Dehydrating removes moisture from food at low temperatures over an extended period, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor without cooking the ingredients. Microwave drying uses high heat to rapidly evaporate moisture, significantly reducing prep time but can compromise texture and nutrient retention. Choosing between dehydrating and microwave drying depends on whether preserving food quality or speed is the priority in quick meal preparation.
Table of Comparison
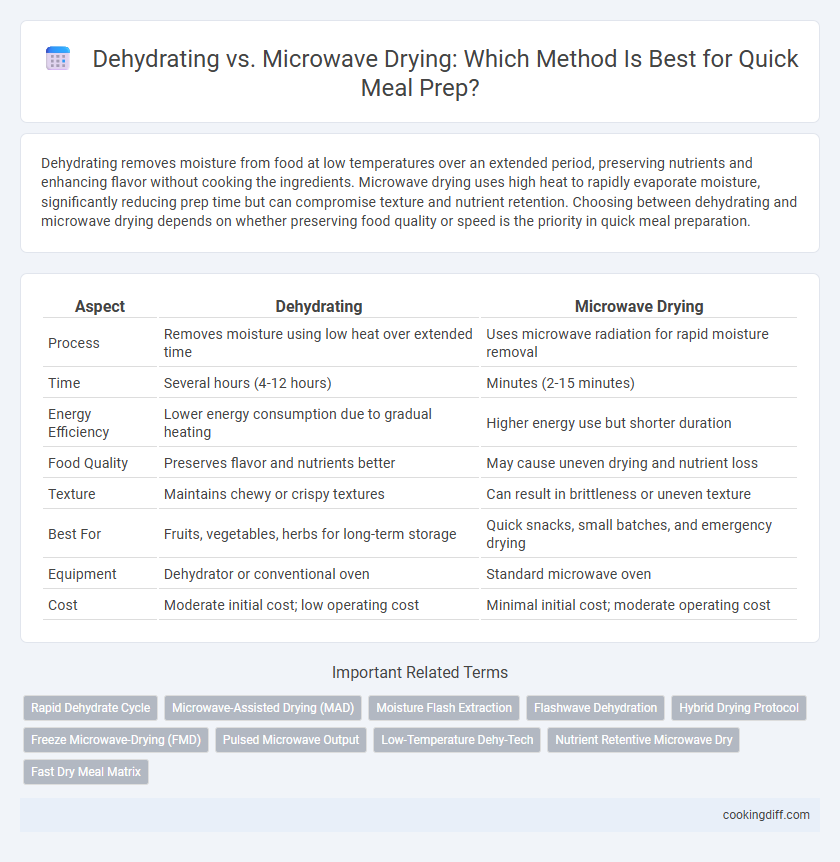
| Aspect | Dehydrating | Microwave Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Removes moisture using low heat over extended time | Uses microwave radiation for rapid moisture removal |
| Time | Several hours (4-12 hours) | Minutes (2-15 minutes) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy consumption due to gradual heating | Higher energy use but shorter duration |
| Food Quality | Preserves flavor and nutrients better | May cause uneven drying and nutrient loss |
| Texture | Maintains chewy or crispy textures | Can result in brittleness or uneven texture |
| Best For | Fruits, vegetables, herbs for long-term storage | Quick snacks, small batches, and emergency drying |
| Equipment | Dehydrator or conventional oven | Standard microwave oven |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; low operating cost | Minimal initial cost; moderate operating cost |
Introduction to Food Drying Methods
Dehydrating and microwave drying are popular food drying methods used for quick meal prep. Dehydrating removes moisture slowly using low heat, preserving nutrients and flavor.
Microwave drying uses high-frequency waves to evaporate water rapidly, significantly reducing drying time. Both methods extend food shelf life but vary in texture and energy consumption.
Understanding Dehydrating: How It Works
Dehydrating removes moisture from food through low heat over an extended period, preserving nutrients and flavors. This process differs from microwave drying by using consistent temperatures that prevent cooking the food.
- Low heat method - Dehydrators maintain temperatures between 95degF to 155degF to gently remove water.
- Nutrient preservation - Slow drying helps retain vitamins and minerals compared to high heat methods.
- Texture and flavor - Dehydrating enhances natural flavors while producing chewy or crisp textures ideal for meal prep.
Microwave Drying Explained
Microwave drying utilizes electromagnetic waves to rapidly remove moisture from food, significantly reducing drying time compared to traditional dehydrating methods. This technique preserves essential nutrients and flavors while enabling quick meal preparation, making it ideal for busy lifestyles. microwave drying also minimizes energy consumption, offering an efficient alternative for preserving meals without compromising quality.
Speed and Efficiency: Which Is Faster?
Which method offers faster drying for quick meal prep, dehydrating or microwave drying? Microwave drying significantly reduces drying time by using high-frequency waves to remove moisture rapidly. Dehydrating, while slower, provides even drying and better preservation of nutrients, making it more efficient for certain food types.
