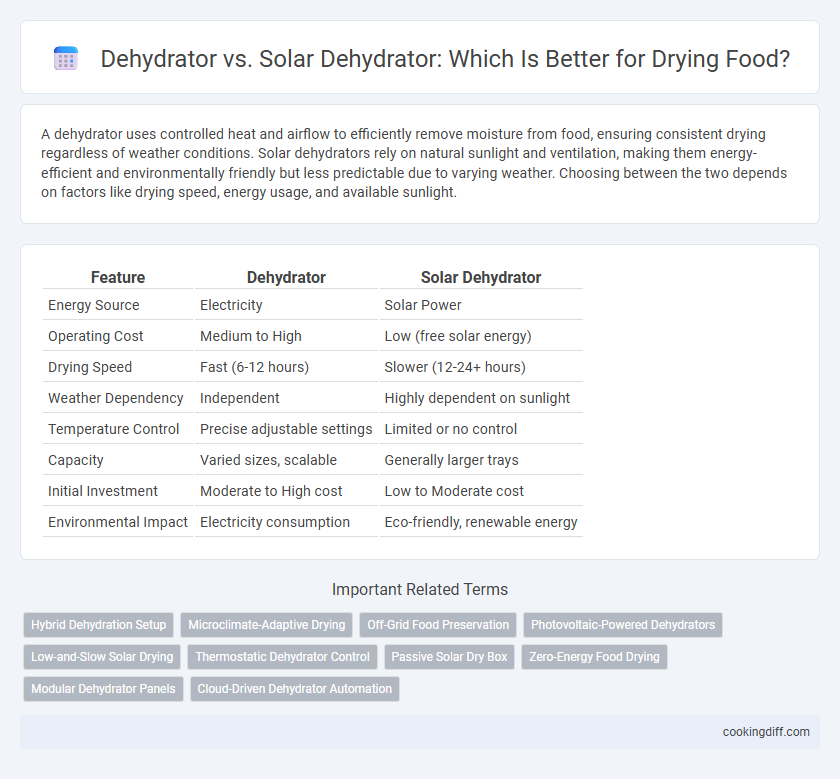
A dehydrator uses controlled heat and airflow to efficiently remove moisture from food, ensuring consistent drying regardless of weather conditions. Solar dehydrators rely on natural sunlight and ventilation, making them energy-efficient and environmentally friendly but less predictable due to varying weather. Choosing between the two depends on factors like drying speed, energy usage, and available sunlight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dehydrator | Solar Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity | Solar Power |
| Operating Cost | Medium to High | Low (free solar energy) |
| Drying Speed | Fast (6-12 hours) | Slower (12-24+ hours) |
| Weather Dependency | Independent | Highly dependent on sunlight |
| Temperature Control | Precise adjustable settings | Limited or no control |
| Capacity | Varied sizes, scalable | Generally larger trays |
| Initial Investment | Moderate to High cost | Low to Moderate cost |
| Environmental Impact | Electricity consumption | Eco-friendly, renewable energy |
Introduction to Food Dehydration Methods
Food dehydration methods include electric dehydrators and solar dehydrators, both designed to remove moisture from food to extend shelf life. Electric dehydrators provide consistent temperature control, enabling precise drying conditions for various food types. Solar dehydrators utilize energy from the sun, offering an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative, though drying times can be longer and weather-dependent.
What is an Electric Dehydrator?
An electric dehydrator uses controlled heat and airflow to efficiently remove moisture from food, preserving its flavor and nutrients. It operates independently of weather conditions, making it a reliable option for consistent drying.
- Temperature Control - Offers adjustable temperature settings to accommodate various types of food for optimal drying.
- Time Efficiency - Dries food faster than solar dehydrators due to consistent and regulated heat.
- Energy Source - Powered by electricity, allowing indoor use regardless of sunlight availability.
Understanding Solar Dehydrators
Solar dehydrators use solar energy to dry food naturally, reducing electricity consumption compared to electric dehydrators. They combine passive and active drying techniques, often incorporating a solar collector and transparent drying chamber to enhance airflow and temperature control.
- Energy Efficiency - Solar dehydrators utilize free, renewable solar power, minimizing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Temperature Control - Adjustable vents and solar collectors help maintain consistent drying temperatures essential for food safety.
- Drying Time - Solar dehydrators generally require longer drying durations but preserve nutrients effectively through gentle heat.
Understanding the mechanics and benefits of solar dehydrators aids in selecting the optimal drying method for sustainable food preservation.
Energy Efficiency: Dehydrator vs Solar Dehydrator
Which option offers better energy efficiency for drying food, a dehydrator or a solar dehydrator? Electric dehydrators consume a consistent amount of electricity, typically between 300 to 1000 watts, providing reliable operation regardless of weather conditions. Solar dehydrators harness renewable solar energy, eliminating electricity costs and reducing carbon footprint, but their efficiency depends heavily on sunlight availability and climate.
Drying Speed and Consistency Comparison
Electric dehydrators provide faster drying speeds, typically reducing moisture in 6-12 hours, while solar dehydrators may take 12-24 hours depending on sunlight intensity. Consistency is higher with electric models due to regulated temperature and airflow, ensuring uniform drying results.
