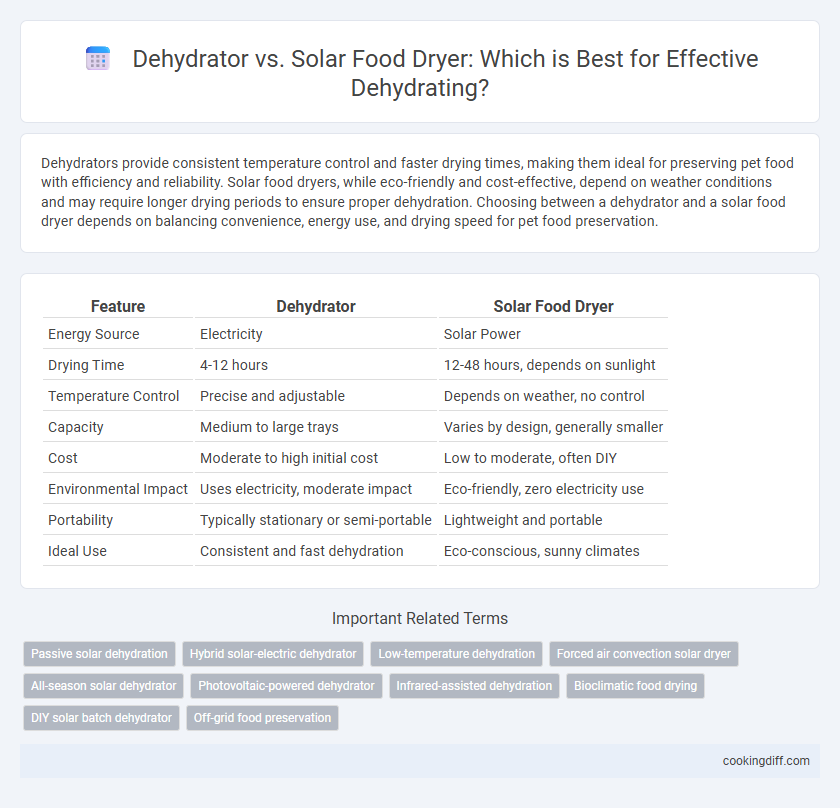
Dehydrators provide consistent temperature control and faster drying times, making them ideal for preserving pet food with efficiency and reliability. Solar food dryers, while eco-friendly and cost-effective, depend on weather conditions and may require longer drying periods to ensure proper dehydration. Choosing between a dehydrator and a solar food dryer depends on balancing convenience, energy use, and drying speed for pet food preservation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dehydrator | Solar Food Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity | Solar Power |
| Drying Time | 4-12 hours | 12-48 hours, depends on sunlight |
| Temperature Control | Precise and adjustable | Depends on weather, no control |
| Capacity | Medium to large trays | Varies by design, generally smaller |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial cost | Low to moderate, often DIY |
| Environmental Impact | Uses electricity, moderate impact | Eco-friendly, zero electricity use |
| Portability | Typically stationary or semi-portable | Lightweight and portable |
| Ideal Use | Consistent and fast dehydration | Eco-conscious, sunny climates |
Understanding Dehydrators and Solar Food Dryers
Dehydrators use electric heating elements and fans to circulate warm air, providing consistent temperature control for efficient moisture removal from food. Solar food dryers rely on natural sunlight and airflow, offering an eco-friendly alternative but with variable drying times depending on weather conditions.
Understanding the mechanics of dehydrators shows they deliver precision and speed, crucial for drying fruits, vegetables, and herbs uniformly. Solar food dryers harness renewable energy, reducing electricity costs while requiring clear, sunny days for optimal performance. Both methods preserve nutrients and extend shelf life, but choosing between them depends on individual needs and environmental factors.
How Each Method Works: Dehydrator vs Solar Dryer
| Dehydrator | Uses electric heating elements and fans to circulate warm air, removing moisture from food at controlled temperatures ranging from 95degF to 160degF. This method ensures consistent drying times and uniform results regardless of weather conditions. It offers precise temperature control, which preserves nutrients and extends shelf life. |
| Solar Food Dryer | Relies on solar energy to heat air within a closed chamber, where natural convection moves warm air through the food layers to evaporate moisture. Drying speed and efficiency depend on sunlight intensity, ambient temperature, and humidity, making it eco-friendly but variable in performance. Solar dryers can reduce microbial growth by maintaining sufficient drying temperatures without electricity. |
Speed and Efficiency: Which Dries Food Faster?
Electric dehydrators typically dry food faster due to controlled temperature and airflow, often reducing drying time by up to 50% compared to solar food dryers. These devices maintain consistent heat, ensuring efficient moisture removal regardless of weather conditions.
Solar food dryers rely on natural sunlight and ambient temperature, making drying speed dependent on geographic location and weather patterns, which may extend drying time considerably. However, solar dryers offer energy-efficient dehydration without electricity costs, appealing to sustainable food preservation enthusiasts.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Electric dehydrators typically consume around 300 to 1000 watts per hour, resulting in a higher energy footprint compared to solar food dryers that utilize renewable sunlight, leading to zero electricity usage. This makes solar food dryers a more energy-efficient option for long-term food preservation, especially in sunny regions.
Solar food dryers produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, significantly reducing their environmental impact compared to electric dehydrators powered by fossil fuels. However, electric dehydrators offer consistent drying conditions regardless of weather, which can affect the efficiency of solar drying methods.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Dehydrators typically require a higher initial investment, ranging from $40 to $300 depending on capacity and features, while solar food dryers often cost between $20 and $100. Long-term expenses for dehydrators include electricity costs averaging $0.10 to $0.30 per hour of use, whereas solar dryers use free solar energy, resulting in minimal ongoing costs. Maintenance for both systems is generally low, but replacing electrical components in dehydrators can add to expenses over time.
