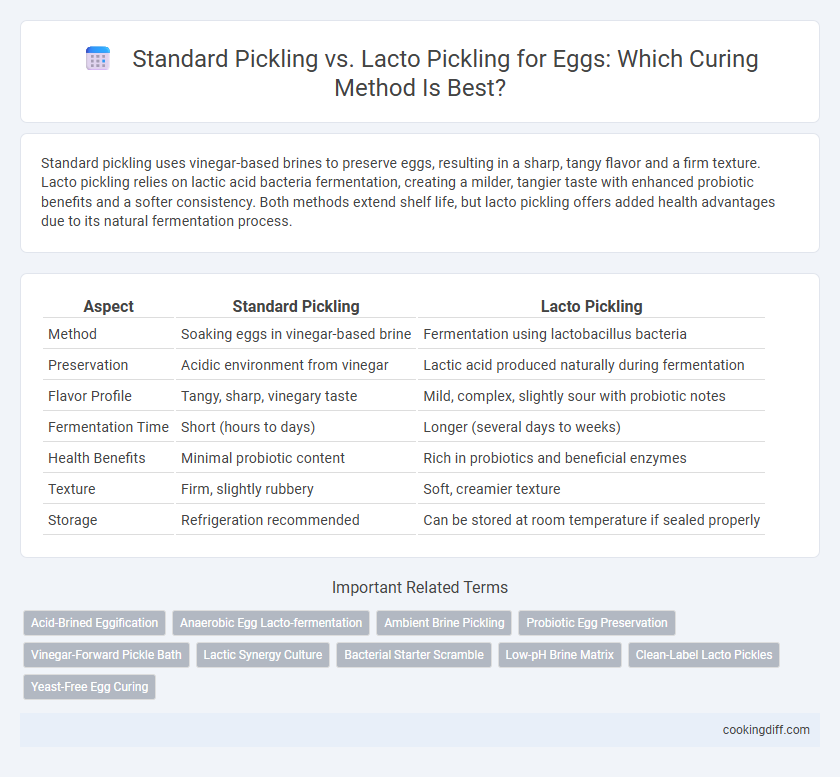
Standard pickling uses vinegar-based brines to preserve eggs, resulting in a sharp, tangy flavor and a firm texture. Lacto pickling relies on lactic acid bacteria fermentation, creating a milder, tangier taste with enhanced probiotic benefits and a softer consistency. Both methods extend shelf life, but lacto pickling offers added health advantages due to its natural fermentation process.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Standard Pickling | Lacto Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Soaking eggs in vinegar-based brine | Fermentation using lactobacillus bacteria |
| Preservation | Acidic environment from vinegar | Lactic acid produced naturally during fermentation |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, sharp, vinegary taste | Mild, complex, slightly sour with probiotic notes |
| Fermentation Time | Short (hours to days) | Longer (several days to weeks) |
| Health Benefits | Minimal probiotic content | Rich in probiotics and beneficial enzymes |
| Texture | Firm, slightly rubbery | Soft, creamier texture |
| Storage | Refrigeration recommended | Can be stored at room temperature if sealed properly |
Understanding Egg Pickling: An Overview
Standard pickling for eggs involves soaking them in a vinegar-based brine, which imparts a tangy flavor and preserves the eggs by lowering the pH. This method is fast-acting and typically results in a firm texture with a sharp taste.
Lacto pickling uses natural fermentation with lactic acid bacteria, creating a milder, tangy flavor while enhancing probiotic content. The process takes longer but yields eggs with a complex, slightly sour taste and beneficial gut health properties.
What Is Standard Pickling for Eggs?
What is standard pickling for eggs? Standard pickling involves soaking hard-boiled eggs in a vinegar-based brine that often includes salt, sugar, and spices to preserve and flavor the eggs. This method relies on the acidic environment of vinegar to inhibit bacterial growth and enhance shelf life.
