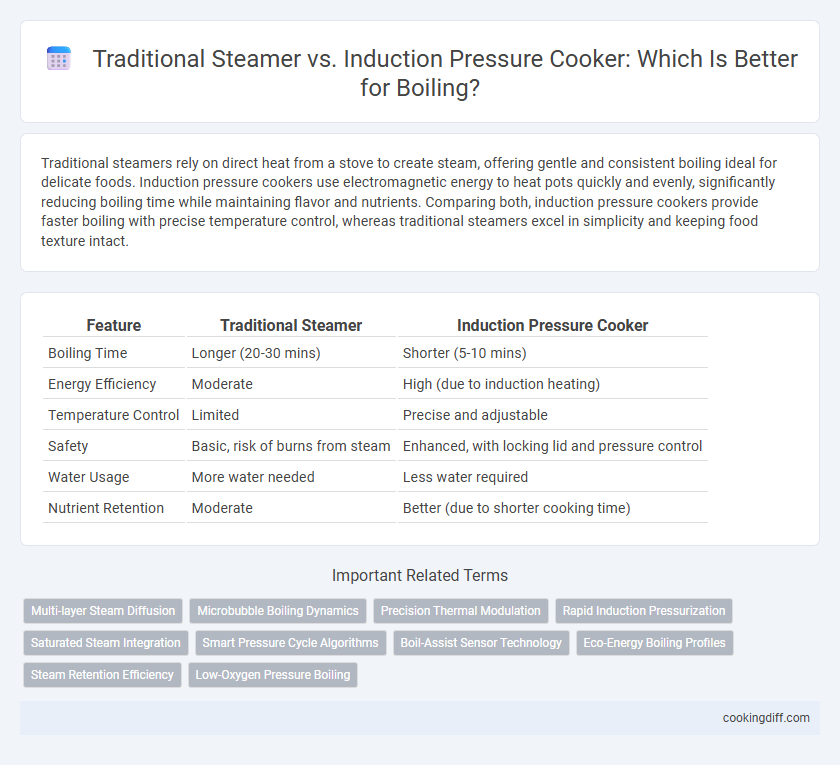
Traditional steamers rely on direct heat from a stove to create steam, offering gentle and consistent boiling ideal for delicate foods. Induction pressure cookers use electromagnetic energy to heat pots quickly and evenly, significantly reducing boiling time while maintaining flavor and nutrients. Comparing both, induction pressure cookers provide faster boiling with precise temperature control, whereas traditional steamers excel in simplicity and keeping food texture intact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Steamer | Induction Pressure Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Time | Longer (20-30 mins) | Shorter (5-10 mins) |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High (due to induction heating) |
| Temperature Control | Limited | Precise and adjustable |
| Safety | Basic, risk of burns from steam | Enhanced, with locking lid and pressure control |
| Water Usage | More water needed | Less water required |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate | Better (due to shorter cooking time) |
Introduction to Boiling: Traditional Steamer vs Induction Pressure Cooker
Boiling is a fundamental cooking process that involves heating water to its boiling point to cook food. Traditional steamers and induction pressure cookers both utilize boiling but differ significantly in efficiency and technique.
- Traditional Steamer - Uses direct heat and steam to cook food gently over boiling water, preserving texture and nutrients.
- Induction Pressure Cooker - Employs electromagnetic energy to heat the pot quickly and cooks food under pressure, reducing cooking time.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction pressure cookers consume less energy due to faster heating and sealed cooking environment compared to open steamers.
Choosing between these methods depends on cooking speed, energy use, and desired food texture.
How Traditional Steamers Work for Boiling
Traditional steamers rely on boiling water to generate steam, which cooks food by surrounding it with moist heat. This method preserves nutrients and flavors by using lower temperatures compared to direct boiling.
- Heat Source - Traditional steamers use external heat, such as gas or electric flames, to boil water at 100degC.
- Steam Circulation - The steam rises naturally to envelop the food, ensuring even heat distribution and gentle cooking.
- Cooking Time - Boiling with steam typically involves longer cooking times compared to pressure cookers due to lower and consistent heat levels.
Mechanics of Induction Pressure Cookers in Boiling
Traditional steamers rely on direct heat transfer from the stove to the water, causing gradual steam generation for boiling. Induction pressure cookers utilize electromagnetic fields to heat the cookware directly, enabling rapid temperature increases and efficient boiling mechanics.
The induction pressure cooker's sealed environment increases internal pressure, raising the boiling point of water and significantly speeding up cooking times. Its precise temperature control reduces energy consumption compared to traditional steamers, which depend on surface heat and open-air steam dispersion. Advanced safety features in induction pressure cookers ensure stable pressure maintenance, optimizing boiling performance and consistency.
Energy Efficiency Comparison for Boiling
Traditional steamers rely on direct heat transfer from the stove to the pot, often resulting in significant energy loss during boiling. Induction pressure cookers utilize electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, improving energy efficiency by up to 50% compared to conventional steamers.
Energy consumption in induction pressure cookers is lower due to faster heat-up times and reduced heat dissipation, making them more cost-effective for boiling tasks. In contrast, traditional steamers require longer boiling times and higher energy input to achieve the same results, leading to increased energy wastage.