Quality and Consistency of Dehydrated Foods
Dehydrators provide precise temperature control, ensuring consistent quality in dehydrated foods by preventing uneven drying and spoilage. Solar food dryers depend on weather conditions, which can lead to variable moisture levels and affect the overall texture and safety of the dried product.
- Controlled Environment - Dehydrators maintain stable heat and airflow, producing uniformly dried foods.
- Weather Dependency - Solar dryers' performance fluctuates with sunlight intensity and ambient humidity.
- Food Safety - Consistent drying in dehydrators reduces the risk of bacterial growth compared to solar methods.
For reliable quality and consistency, electric dehydrators are the preferred option over solar food dryers.
Usability: Convenience and User Experience
Dehydrators offer consistent temperature control and automated timers, enhancing convenience for precise and reliable food drying. Solar food dryers rely on sunlight, making them eco-friendly but less predictable and requiring manual monitoring. Users seeking ease of use and time efficiency often prefer electric dehydrators over solar options for everyday dehydrating tasks.
Maintenance and Longevity of Equipment
Dehydrators generally require less frequent maintenance compared to solar food dryers due to their controlled environment and built-in components. Solar food dryers, while eco-friendly, often experience wear from outdoor exposure, impacting their longevity and necessitating regular upkeep.
- Dehydrators have sealed units - This design reduces dust and debris buildup, extending the equipment's lifespan with minimal cleaning.
- Solar food dryers are exposed to elements - Prolonged sun, rain, and wind exposure can degrade materials, requiring periodic repairs or replacements.
- Electrical components in dehydrators - Regular inspection ensures heating elements and fans function efficiently, preventing early failure.
Best Foods for Dehydrators vs Solar Food Dryers
Dehydrators excel at drying fruits and vegetables quickly with controlled low temperatures, preserving nutrients and flavor efficiently. Solar food dryers are ideal for dry climates and sun-loving foods, utilizing natural sunlight to dehydrate with minimal energy use.
- Best for Dehydrators - Fruits like apples, bananas, and berries dry evenly and retain sweetness due to consistent heat control.
- Best for Solar Food Dryers - Herbs and sun-resilient vegetables such as tomatoes and peppers benefit from natural sunlight drying to preserve aroma and taste.
- Energy Efficiency - Solar dryers offer eco-friendly dehydration with zero electricity, while dehydrators provide faster and predictable drying times regardless of weather.
Related Important Terms
Passive solar dehydration
Passive solar dehydration utilizes natural sunlight and airflow to remove moisture from food without electricity, making it energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Compared to electric dehydrators, passive solar food dryers offer sustainable, low-cost operation but may require longer drying times and consistent sunny conditions for optimal results.
Hybrid solar-electric dehydrator
Hybrid solar-electric dehydrators combine the energy efficiency of solar food dryers with the reliability of electric dehydrators, ensuring consistent dehydration regardless of weather conditions. These systems optimize moisture removal by harnessing solar energy during the day and switching to electric power when sunlight is insufficient, enhancing drying speed and food preservation quality.
Low-temperature dehydration
Low-temperature dehydration preserves nutrients and enzymes more effectively, making electric dehydrators ideal due to their precise temperature control between 95degF and 115degF. Solar food dryers rely on ambient sunlight and often lack consistent low-temperature regulation, leading to uneven drying and potential nutrient loss.
Forced air convection solar dryer
Forced air convection solar dryers optimize dehydration by combining solar energy with a fan-driven airflow system, accelerating moisture removal while preserving nutritional value and flavor. Unlike traditional dehydrators that rely solely on electric heat, these solar dryers reduce energy consumption and improve drying efficiency through uniform air circulation and controlled temperature.
All-season solar dehydrator
An all-season solar dehydrator offers consistent food drying performance by utilizing solar energy combined with engineered airflow systems, ensuring effective moisture removal even during low sunlight or cooler temperatures. Unlike traditional dehydrators that rely solely on electricity, all-season solar dehydrators reduce energy costs and environmental impact while maintaining optimal dehydration conditions year-round.
Photovoltaic-powered dehydrator
Photovoltaic-powered dehydrators offer efficient, eco-friendly dehydration by harnessing solar energy to maintain consistent temperatures and airflow, unlike traditional solar food dryers that depend solely on ambient sunlight and weather conditions. These solar-powered electric dehydrators enhance drying speed and nutrient retention, making them ideal for sustainable food preservation.
Infrared-assisted dehydration
Infrared-assisted dehydration in both dehydrators and solar food dryers enhances moisture removal efficiency by penetrating food layers to disrupt water molecules at a molecular level, resulting in faster drying times and better preservation of nutrients. While electric dehydrators offer controlled temperature and consistent infrared emission for optimal drying conditions, solar food dryers depend on natural sunlight, making infrared efficiency variable but eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Bioclimatic food drying
Dehydrators provide consistent temperature control for efficient bioclimatic food drying, ensuring optimal moisture removal and preservation of nutrients. Solar food dryers harness natural sunlight and airflow, offering an eco-friendly and energy-saving alternative best suited for warm, dry climates.
DIY solar batch dehydrator
A DIY solar batch dehydrator offers an energy-efficient and eco-friendly alternative to electric dehydrators by using sunlight to remove moisture from foods, ideal for preserving fruits and vegetables with minimal cost. Unlike traditional dehydrators that rely on electricity, solar batch dryers provide consistent heat through passive solar energy, making them suitable for sustainable food preservation in off-grid or low-energy environments.
Dehydrator vs Solar food dryer for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com