Exploring Lacto Pickling Methods for Eggs
Lacto pickling for eggs uses natural fermentation with lactic acid bacteria, creating a tangier and probiotic-rich flavor compared to standard vinegar-based pickling. This method also enhances shelf life while preserving more nutritional benefits.
- Natural fermentation - Lacto pickling relies on lactic acid bacteria to ferment sugars, producing a distinctive sourness without vinegar.
- Probiotic benefits - The fermentation process develops beneficial probiotics that support gut health.
- Improved texture - Lacto pickling maintains a firmer egg white and yolk texture than traditional pickling methods.
Exploring lacto pickling offers a flavorful and health-conscious alternative to standard egg curing techniques.
Key Ingredients in Standard Pickling vs. Lacto Pickling
Standard pickling for eggs primarily uses vinegar, salt, and spices as key ingredients to achieve preservation and a tangy flavor. Lacto pickling, however, relies on natural fermentation with lactic acid bacteria, using salt and water to create a probiotic-rich environment without vinegar.
The key ingredients in standard pickling are distilled white vinegar and a blend of spices such as dill, garlic, and peppercorns, which provide a sharp, acidic taste and long shelf life. In contrast, lacto pickling employs salt brine that encourages fermentation by beneficial bacteria, resulting in a milder sourness and enhanced nutritional benefits. This process fosters the development of probiotics, making lacto pickled eggs a healthier alternative.
The Science Behind Pickling: Acid vs. Fermentation
Standard pickling of eggs involves immersing them in an acidic brine, typically vinegar-based, which lowers the pH and inhibits harmful microbial growth through chemical preservation. Lacto pickling relies on fermentation by lactic acid bacteria, which naturally produce lactic acid and beneficial probiotics, enhancing the egg's flavor and nutritional profile. The key scientific difference lies in acidification method: direct acid addition versus microbial fermentation, each impacting texture, taste, and shelf-life uniquely.
Flavor Differences: What to Expect from Each Method
Standard pickling uses vinegar and brine to create a sharp, tangy flavor that penetrates the egg quickly, offering a bright and acidic taste. Lacto pickling relies on natural fermentation with lactic acid bacteria, producing a complex, mildly sour flavor profile with subtle umami notes. Expect standard pickled eggs to be more immediately tart, while lacto-fermented eggs develop depth and probiotic richness over time.
Safety Considerations in Standard and Lacto Pickling
Standard pickling uses vinegar and salt to create an acidic environment that inhibits harmful bacterial growth, ensuring egg safety. The high acidity level, typically below pH 4.6, prevents the proliferation of pathogens such as Clostridium botulinum during storage.
Lacto pickling relies on lactic acid bacteria fermentation, gradually lowering the pH and producing antimicrobial compounds that enhance safety. Proper temperature control and fermentation time are critical to prevent spoilage and ensure the eggs remain safe for consumption.
Texture and Shelf Life: Lacto Pickling vs. Standard Pickling
Lacto pickling of eggs creates a creamier texture due to the natural fermentation process, whereas standard pickling results in a firmer, crisper bite. Shelf life tends to be longer with lacto pickling because the beneficial bacteria inhibit spoilage more effectively than vinegar alone.
- Lacto pickling enhances creaminess - Fermentation breaks down proteins, softening egg texture significantly.
- Standard pickling maintains firmness - Vinegar preserves eggs with a firmer, more brittle consistency.
- Extended shelf life in lacto pickling - Beneficial microbes prevent spoilage, often lasting several weeks beyond standard pickles.
Step-by-Step Guide: Standard Pickled Eggs
Standard pickling of eggs involves immersing hard-boiled eggs in a vinegar-based brine that imparts a tangy flavor and preserves them for extended shelf life. This method contrasts with lacto pickling, which uses fermented brine and results in a more complex, probiotic-rich product.
- Boil and Peel Eggs - Hard boil the eggs and carefully remove the shells to prepare them for pickling.
