Electric dehydrators provide consistent airflow and controlled temperature, making them ideal for evenly drying fruits, vegetables, and meats into snacks. Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat to penetrate food more deeply, reducing dehydration time and preserving nutrients and flavors more effectively. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize faster drying with nutrient retention or uniform dehydration for delicate snack textures.
Table of Comparison
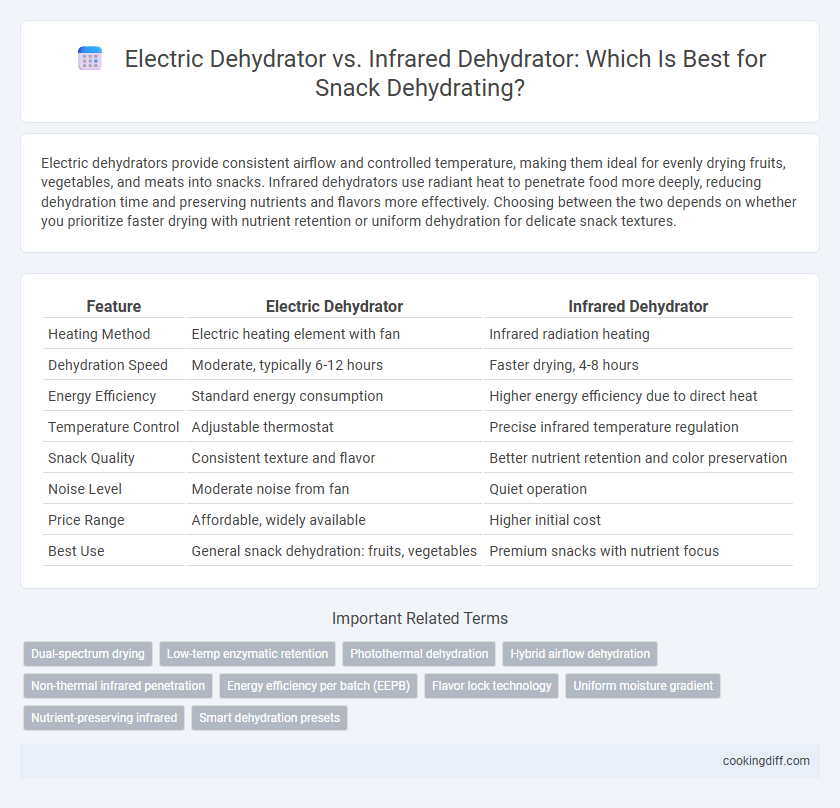
| Feature | Electric Dehydrator | Infrared Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electric heating element with fan | Infrared radiation heating |
| Dehydration Speed | Moderate, typically 6-12 hours | Faster drying, 4-8 hours |
| Energy Efficiency | Standard energy consumption | Higher energy efficiency due to direct heat |
| Temperature Control | Adjustable thermostat | Precise infrared temperature regulation |
| Snack Quality | Consistent texture and flavor | Better nutrient retention and color preservation |
| Noise Level | Moderate noise from fan | Quiet operation |
| Price Range | Affordable, widely available | Higher initial cost |
| Best Use | General snack dehydration: fruits, vegetables | Premium snacks with nutrient focus |
Introduction to Dehydrating Snacks: Electric vs Infrared
Electric dehydrators use consistent low heat and a fan to evenly remove moisture from snacks, preserving flavor and nutrients with controlled airflow. Infrared dehydrators employ infrared radiation to penetrate food, accelerating drying while maintaining texture and color.
Electric dehydrators are ideal for uniform drying of fruits, vegetables, and jerky, offering precise temperature settings. Infrared dehydrators provide faster dehydration times and energy efficiency, making them suitable for quick snack preparation.
How Electric Dehydrators Work
Electric dehydrators use a fan and a heating element to circulate warm air evenly around the food, removing moisture efficiently. The temperature and airflow are controlled to preserve nutrients and flavors while drying snacks like fruits, vegetables, and meats. This method ensures consistent dehydration results, making electric dehydrators popular for home use and small-scale snack production.
