Conventional dehydrators use heated air circulation to remove moisture from jerky, ensuring even drying but often requiring longer processing times. Infrared dehydrators utilize infrared radiation to penetrate the meat, speeding up moisture removal while preserving flavor and nutrients more effectively. Comparing both, infrared dehydrators offer faster drying and energy efficiency, while conventional models provide consistent airflow and simplicity for traditional jerky preparation.
Table of Comparison
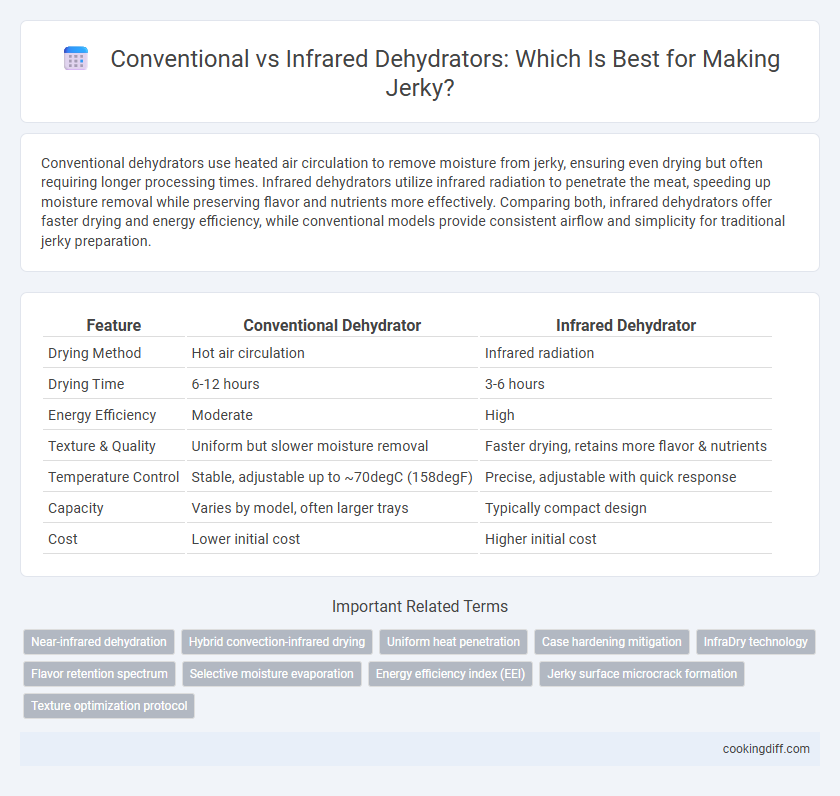
| Feature | Conventional Dehydrator | Infrared Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Hot air circulation | Infrared radiation |
| Drying Time | 6-12 hours | 3-6 hours |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Texture & Quality | Uniform but slower moisture removal | Faster drying, retains more flavor & nutrients |
| Temperature Control | Stable, adjustable up to ~70degC (158degF) | Precise, adjustable with quick response |
| Capacity | Varies by model, often larger trays | Typically compact design |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
Introduction to Jerky Dehydration Methods
Conventional dehydrators remove moisture from jerky using consistent low heat and airflow, preserving flavor and texture over extended drying periods. Infrared dehydrators employ radiant heat technology, which penetrates the meat more deeply and can reduce drying time significantly.
Jerky dehydration methods vary primarily in heat source and drying efficiency. Conventional dehydrators rely on circulating warm air, which evenly dehydrates the jerky but may take several hours to complete. Infrared dehydrators accelerate moisture evaporation by directly heating the meat's surface, enhancing energy efficiency and maintaining nutritional value while preventing over-drying. Choosing between these methods depends on desired texture, drying speed, and equipment cost.
Overview: Conventional Dehydrator Technology
| Conventional dehydrators use heated air circulated by fans to remove moisture from jerky, relying on temperatures typically between 130degF to 160degF for effective drying. The process ensures consistent airflow and gradual dehydration, preserving texture and flavor without cooking the meat. This technology is widely adopted due to its simplicity, affordability, and reliable performance in small- to medium-scale jerky production. |
Understanding Infrared Dehydrator Technology
Infrared dehydrator technology uses infrared radiation to penetrate jerky evenly, reducing drying time and preserving nutrients. Conventional dehydrators rely on hot air circulation, which often results in uneven drying and longer processing times.
- Infrared Penetration - Infrared wavelengths penetrate meat fibers, ensuring thorough and uniform dehydration.
- Energy Efficiency - Infrared dehydrators consume less energy by focusing heat directly on the product rather than heating the surrounding air.
- Preservation Quality - Infrared drying maintains better texture and flavor by preventing over-drying and nutrient loss.
Infrared dehydrator technology offers a faster, more efficient way to produce high-quality jerky compared to conventional methods.
Drying Efficiency: Conventional vs Infrared
How does drying efficiency compare between conventional and infrared dehydrators for jerky? Conventional dehydrators rely on hot air circulation, which can take several hours to achieve consistent dryness. Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat to penetrate the meat more quickly, reducing drying time and retaining more moisture for optimal jerky texture.
Energy Consumption and Cost Comparison
Conventional dehydrators typically consume between 300 to 600 watts, leading to higher energy costs over extended use, whereas infrared dehydrators operate more efficiently, often using around 150 to 300 watts. This energy efficiency results in significant savings on electricity bills, especially when dehydrating large batches of jerky regularly.
