Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat that penetrates the food more evenly, preserving nutrients and reducing drying time compared to regular food dehydrators, which rely on circulating hot air. For dehydrating pet food, infrared technology ensures a more thorough dry, minimizing moisture pockets that can cause spoilage or bacterial growth. Regular food dehydrators are often more affordable but may require longer drying periods, potentially affecting the texture and nutritional quality of pet treats.
Table of Comparison
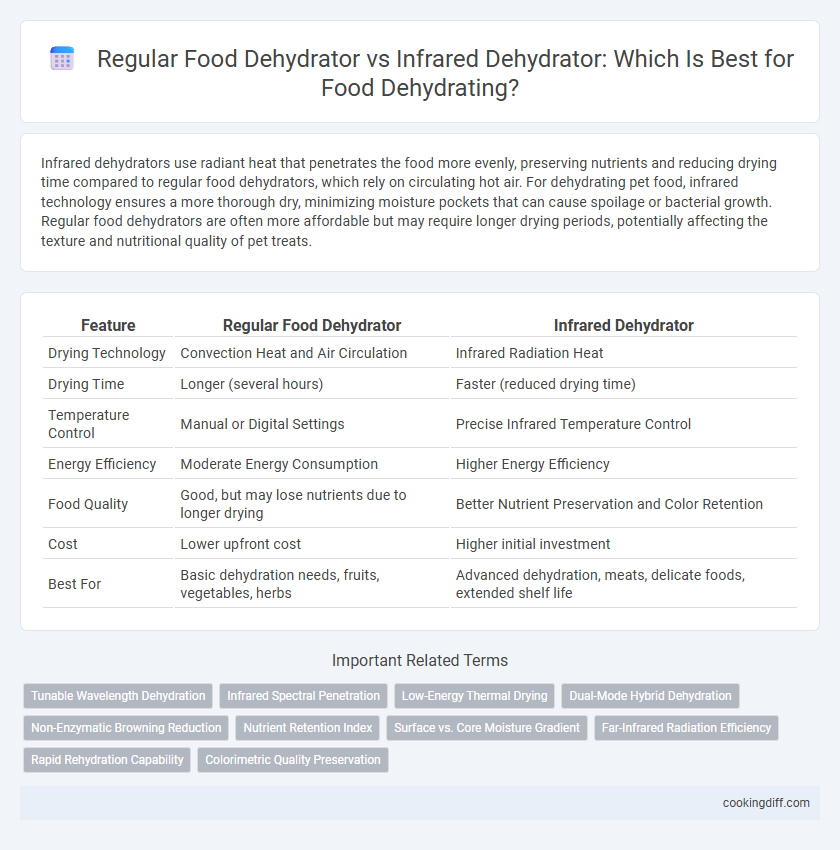
| Feature | Regular Food Dehydrator | Infrared Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Technology | Convection Heat and Air Circulation | Infrared Radiation Heat |
| Drying Time | Longer (several hours) | Faster (reduced drying time) |
| Temperature Control | Manual or Digital Settings | Precise Infrared Temperature Control |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate Energy Consumption | Higher Energy Efficiency |
| Food Quality | Good, but may lose nutrients due to longer drying | Better Nutrient Preservation and Color Retention |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Best For | Basic dehydration needs, fruits, vegetables, herbs | Advanced dehydration, meats, delicate foods, extended shelf life |
Introduction to Food Dehydration Methods
What are the key differences between a regular food dehydrator and an infrared dehydrator for food drying? Regular food dehydrators use heated air circulation to remove moisture, providing even drying and energy efficiency. Infrared dehydrators employ infrared radiation to penetrate food layers, offering faster dehydration and enhanced nutrient retention.
Overview of Regular Food Dehydrators
Regular food dehydrators use electric heating elements and fans to circulate warm air, effectively removing moisture from food. These devices are widely available, affordable, and suitable for drying fruits, vegetables, herbs, and meats at consistent temperatures. Their popularity stems from ease of use and proven reliability in preserving food nutrients and flavors.
What Is an Infrared Dehydrator?
An infrared dehydrator uses infrared radiation to penetrate food, drying it efficiently from the inside out, whereas regular food dehydrators rely on heated air circulation to remove moisture. This technology enables better retention of nutrients and faster dehydration times, making infrared dehydrators a modern alternative in food preservation.
- Infrared Radiation - Infrared dehydrators emit wavelengths that penetrate food deeply, speeding up moisture removal.
- Nutrient Preservation - The gentle infrared heat helps maintain vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants better than conventional methods.
- Energy Efficiency - Infrared models often consume less power by targeting heat more directly, reducing dehydration time.
Efficiency and Drying Speed Comparison
Regular food dehydrators rely on convection heat and fans to circulate warm air, resulting in moderate drying speeds and consistent moisture removal. Infrared dehydrators utilize infrared radiation to penetrate food items, accelerating drying times and enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Infrared technology reduces dehydration time by up to 30% compared to conventional models, making it ideal for users seeking faster results. While traditional dehydrators are effective for uniform drying, infrared units excel in preserving nutrients due to shorter exposure to heat.
Energy Consumption: Which is More Efficient?
Infrared dehydrators typically consume less energy than regular food dehydrators due to their efficient heat transfer method. Regular dehydrators rely on indirect heating and fans, which can lead to higher electricity usage over longer drying periods.
- Infrared technology - Penetrates food more directly, reducing drying time and overall energy consumption.
