Candying preserves fruits by simmering them in sugar syrup, creating a sweet, glossy coating that enhances flavor and texture while extending shelf life. Vacuum infusion forces flavored liquids into foods under reduced pressure, resulting in faster, more uniform flavor absorption without the increased sugar content. Candying is ideal for sweet treats and desserts, whereas vacuum infusion offers versatility for both savory and sweet culinary applications.
Table of Comparison
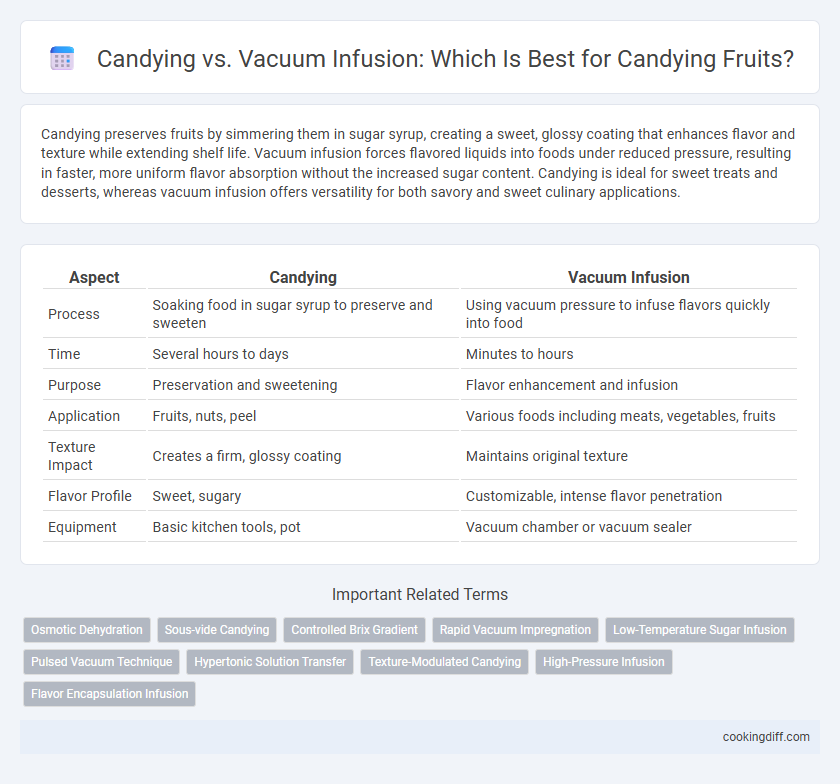
| Aspect | Candying | Vacuum Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Soaking food in sugar syrup to preserve and sweeten | Using vacuum pressure to infuse flavors quickly into food |
| Time | Several hours to days | Minutes to hours |
| Purpose | Preservation and sweetening | Flavor enhancement and infusion |
| Application | Fruits, nuts, peel | Various foods including meats, vegetables, fruits |
| Texture Impact | Creates a firm, glossy coating | Maintains original texture |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, sugary | Customizable, intense flavor penetration |
| Equipment | Basic kitchen tools, pot | Vacuum chamber or vacuum sealer |
Introduction to Candying and Vacuum Infusion
Candying is a preservation technique where fruit or vegetables are slowly cooked in sugar syrup until fully saturated, enhancing flavor and texture. Vacuum infusion uses a pressure vacuum to rapidly infuse flavors or liquids into food, offering precision and efficiency.
- Candying - Involves prolonged simmering in sugar syrup to replace fruit moisture with sugar for preservation and sweetness.
- Vacuum Infusion - Uses reduced pressure to open food pores, allowing faster and deeper penetration of flavors or marinades.
- Cooking Applications - Candying is ideal for traditional sweet treats; vacuum infusion suits innovative gastronomy and fast flavor enhancement.
Defining Candying: Traditional Methods Explained
| Candying: Traditional Methods |
|---|
| Candying is a preservation technique that involves simmering fruits or vegetables in sugar syrup until they absorb the sugar and develop a sweet, glossy coating. This method relies on gradual dehydration and sugar infusion to inhibit microbial growth, enhancing flavor and extending shelf life. The process typically requires several days of soaking and drying to achieve optimal texture and sweetness. |
Understanding Vacuum Infusion: Modern Culinary Science
How does vacuum infusion differ from traditional candying in flavor absorption? Vacuum infusion uses low pressure to rapidly infuse flavors and liquids into food, enhancing taste and texture with precise control. This modern culinary technique outperforms traditional candying by reducing infusion time while maintaining ingredient integrity.
Key Differences Between Candying and Vacuum Infusion
Candying involves preserving fruit or vegetables by slowly cooking them in sugar syrup to replace water content with sugar, creating a sweet, dense texture. Vacuum infusion uses a vacuum chamber to rapidly force flavored syrups or marinades into porous foods, enhancing taste and moisture retention without prolonged cooking. The key difference lies in candying's focus on sugar absorption through extended heat exposure, whereas vacuum infusion emphasizes quick flavor penetration under reduced pressure.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes: Candying vs Vacuum Infusion
Candying enhances flavor by infusing fruit with a concentrated sugar syrup, resulting in a sweet, chewy texture that preserves the fruit's natural structure. Vacuum infusion accelerates flavor penetration by removing air from the fruit's cells, producing a more evenly flavored and moist texture.
Candying locks in sweetness and creates a glossy, firm exterior that adds a satisfying bite, ideal for confections and garnishes. Vacuum infusion allows for precise control over flavor intensity and texture, making it suitable for delicate fruits and complex flavor profiles. Both techniques offer unique advantages depending on the desired balance of sweetness and fruit texture in culinary applications.