Nutritional Retention Comparison
| Method | Nutritional Retention | Impact on Vitamins | Enzyme Activity Preservation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrating | High retention of nutrients due to low-temperature drying | Better preservation of heat-sensitive vitamins like Vitamin C and B-complex | Maintains more natural enzymes, supporting digestion |
| Microwave Drying | Moderate retention; quick drying may degrade some nutrients | Higher risk of vitamin loss, especially water-soluble vitamins | Enzyme activity often reduced due to uneven heating |
Flavor and Texture Differences
Dehydrating preserves flavor by slowly removing moisture, which intensifies natural tastes and maintains food's original texture. This method results in a chewy or crisp finish, depending on the item, ideal for snacks and long-term storage.
Microwave drying quickly reduces moisture but can cause uneven heating, leading to texture inconsistencies and potential flavor loss. It often produces a less natural taste and a brittle or tough texture, making it less suitable for delicate ingredients.
Equipment and Energy Usage
Dehydrating uses specialized low-temperature equipment designed for gradual moisture removal, making it energy-efficient but time-consuming. Microwave drying relies on household microwaves for rapid moisture extraction, consuming more energy over a short period.
- Dehydrator Equipment - Dehydrators feature stacked trays and built-in fans for uniform drying and precise temperature control.
- Microwave Usage - Microwaves use electromagnetic waves to quickly heat water molecules but lack consistent temperature regulation.
- Energy Efficiency - Dehydrators consume less continuous energy while operating for several hours, whereas microwaves use higher power in short bursts.
Suitability for Different Ingredients
Dehydrating is ideal for preserving fruits, vegetables, and herbs by removing moisture slowly to maintain texture and nutrients. Microwave drying suits quick meal prep of small, thin, or uniform ingredients but may cause uneven drying or loss of flavor in sensitive items. Each method's suitability depends on ingredient type and desired preservation quality in meal preparation.
Cost-Effectiveness for Quick Meal Prep
Dehydrating offers a cost-effective solution for quick meal prep by using less electricity than microwave drying, resulting in lower energy bills over time. Microwave drying requires higher immediate power consumption, increasing operational costs despite faster processing times.
- Lower Energy Usage - Dehydrators consume significantly less electricity per hour compared to microwaves, reducing utility costs.
- Equipment Cost - Dehydrators typically have a moderate upfront cost, often cheaper than high-powered microwave units designed for drying.
- Reusable Efficiency - Dehydrated meals have longer shelf life, minimizing food waste and additional grocery expenses.
Prioritizing dehydration for meal prep balances cost savings with efficient food preservation.
Related Important Terms
Rapid Dehydrate Cycle
Rapid Dehydrate Cycle offers faster moisture removal compared to traditional microwave drying, preserving nutrients and flavors more effectively for quick meal prep. This advanced dehydration method optimizes temperature and airflow, ensuring uniform drying while minimizing cooking time and energy consumption.
Microwave-Assisted Drying (MAD)
Microwave-Assisted Drying (MAD) significantly reduces drying time by rapidly heating water molecules within food, preserving nutritional content and texture better than traditional dehydrating methods. MAD offers uniform moisture removal and energy efficiency, making it ideal for quick meal prep while maintaining product quality and safety.
Moisture Flash Extraction
Moisture Flash Extraction in dehydrating efficiently removes water content at low temperatures, preserving nutrients and texture better than microwave drying, which can cause uneven heating and partial cooking. This method extends shelf life and maintains food quality, making it superior for quick meal prep where nutrient retention and texture are critical.
Flashwave Dehydration
Flashwave Dehydration outperforms traditional microwave drying by preserving nutrients and flavors while reducing moisture content efficiently, making it ideal for quick meal prep. Its advanced technology enables uniform drying without overheating, ensuring superior texture and extended shelf life compared to conventional microwave methods.
Hybrid Drying Protocol
Hybrid drying protocols combine dehydrating and microwave drying techniques to optimize moisture removal while preserving nutrient quality and texture in quick meal prep. This approach reduces overall drying time by leveraging the low-temperature, energy-efficient dehydration followed by rapid microwave drying, enhancing flavor retention and shelf stability.
Freeze Microwave-Drying (FMD)
Freeze Microwave-Drying (FMD) combines the low-temperature preservation of freeze drying with microwave energy to rapidly remove moisture while maintaining nutrient integrity, making it superior for quick meal prep compared to traditional dehydrating. FMD produces lightweight, shelf-stable meals with enhanced texture and flavor retention, significantly reducing drying time without compromising food quality.
Pulsed Microwave Output
Pulsed microwave output in microwave drying offers precise control over heat application, reducing the risk of overcooking and maintaining nutrient retention compared to traditional dehydrating methods. This technology accelerates moisture removal while preserving texture and flavor, making it ideal for rapid meal preparation.
Low-Temperature Dehy-Tech
Low-Temperature Dehy-Tech preserves nutrient integrity and flavor by drying meals below 140degF, unlike microwave drying which often uses higher heat leading to uneven dehydration and nutrient loss. This method ensures a longer shelf life and superior texture for quick meal prep, optimizing both health benefits and food quality.
Nutrient Retentive Microwave Dry
Microwave drying preserves nutrients more effectively than traditional dehydrating methods by using shorter cooking times and lower temperatures, reducing nutrient degradation. This rapid moisture removal technique maintains higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants, making it ideal for quick meal preparation without compromising nutritional value.
Dehydrating vs Microwave Drying for quick meal prep. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com