Initial costs for conventional dehydrators are generally lower, ranging from $40 to $150, but operational expenses accumulate due to their higher energy consumption. Infrared dehydrators have a higher upfront price, usually between $100 and $300, but lower energy use offers better long-term cost-effectiveness.
Jerky Texture and Flavor Differences
Conventional dehydrators use low heat and air circulation to slowly remove moisture, resulting in a chewier jerky texture that preserves traditional smoky flavors. Infrared dehydrators penetrate meat fibers more deeply, producing a tender jerky with enhanced flavor retention and a slightly caramelized surface. Texture differences arise as infrared methods reduce drying time, maintaining juiciness and intensifying spices compared to the drier, more fibrous outcome of conventional drying.
Nutrient Retention in Jerky: Infrared vs Conventional
Infrared dehydrators preserve more nutrients in jerky by using radiant heat that penetrates food evenly, reducing nutrient degradation. Conventional dehydrators rely on circulating hot air, which can lead to longer drying times and greater nutrient loss.
Studies show infrared drying retains higher levels of vitamins B and C compared to traditional methods. Faster drying with infrared technology minimizes exposure to heat and oxygen, enhancing the jerky's overall nutritional value.
Setup, Maintenance, and Ease of Use
Conventional dehydrators for jerky typically require more setup time due to multiple trays and manual temperature adjustments, while infrared dehydrators offer quicker, more streamlined setup with consistent heat distribution. Maintenance of conventional models involves regular cleaning of trays and fans to prevent residue buildup, whereas infrared dehydrators usually have fewer parts and self-cleaning elements, reducing effort. Ease of use favors infrared dehydrators because of intuitive controls and faster drying times, making them ideal for consistent jerky preparation.
Suitability for Home and Commercial Use
Conventional dehydrators are widely used in home settings due to their affordability and straightforward operation, making them ideal for hobbyists preparing jerky. Infrared dehydrators offer faster drying times and more even heat distribution, which benefits commercial operations requiring consistent high-volume production.
- Home Use Suitability - Conventional dehydrators are cost-effective and easy to use, perfect for occasional jerky makers.
- Commercial Use Efficiency - Infrared dehydrators provide rapid and uniform dehydration, supporting large-scale jerky production.
- Operational Considerations - Conventional models focus on simplicity, while infrared units emphasize speed and product quality for businesses.
Related Important Terms
Near-infrared dehydration
Near-infrared dehydration in jerky preparation penetrates meat fibers more effectively than conventional dehydrators, reducing drying time and preserving flavor while maintaining optimal texture. This method enhances energy efficiency and microbial safety by targeting water molecules directly, resulting in consistent, high-quality jerky production.
Hybrid convection-infrared drying
Hybrid convection-infrared drying combines conventional dehydrator airflow with infrared radiation to accelerate jerky drying while preserving flavor and texture. This method enhances moisture removal efficiency and ensures uniform heating, reducing drying time compared to traditional convection-only dehydrators.
Uniform heat penetration
Conventional dehydrators rely on heated air circulation, which can result in uneven drying and inconsistent texture in jerky due to surface-level heat exposure. Infrared dehydrators provide uniform heat penetration by emitting infrared waves that penetrate deeper into the meat, ensuring consistent moisture removal and superior jerky quality.
Case hardening mitigation
Infrared dehydrators reduce the risk of case hardening in jerky by promoting uniform heat distribution and faster moisture removal compared to conventional dehydrators, which often cause uneven drying and tough outer layers. Optimized infrared wavelengths penetrate the meat surface, preventing crust formation while maintaining internal moisture balance for consistent texture and safety.
InfraDry technology
InfraDry technology in infrared dehydrators uses targeted heat waves to penetrate jerky meat evenly, preserving texture and enhancing flavor while reducing dehydration time by up to 30% compared to conventional dehydrators. This method maintains essential nutrients and minimizes bacterial growth, resulting in higher-quality, safer jerky products.
Flavor retention spectrum
Infrared dehydrators preserve a broader flavor retention spectrum in jerky by evenly penetrating meat fibers and minimizing oxidation compared to conventional dehydrators, which rely on hot air that can lead to uneven drying and flavor degradation. This results in infrared-dried jerky maintaining richer aromas and a more intense, natural taste profile throughout the product.
Selective moisture evaporation
Conventional dehydrators rely on hot air circulation to remove moisture from jerky, often resulting in uneven drying and potential nutrient loss. Infrared dehydrators use targeted infrared radiation to selectively evaporate water molecules, enabling faster, more uniform drying while preserving flavor and nutritional content.
Energy efficiency index (EEI)
Infrared dehydrators exhibit a higher Energy Efficiency Index (EEI) compared to conventional dehydrators, utilizing less electricity while achieving faster moisture removal in jerky production. This efficiency reduces operational costs and environmental impact by optimizing energy consumption during the dehydration process.
Jerky surface microcrack formation
Conventional dehydrators rely on hot air circulation, which can cause uneven drying and more pronounced microcrack formation on jerky surfaces, leading to texture degradation. Infrared dehydrators provide more uniform heat penetration, minimizing surface microcracks and preserving jerky's structural integrity and moisture retention.
Conventional dehydrator vs Infrared dehydrator for jerky. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com