- Regular dehydrator design - Uses convection heating that requires more continuous energy to maintain even temperatures.
- Energy efficiency comparison - Infrared dehydrators can save up to 30% more energy compared to traditional models.
Choosing an infrared dehydrator offers a more energy-efficient solution for long-term food drying needs.
Nutrient Retention: Infrared vs Regular Dehydrators
Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat to penetrate food more evenly, preserving higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants compared to regular dehydrators. Traditional food dehydrators rely on hot air circulation, which may lead to greater nutrient degradation over longer drying periods.
- Infrared heat preserves nutrients better - Infrared waves maintain vitamin C and other heat-sensitive nutrients more effectively than convective drying.
- Uniform drying reduces oxidation - Infrared dehydrators dry food consistently, minimizing nutrient loss from uneven exposure.
- Regular dehydrators risk nutrient depletion - Extended drying times and higher temperatures in conventional models accelerate degradation of antioxidants.
Flavor and Texture Preservation
Regular food dehydrators use convection heat and airflow to slowly remove moisture, which helps maintain the natural flavor but can sometimes cause uneven texture due to air circulation variations. Infrared dehydrators penetrate food with infrared light, preserving deeper flavors and ensuring uniform texture by evenly heating from the inside out.
Infrared technology reduces nutrient loss and enhances moisture retention, resulting in a richer taste and chewier texture compared to conventional dehydrators. Regular dehydrators may cause slight flavor degradation and crispier edges, making them better suited for thinly sliced items rather than thick or dense foods.
User Experience and Ease of Use
Regular food dehydrators typically offer simple controls and straightforward tray stacking, which enhances ease of use for beginners. Infrared dehydrators provide faster, more even drying by penetrating food layers, improving user experience with less monitoring required. Users often find infrared models more efficient, but regular dehydrators remain popular for their affordability and intuitive operation.
Maintenance and Durability Differences
Regular food dehydrators require frequent cleaning due to exposed heating elements and fans, which can accumulate food particles and dust. Infrared dehydrators feature sealed heating systems that reduce maintenance needs and contamination risks.
Durability-wise, IR dehydrators often last longer as their components face less wear from airflow and debris. Regular dehydrators may suffer from fan motor failures or element corrosion over time. Investment in an infrared model offers improved longevity and lower upkeep costs.
Related Important Terms
Tunable Wavelength Dehydration
Infrared dehydrators with tunable wavelength technology target specific moisture content and nutrient preservation more efficiently than regular food dehydrators, enabling customized drying cycles that enhance flavor and retain essential vitamins. This precise dehydration method reduces energy consumption and drying time by optimizing infrared radiation absorption based on the food type.
Infrared Spectral Penetration
Infrared dehydrators utilize infrared spectral penetration to evenly and efficiently remove moisture from food at a cellular level, preserving nutrients and flavors better than regular food dehydrators that rely on convection heat alone. This deep spectral penetration accelerates drying time while maintaining higher food quality and texture consistency.
Low-Energy Thermal Drying
Regular food dehydrators use conventional heating elements and fans to remove moisture through evaporative drying, consuming more energy due to longer drying times and less efficient heat transfer. Infrared dehydrators leverage low-energy thermal drying by directly targeting water molecules with infrared radiation, resulting in faster dehydration, reduced energy consumption, and better nutrient preservation.
Dual-Mode Hybrid Dehydration
Dual-mode hybrid dehydration combines the consistent low heat of regular food dehydrators with the penetrating infrared energy to achieve faster, more even moisture removal and nutrient preservation. This method enhances drying efficiency by reducing dehydration time up to 30% while maintaining food texture and flavor compared to single-mode dehydrators.
Non-Enzymatic Browning Reduction
Regular food dehydrators use hot air circulation to remove moisture, which often leads to non-enzymatic browning due to Maillard reactions at higher temperatures. Infrared dehydrators operate at lower temperatures with radiant heat, significantly reducing non-enzymatic browning and preserving the food's natural color and nutrients during dehydration.
Nutrient Retention Index
Regular food dehydrators use hot air circulation to remove moisture, often causing nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to heat, resulting in a lower Nutrient Retention Index. Infrared dehydrators employ infrared radiation that penetrates food more efficiently, preserving vitamins and antioxidants better and achieving a higher Nutrient Retention Index.
Surface vs. Core Moisture Gradient
Regular food dehydrators primarily remove moisture from the surface, creating a moisture gradient that slows drying at the core, while infrared dehydrators penetrate deeper, reducing the surface-to-core moisture gradient and ensuring more uniform dehydration. Infrared technology accelerates core drying by directly targeting internal moisture, resulting in improved texture and reduced drying time compared to conventional surface-evaporation methods.
Far-Infrared Radiation Efficiency
Regular food dehydrators typically use convection heat and airflow to remove moisture, resulting in slower drying times and less energy efficiency. Infrared dehydrators leverage far-infrared radiation, which penetrates food more deeply and evenly, enhancing dehydration speed and preserving nutritional content with significantly higher energy efficiency.
Rapid Rehydration Capability
Infrared dehydrators enhance rapid rehydration capability by penetrating food at a molecular level, preserving cellular structure and moisture-retention properties better than regular food dehydrators. This results in faster and more efficient rehydration, maintaining texture and nutrient content in dried foods.
Regular food dehydrator vs Infrared Dehydrator for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com