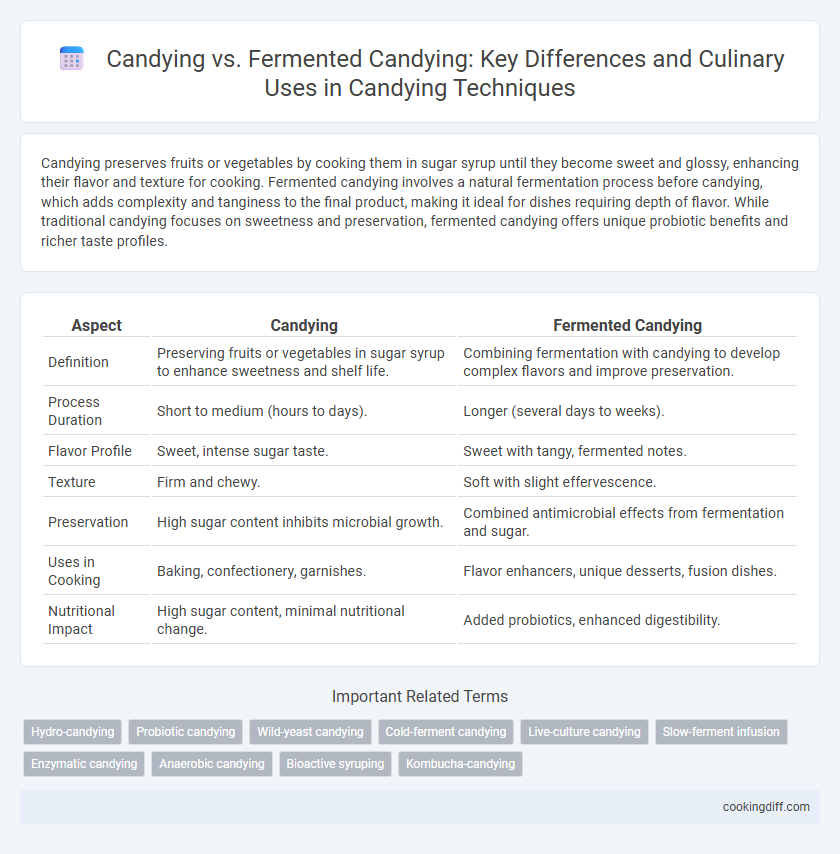
Candying preserves fruits or vegetables by cooking them in sugar syrup until they become sweet and glossy, enhancing their flavor and texture for cooking. Fermented candying involves a natural fermentation process before candying, which adds complexity and tanginess to the final product, making it ideal for dishes requiring depth of flavor. While traditional candying focuses on sweetness and preservation, fermented candying offers unique probiotic benefits and richer taste profiles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Candying | Fermented Candying |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preserving fruits or vegetables in sugar syrup to enhance sweetness and shelf life. | Combining fermentation with candying to develop complex flavors and improve preservation. |
| Process Duration | Short to medium (hours to days). | Longer (several days to weeks). |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, intense sugar taste. | Sweet with tangy, fermented notes. |
| Texture | Firm and chewy. | Soft with slight effervescence. |
| Preservation | High sugar content inhibits microbial growth. | Combined antimicrobial effects from fermentation and sugar. |
| Uses in Cooking | Baking, confectionery, garnishes. | Flavor enhancers, unique desserts, fusion dishes. |
| Nutritional Impact | High sugar content, minimal nutritional change. | Added probiotics, enhanced digestibility. |
Introduction to Candying and Fermented Candying
Candying is a traditional cooking technique that involves preserving fruit or vegetables by slowly simmering them in a sugar syrup until fully saturated and glossy. This method enhances flavor, texture, and shelf life, making ingredients like citrus peel or ginger perfect for desserts and confections.
Fermented candying combines candying with natural fermentation, allowing beneficial microbes to develop complex, tangy flavors and improve digestibility. This process requires careful control of time and temperature to encourage fermentation alongside sugar infusion. The resulting product offers a unique taste profile and potential health benefits compared to standard candying methods.
Understanding Traditional Candying Methods
Traditional candying involves preserving fruit by cooking it in sugar syrup until fully saturated, creating a sweet, glossy texture ideal for desserts. This method relies on high sugar concentration to inhibit microbial growth and preserve the fruit's natural flavor and color.
Fermented candying, contrastingly, introduces controlled fermentation before candying, enhancing complexity with tangy undertones and altered texture. This technique combines microbial activity and sugar preservation, often resulting in a unique balance of sweetness and acidity beneficial for gourmet culinary applications.
What is Fermented Candying?
| Fermented candying is a traditional technique where fruits or vegetables undergo natural fermentation before being candied, enhancing flavor complexity and preserving nutrients more effectively than conventional candying. |
| This method uses beneficial microbes to break down sugars and develop unique textures, resulting in a product with a tangy, rich taste profile ideal for gourmet cooking. |
| Fermented candying extends shelf life and provides probiotic benefits not found in standard candying, merging preservation with culinary innovation. |
Key Ingredient Differences
Candying uses sugar or syrup to preserve and flavor fruits or vegetables by soaking them in concentrated sugar solutions, while fermented candying relies on natural fermentation processes to develop complex flavors and textures. The key ingredient differences impact both preservation methods and the final taste profile of the candied product.
- Sugar or Syrup in Candying - Acts as the primary preservative and sweetener, creating a high-sugar environment that inhibits microbial growth.
- Microorganisms in Fermented Candying - Utilize natural bacteria or yeasts to ferment the product, enhancing flavors and increasing acidity.
- Acidity Levels - Higher acidity in fermented candying alters texture and flavor complexity, contrasting with the straightforward sweetness of traditional candying.