Boiling Speed: Steamer vs Induction Pressure Cooker
| Boiling Speed | Traditional Steamer | Induction Pressure Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Boil Water (liters) | 7-10 minutes | 3-5 minutes |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Lower due to indirect heat and steam loss | High, with precise induction heating and sealed environment |
| Energy Consumption | Higher, prolonged boiling increases usage | Lower, faster boiling reduces energy use |
Nutrient Retention While Boiling
Traditional steamers use gentle heat and longer cooking times, which can cause some nutrient loss through prolonged exposure to heat and water. Induction pressure cookers boil food quickly under high pressure, significantly preserving vitamins and minerals by reducing cooking time and water usage.
- Traditional Steamer Heat Exposure - Prolonged steaming at lower temperatures may degrade water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex.
- Induction Pressure Cooker Efficiency - Rapid cooking under pressure maintains higher nutrient levels in vegetables compared to traditional stewing methods.
- Water Usage Impact - Less water in pressure cooking prevents leaching of minerals, enhancing overall nutrient retention during boiling.
Flavors and Texture After Boiling
The traditional steamer preserves the natural flavors and texture of ingredients by allowing gentle, even heat distribution without direct contact with boiling water. In contrast, an induction pressure cooker accelerates the boiling process with high pressure and temperature, which can intensify flavors but may slightly alter texture, making some foods softer or more tender. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired outcome: subtle, fresh flavors with firmer textures or enriched, concentrated flavors with a more tender finish.
Safety Aspects in Boiling Methods
Traditional steamers rely on open flames or electric coils, increasing the risk of burns or fire hazards during boiling. Induction pressure cookers use electromagnetic energy for precise temperature control, significantly reducing the likelihood of accidental burns and overheating.
Pressure cookers are equipped with multiple safety mechanisms such as pressure release valves and locking lids, preventing lid opening under high pressure. Traditional steamers lack these advanced safety features, making induction pressure cookers a safer choice for boiling tasks.
Versatility in Boiling Various Foods
Traditional steamers excel at gently boiling vegetables and seafood, preserving texture and nutrients with even steam distribution. Induction pressure cookers offer versatile boiling capabilities, rapidly cooking tougher foods like beans and meats under high pressure while retaining moisture. The precision temperature control in induction pressure cookers ensures consistent boiling results across diverse ingredients, making them ideal for multi-purpose cooking.
Related Important Terms
Multi-layer Steam Diffusion
Traditional steamers rely on direct steam exposure with uneven heat distribution, while induction pressure cookers utilize multi-layer steam diffusion technology to ensure consistent and rapid boiling. This advanced diffusion system enhances heat retention and circulation, resulting in faster cooking times and improved nutrient preservation.
Microbubble Boiling Dynamics
Traditional steamers rely on natural convection and generate larger steam bubbles that result in slower heat transfer, whereas induction pressure cookers utilize electromagnetic fields to produce rapid microbubble formation, enhancing boiling efficiency and heat distribution. The microbubble boiling dynamics in induction pressure cookers intensify nucleate boiling by increasing surface area and promoting faster bubble collapse, which significantly accelerates the boiling process compared to conventional steamers.
Precision Thermal Modulation
Traditional steamers offer basic boiling through consistent steam generation but lack precise temperature control, leading to variable cooking results. Induction pressure cookers utilize advanced precision thermal modulation, allowing exact temperature adjustments and maintaining optimal pressure, resulting in faster, more consistent boiling and improved energy efficiency.
Rapid Induction Pressurization
Induction pressure cookers achieve rapid induction pressurization by using electromagnetic energy that heats the cookware directly, leading to faster boiling times compared to traditional steamers which rely on indirect heat transfer. This efficient energy conversion reduces cooking duration, conserves fuel, and maintains nutrient retention during boiling processes.
Saturated Steam Integration
Traditional steamers generate saturated steam through direct boiling of water, providing consistent moisture ideal for even cooking, while induction pressure cookers integrate saturated steam under high pressure, accelerating heat transfer and reducing cooking time significantly. The enhanced control over temperature and pressure in induction pressure cookers optimizes the saturation point of steam, improving food texture and nutrient retention compared to conventional steaming methods.
Smart Pressure Cycle Algorithms
Traditional steamers rely on consistent external heat application, which can result in uneven boiling and longer cooking times, whereas induction pressure cookers utilize smart pressure cycle algorithms to precisely regulate temperature and pressure, ensuring rapid, uniform boiling and energy efficiency. These algorithms dynamically adjust heat input based on real-time pressure feedback, optimizing boiling speed while preserving nutrients and texture in the food.
Boil-Assist Sensor Technology
Traditional steamers rely on direct heat to generate steam for boiling, which can result in uneven temperature control and longer cooking times. Induction pressure cookers equipped with Boil-Assist Sensor Technology precisely monitor and adjust the heat to maintain optimal boiling conditions, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing cooking time significantly.
Eco-Energy Boiling Profiles
Traditional steamers rely on direct heat and longer cooking times, resulting in higher energy consumption and increased water evaporation during boiling. Induction pressure cookers use precise temperature control and airtight sealing to reduce energy use by up to 70%, while preserving nutrients and minimizing water waste in eco-energy boiling profiles.
Steam Retention Efficiency
Traditional steamers lose significant heat as steam escapes through vent holes, reducing steam retention efficiency and prolonging boiling times. Induction pressure cookers create a sealed environment that maintains high steam pressure and temperature, maximizing steam retention efficiency and enabling faster, energy-efficient boiling.
Traditional Steamer vs Induction Pressure Cooker for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com