, making sauciers ideal for delicate sauces and precise liquid reduction.
Angular Sidewall Scald Prevention
A saucier's rounded, sloping sidewalls allow more even heat distribution and prevent food from sticking or scorching, significantly reducing the risk of scalding during boiling compared to the sharp, angular sidewalls of a standard pot. This design enhances liquid circulation and minimizes hotspots, making sauciers ideal for delicate boiling tasks where scald prevention is critical.
Rapid Rolling Boil Acceleration
A saucier's rounded sides promote superior heat circulation and prevent food from sticking, accelerating the time it takes to reach a rapid rolling boil. In contrast, a pot's straight sides may trap heat unevenly, resulting in slower boiling acceleration and less efficient heat distribution.
Pot vs Saucier for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com