Flavor Profiles: Candying vs Fermented Candying
Candying preserves the natural sweetness and enhances the fruit's original flavor with a glossy, sugary coating, resulting in a bright, sweet taste ideal for desserts. In contrast, fermented candying introduces complex, tangy, and slightly sour notes through microbial activity, creating depth and a nuanced flavor profile favored in artisanal cooking. The choice between candying and fermented candying depends on whether a straightforward sweet flavor or a more intricate, savory-sweet balance is desired.
Texture Comparison and Appeal
Candied fruits have a firm, chewy texture with a glossy finish that enhances their visual appeal and sweetness, making them ideal for garnishing baked goods. Fermented candying produces a softer, slightly tangy texture due to natural fermentation, offering a unique flavor complexity and a delicate mouthfeel. The choice between candying and fermented candying depends on whether a crisp bite or a tender, nuanced texture is preferred in culinary applications.
Culinary Uses and Applications
Candying preserves fruits and vegetables by soaking them in a sugar syrup, enhancing their natural sweetness and texture, making them ideal for garnishing desserts and confectionery. This method is often used in baking for toppings or incorporated into pastries to provide a sweet, chewy contrast.
Fermented candying introduces natural fermentation before candying, which adds complex flavors and slight tanginess, perfect for sophisticated culinary applications like artisanal chocolates or gourmet sauces. The fermentation process also enhances nutritional benefits and introduces unique probiotics, broadening its use in health-conscious cooking.
Health and Nutritional Considerations
Candying involves preserving fruits in sugar syrup, resulting in high sugar content with limited nutritional benefits. Fermented candying incorporates natural fermentation, which can enhance probiotic properties and improve nutrient absorption.
- Glycemic Impact - Candying typically results in elevated glycemic index due to added sugars, while fermented candying may moderate blood sugar spikes through fermentation byproducts.
- Probiotic Content - Fermented candying introduces beneficial bacteria that support gut health, absent in traditional candying methods.
- Vitamin Retention - Fermentation can help preserve or even increase certain vitamins, particularly B-complex, compared to nutrient degradation in simple candying processes.
Choosing fermented candying can offer improved health benefits by balancing sweetness with enhanced nutritional value and digestive support.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Candied fruits preserve natural flavors and sweetness through sugar infusion, whereas fermented candying introduces complex tangy notes via controlled microbial activity. Choosing between traditional candying and fermented candying depends on desired flavor profiles, shelf life, and textural preferences.
- Candying preserves freshness - The traditional method maintains the original fruit taste and texture by replacing water with sugar syrup.
- Fermented candying adds depth - Fermentation enhances flavor complexity with beneficial acids and probiotics but may alter texture.
- Candying offers longer shelf life - High sugar concentration inhibits microbial growth, making it ideal for extended storage.
Related Important Terms
Hydro-candying
Hydro-candying involves immersing fruits in hot sugar syrup to preserve texture and enhance sweetness, differing from fermented candying which relies on natural fermentation processes to develop complex flavors and tanginess. Hydro-candying offers a controlled, faster method ideal for maintaining bright colors and firm textures in culinary applications.
Probiotic candying
Probiotic candying enhances traditional candying by integrating beneficial bacteria, promoting gut health while preserving the fruit's natural sweetness. Unlike fermented candying, which relies on microbial fermentation for flavor and preservation, probiotic candying specifically targets the introduction of live probiotics to support digestion and immunity.
Wild-yeast candying
Wild-yeast candying harnesses natural fermentation through native yeasts, enhancing flavor complexity and preserving fruit texture without artificial additives. Fermented candying differs by relying on controlled microbial activity to develop deeper umami notes, while traditional candying primarily uses sugar saturation to extend shelf life and sweetness.
Cold-ferment candying
Cold-ferment candying preserves the natural flavors and nutrients by slowly soaking fruits in sugar or syrup at low temperatures, resulting in a tender texture and enhanced aromatic profile. Unlike traditional candying, which relies on heat to infuse sweetness and preserve, cold-ferment methods prevent nutrient degradation and produce a superior balance of acidity and sweetness ideal for gourmet cooking.
Live-culture candying
Live-culture candying utilizes beneficial bacteria to create fermented candies that enhance flavor complexity and preservation compared to traditional candying, which primarily relies on sugar infusion without microbial activity. This fermentation process increases probiotic content and introduces unique tangy notes, promoting gut health while maintaining natural sweetness in culinary applications.
Slow-ferment infusion
Slow-ferment infusion enhances candying by using natural fermentation to develop deeper, more complex flavors while preserving the fruit's texture and nutrients, unlike traditional candying which relies on direct sugar absorption. This method creates a balanced sweetness with subtle tangy notes, improving the overall culinary experience and shelf life of the product.
Enzymatic candying
Enzymatic candying utilizes specific enzymes to break down fruit pectin, resulting in a tender texture and enhanced flavor penetration compared to traditional candying methods. Fermented candying involves microbial fermentation that alters sugar profiles and introduces complex flavors, but enzymatic candying offers more controlled enzymatic activity for consistent culinary outcomes.
Anaerobic candying
Anaerobic candying preserves fruit by submerging it in a sugar solution without oxygen exposure, enhancing flavor concentration and texture compared to traditional fermentation methods that rely on microbial activity for preservation. This controlled anaerobic environment prevents spoilage and maintains vibrant color while avoiding the tangy, fermented notes typical in fermented candying.
Bioactive syruping
Candying preserves fruits by soaking them in concentrated sugar syrup, enhancing sweetness and texture without fermentation, while fermented candying involves microbial activity that produces bioactive compounds, enriching flavor and potential health benefits. Bioactive syruping in fermented candying increases antioxidant properties and can improve digestive health, differentiating it from traditional candying methods.
Candying vs Fermented Candying for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com