Solar dehydrators rely on natural sunlight and ambient temperature, causing variability in drying speed and product moisture levels. In contrast, electric dehydrators maintain a stable drying environment with precise temperature control, minimizing the risk of under- or over-drying. The choice between methods depends on energy availability and desired drying uniformity.
Impact on Food Quality and Nutritional Value
Dehydrators use controlled heat and airflow to preserve food's color, texture, and nutritional content more consistently compared to solar dehydrators, which rely on variable sunlight and ambient conditions. Solar dehydrators may cause uneven drying, potentially leading to nutrient loss and decreased food quality due to prolonged exposure to fluctuating temperatures and humidity. The precise temperature control in electric dehydrators helps retain vitamins and antioxidants, ensuring higher nutritional value in dried foods.
Cost Analysis: Purchase, Operation, and Maintenance
Dehydrators generally require a higher initial investment compared to solar dehydrators, which are often more affordable due to the use of natural energy sources. Operational costs for electric dehydrators are significantly more expensive due to consistent electricity consumption, while solar dehydrators operate with minimal to no energy costs.
- Purchase Cost - Electric dehydrators typically cost between $50 to $300, whereas solar dehydrators can be built or bought for $20 to $150.
- Operational Cost - Electric models consume between 300 to 1000 watts per hour, leading to higher electricity bills compared to the free solar energy used by solar dehydrators.
- Maintenance Cost - Electric dehydrators require occasional component replacements and cleaning, whereas solar dehydrators mostly need structural maintenance with lower overall costs.
Best Foods for Electric vs Solar Dehydration
| Dehydrator Type | Best Foods | Drying Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Dehydrator | Fruits like apples, bananas, and berries; vegetables such as tomatoes and mushrooms; jerky and herbs | Provides consistent temperature control ideal for delicate foods; faster drying times reduce spoilage risk |
| Solar Dehydrator | Fruits such as mangoes and pineapples; vegetables like peppers and zucchini; nuts and seeds | Energy-efficient for dry climates; slower drying enhances flavor intensity and nutrient retention |
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
Electric dehydrators consume significant energy, typically powered by non-renewable electricity sources, contributing to a higher carbon footprint. Solar dehydrators use renewable solar energy, drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions during food drying processes.
Solar dehydrators promote sustainability by harnessing natural sunlight, minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering operational costs. However, their effectiveness depends on weather conditions, making electric dehydrators more reliable for consistent, year-round use despite environmental trade-offs.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Dehydration Setup
A hybrid dehydration setup combines the consistent, controlled heat of an electric dehydrator with the eco-friendly, energy-saving benefits of a solar dehydrator, optimizing drying efficiency and preserving nutritional value. This approach reduces energy costs and extends drying capacity, making it ideal for both small-scale and commercial food preservation.
Microclimate-Adaptive Drying
Dehydrators offer controlled temperature and airflow, enabling consistent drying regardless of external conditions, while solar dehydrators rely on ambient solar energy, making their efficiency dependent on local microclimate factors such as sunlight intensity, humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Microclimate-adaptive drying in solar dehydrators optimizes natural airflow and heat capture to enhance drying rates, but electric dehydrators provide precise environment control for uniform moisture removal in varied climatic conditions.
Off-Grid Food Preservation
A solar dehydrator harnesses renewable sunlight, making it ideal for off-grid food preservation by reducing dependence on electricity and lowering energy costs. Traditional electric dehydrators offer precise temperature control and faster drying times but require reliable power sources, limiting their use in remote or off-grid settings.
Photovoltaic-Powered Dehydrators
Photovoltaic-powered dehydrators harness solar energy through photovoltaic panels to efficiently dry food, offering consistent temperature control unlike traditional solar dehydrators that rely solely on ambient sunlight. These systems reduce energy consumption and enhance drying speed by converting solar power into electrical energy, ensuring food preservation even during cloudy conditions.
Low-and-Slow Solar Drying
Low-and-slow solar drying utilizes consistent, moderate temperatures and extended drying times, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor retention compared to faster dehydrators. Solar dehydrators reduce energy costs and environmental impact while maintaining effective moisture removal, making them ideal for drying fruits, vegetables, and herbs sustainably.
Thermostatic Dehydrator Control
Thermostatic control in electric dehydrators precisely regulates temperature, ensuring optimal drying conditions that preserve food nutrients and texture more consistently than solar dehydrators. Solar dehydrators, relying on ambient sunlight and temperature, often lack this precise thermal management, leading to variable drying times and potential quality variations.
Passive Solar Dry Box
A Passive Solar Dry Box uses natural sunlight and airflow to efficiently dehydrate food without electricity, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to electric dehydrators. Its design maximizes heat retention and air circulation, preserving nutrients while reducing energy consumption during the drying process.
Zero-Energy Food Drying
Solar dehydrators harness renewable energy from the sun to efficiently dry food without electricity, reducing carbon footprint and operational costs compared to electric dehydrators. Zero-energy food drying with solar dehydrators preserves nutrients and extends shelf life while promoting sustainable food preservation practices.
Modular Dehydrator Panels
Modular dehydrator panels offer scalable drying capacity by allowing users to customize the size and number of drying trays, enhancing airflow and consistent heat distribution compared to traditional solar dehydrators. These panels improve efficiency in dehydrators by providing controlled temperature settings, reducing drying time and preserving nutrient retention in various foods.
Dehydrator vs Solar Dehydrator for drying food. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com