- Prepare Vinegar Brine - Combine vinegar, water, salt, sugar, and spices, then bring the mixture to a boil to create the pickling solution.
- Submerge Eggs in Brine - Place peeled eggs in a sterilized jar and cover them entirely with the hot vinegar brine before sealing and refrigerating.
Related Important Terms
Acid-Brined Eggification
Standard pickling uses a vinegar-based brine that rapidly lowers pH to inhibit bacterial growth and achieve a sharp, tangy flavor, while lacto pickling relies on natural fermentation by lactic acid bacteria to develop a complex, mildly sour taste with enhanced probiotic benefits. Acid-brined eggification through standard pickling prioritizes immediate preservation and acidity control, whereas lacto pickling emphasizes gradual acidification and nutrient enrichment via microbial activity.
Anaerobic Egg Lacto-fermentation
Standard pickling uses vinegar-based brine to preserve eggs with a sharp, acidic flavor, while anaerobic egg lacto-fermentation relies on naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria to ferment eggs in an oxygen-free environment, enhancing probiotic content and developing complex tangy flavors. This method promotes beneficial microorganisms, preserving eggs through controlled anaerobic conditions that boost nutritional value and shelf-life compared to traditional vinegar curing.
Ambient Brine Pickling
Standard pickling uses vinegar-based brine with high acidity for rapid curing, while lacto pickling employs ambient brine fermentation, promoting natural lactic acid bacteria growth that enhances egg flavor and texture. Ambient brine pickling maintains consistent room temperature, allowing gradual acidification and preservation without chemical additives, resulting in a more complex taste and extended shelf life.
Probiotic Egg Preservation
Standard pickling uses vinegar and salt to preserve eggs by creating an acidic environment that inhibits bacterial growth but does not promote probiotics. Lacto pickling relies on lactic acid bacteria fermentation, enhancing probiotic content and improving gut health while naturally preserving eggs through beneficial microbes.
Vinegar-Forward Pickle Bath
Standard pickling for eggs uses a vinegar-forward pickle bath that creates a sharp, tangy flavor and preserves the eggs through acidic brining, while lacto pickling employs natural fermentation by lactic acid bacteria, resulting in a milder, probiotic-rich product with complex sour notes. Vinegar-based baths offer quicker preservation and a distinctive, bold taste, whereas lacto pickling enhances texture and nutritional value through prolonged fermentation.
Lactic Synergy Culture
Lacto pickling for eggs utilizes Lactic Synergy Culture, which enhances fermentation by promoting beneficial lactic acid bacteria that improve flavor, texture, and preservation compared to standard pickling methods. This controlled microbial environment accelerates acidification, increases shelf-life, and offers superior probiotic benefits, making it a preferred technique in modern curing processes.
Bacterial Starter Scramble
Standard pickling preserves eggs primarily using acidic solutions like vinegar to inhibit bacterial growth, whereas lacto pickling employs lactic acid bacteria as a bacterial starter that ferments sugars, producing natural acids that enhance preservation and flavor complexity. The bacterial starter in lacto pickling not only accelerates fermentation but also promotes the proliferation of beneficial microbes, creating a safer and tangier product compared to the chemically stabilized standard pickling method.
Low-pH Brine Matrix
Standard pickling uses a vinegar-based low-pH brine matrix that quickly penetrates eggshells, ensuring preservation and tangy flavor development. Lacto pickling relies on a fermentation process in a lactic acid-rich brine, creating complex flavors and a probiotic-rich environment while maintaining acidity for safe curing.
Clean-Label Lacto Pickles
Standard pickling uses vinegar and salt for preservation, resulting in a tangy flavor and longer shelf life but often includes additives that may not meet clean-label standards. Lacto pickling relies on natural fermentation by lactic acid bacteria, producing clean-label eggs with enhanced probiotic benefits, a milder taste, and improved digestive health properties.
Standard Pickling vs Lacto Pickling for eggs. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com