Ingredients Suitable for Candying and Vacuum Infusion
Ingredients suitable for candying typically include fruits like citrus peels, cherries, and ginger, as well as nuts and root vegetables due to their ability to absorb sugar syrup effectively. These ingredients benefit from the prolonged simmering process that allows sugar crystals to form and create a glossy, preserved outer layer.
Vacuum infusion works best with porous ingredients like berries, melons, and softer fruits, enabling rapid absorption of flavored liquids under reduced pressure. This method preserves the texture and freshness of delicate items while infusing flavors evenly without the heat exposure used in candying.
Step-by-Step Process: Candying Techniques
Candied fruit is created by slowly simmering fruit in sugar syrup until fully saturated, requiring repeated syrup changes over several days to achieve the desired texture and sweetness. The process begins with blanching the fruit, followed by multiple immersions in progressively concentrated syrup, allowing sugar to penetrate while preserving the fruit's shape. In contrast, vacuum infusion accelerates flavor absorption by using reduced pressure to force syrup into fruit cells, significantly reducing the traditional candying timeframe.
Step-by-Step Process: Vacuum Infusion Techniques
Vacuum infusion involves placing ingredients in a sealed chamber where pressure is reduced to extract air and allow liquid to penetrate quickly and deeply. This technique accelerates flavor absorption compared to traditional candying, which relies on gradual soaking in sugar syrup.
- Preparation - Select and prepare the fruit or ingredient by slicing or scoring to increase surface area for infusion.
- Vacuum application - Place the ingredient in a vacuum chamber with the flavoring liquid and apply vacuum to remove air and open the pores.
- Infusion and sealing - Release the vacuum to atmospheric pressure, enabling the liquid to rapidly infuse into the ingredient before setting or cooking.
Vacuum infusion delivers enhanced flavor penetration and reduced processing time compared to traditional candying methods.
Pros and Cons of Candying and Vacuum Infusion
Candying enhances flavor by preserving ingredients in a sugar syrup, creating a sweet, shelf-stable product, while vacuum infusion introduces flavors quickly and evenly through controlled pressure. Each method offers unique benefits and limitations depending on texture, flavor penetration, and preparation time.
- Candying preserves texture - It maintains the natural firmness of fruits by slow sugar absorption, preventing sogginess.
- Vacuum infusion speeds flavor absorption - Pressure cycles allow for rapid and uniform taste enhancement within minutes.
- Candying has longer preparation time - It requires hours to days, limiting quick experimentation or batch adjustments.
Related Important Terms
Osmotic Dehydration
Candying relies on osmotic dehydration, where sugar solutions draw moisture out of fruit, preserving texture and flavor by creating a high-sugar concentration that inhibits microbial growth; in contrast, vacuum infusion uses reduced pressure to accelerate flavor penetration but does not primarily remove moisture. Osmotic dehydration in candying is key for achieving extended shelf life and a unique chewy texture, whereas vacuum infusion focuses more on rapid flavor enhancement without significant dehydration.
Sous-vide Candying
Sous-vide candying uses precise temperature control to evenly infuse sugar solutions into fruits or vegetables, preserving texture and flavor more effectively than traditional candying methods. Compared to vacuum infusion, sous-vide candying maintains consistent heat for extended periods, allowing deeper penetration and enhanced taste without the risk of oxidation.
Controlled Brix Gradient
Candying achieves a controlled Brix gradient by gradually increasing sugar concentration, ensuring even penetration and moisture retention in fruits. Vacuum infusion accelerates sugar uptake but may cause uneven Brix distribution, affecting texture and flavor balance.
Rapid Vacuum Impregnation
Rapid Vacuum Impregnation outperforms traditional candying by using controlled vacuum and pressure cycles to infuse sugars and flavors deep into fruits, reducing processing time from hours to minutes. This technique ensures uniform distribution of syrups and preserves texture while enhancing taste intensity, surpassing the surface-level penetration typical of conventional candying methods.
Low-Temperature Sugar Infusion
Low-temperature sugar infusion in candying preserves fruit texture and natural flavor by gently penetrating sugar without heat-induced damage, unlike vacuum infusion which uses reduced pressure to accelerate sugar absorption but may alter delicate fruit structure. Candying's slow, low-heat process enhances moisture retention and creates a denser, more stable sugar crystal matrix, ideal for high-quality candied fruits and confections.
Pulsed Vacuum Technique
The Pulsed Vacuum Technique in candying enhances flavor absorption and texture by alternating pressure cycles that drive syrup deeper into fruit fibers, outperforming traditional Vacuum Infusion methods in uniformity and infusion speed. This technique improves candying efficiency by reducing processing time while preserving fruit integrity and preventing cellular damage, resulting in higher-quality, more flavorful candied products.
Hypertonic Solution Transfer
Candying relies on hypertonic solution transfer to draw sugar into fruit cells, creating a sweet, preserved texture by osmosis. Vacuum infusion accelerates this process by reducing pressure, allowing the hypertonic syrup to penetrate deeper and faster into the fruit matrix for more uniform flavor distribution.
Texture-Modulated Candying
Texture-modulated candying preserves the structural integrity of fruits by slowly infusing sugar syrup, resulting in a tender yet firm bite distinct from the rapid saturation seen in vacuum infusion. Vacuum infusion accelerates flavor and moisture penetration using reduced pressure but can produce a softer texture, often less ideal for maintaining the cell structure desired in premium candied products.
High-Pressure Infusion
High-pressure infusion enhances candying by forcing sugar syrup deep into the cellular structure of fruits, resulting in more intense flavor absorption and faster processing compared to traditional vacuum infusion methods. This technique maintains fruit integrity while improving texture and shelf life through precise pressure control and increased infusion efficiency.
Candying vs Vacuum Infusion for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com