Understanding Infrared Dehydrators
| Infrared Dehydrators | Use infrared radiation to heat food directly, preserving more nutrients and reducing dehydration time compared to electric dehydrators. |
| Electric Dehydrators | Rely on circulating hot air to remove moisture, offering uniform drying but potentially longer processing times and nutrient degradation. |
| Advantages of Infrared Technology | Enhances energy efficiency, maintains flavor integrity, and provides faster drying especially for thin snacks like fruit chips. |
Energy Efficiency: Electric vs Infrared Dehydrators
Electric dehydrators typically consume more energy due to their reliance on heating elements and fans, whereas infrared dehydrators use radiant heat, which can be more energy-efficient for drying snacks. Infrared technology heats food directly, reducing overall drying time and energy use.
Electric dehydrators maintain consistent temperatures with adjustable settings but may require longer running times, increasing electricity consumption. Infrared dehydrators offer faster dehydration by targeting moisture within the food, leading to lower energy costs and less heat loss. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing energy efficiency against initial investment and drying capacity.
Drying Speed and Performance Comparison
Electric dehydrators typically offer consistent drying speeds due to controlled airflow and temperature settings, making them ideal for evenly dehydrating snacks. Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat to penetrate food, often resulting in faster moisture removal but may vary in performance depending on the food type and infrared wavelength.
- Drying Speed - Electric dehydrators generally require 6-12 hours for drying fruits and vegetables, while infrared dehydrators can reduce this time by up to 30%.
- Energy Efficiency - Infrared dehydrators tend to be more energy-efficient as they directly heat the food rather than the surrounding air.
- Uniformity - Electric dehydrators provide more uniform drying due to consistent airflow, minimizing uneven dehydration common in some infrared models.
Choosing between electric and infrared dehydrators depends on prioritizing drying speed or evenness of snack dehydration.
Flavor and Nutrient Retention in Dehydrated Snacks
Electric dehydrators use consistent low heat and airflow, which helps preserve the natural flavor and nutrients of snacks without overheating. Infrared dehydrators apply radiant heat that can penetrate food more deeply, potentially enhancing flavor while maintaining a higher nutrient retention in some cases.
- Electric dehydrators maintain flavor - Their controlled airflow prevents oxidation, preserving taste and color in dried snacks.
- Infrared dehydrators boost nutrient retention - Infrared heat reduces drying time, minimizing nutrient loss caused by prolonged exposure to heat and air.
- Flavor intensity differs - Infrared drying can intensify certain flavors due to deeper heat penetration, while electric drying retains a more natural taste profile.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Electric dehydrators offer straightforward operation with digital controls, making them user-friendly for snack preparation. Infrared dehydrators require minimal maintenance due to their efficient heat distribution, reducing cleaning frequency.
- Electric dehydrator controls - Digital panels enable precise temperature settings for consistent results.
- Infrared heat system - Promotes even drying, lowering the risk of food sticking to trays.
- Maintenance requirements - Infrared units generally have fewer movable parts, simplifying upkeep.
Best Snacks for Electric and Infrared Dehydrators
Electric dehydrators are ideal for drying fruits, herbs, and jerky due to their consistent low heat and adjustable temperature settings, which preserve flavor and nutrients effectively. Infrared dehydrators excel at quickly drying snacks like nuts and thin vegetable slices by penetrating deeper layers with infrared waves, resulting in evenly dried products without overcooking. Choosing the best snacks depends on dehydration goals: electric models suit moisture-sensitive items, while infrared units optimize texture and crispiness in thin or dense snacks.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Value
Which offers better cost efficiency for snack dehydration: electric or infrared dehydrators? Electric dehydrators generally have a lower initial investment, ranging from $40 to $150, while infrared models can cost between $200 and $500 due to advanced technology. Over time, infrared dehydrators provide greater long-term value by consuming less energy and drying snacks faster, reducing operational costs significantly.
Related Important Terms
Dual-spectrum drying
Electric dehydrators use consistent low heat and airflow to evenly remove moisture from snacks, preserving nutrients and texture. Infrared dehydrators combine heat and radiant energy for faster drying times and enhanced flavor retention, making dual-spectrum drying an efficient method that balances speed and quality.
Low-temp enzymatic retention
Electric dehydrators maintain consistent low temperatures ideal for preserving enzymes during snack dehydration, optimizing nutritional retention and flavor integrity. Infrared dehydrators, while efficient, often generate uneven heat that can exceed enzymatic thresholds, potentially reducing the bioactive compounds in low-temp drying processes.
Photothermal dehydration
Electric dehydrators use forced air circulation to remove moisture, providing consistent temperature control ideal for dehydrating snacks; infrared dehydrators employ photothermal dehydration by converting infrared radiation into heat, accelerating moisture evaporation while preserving nutrient content and flavor. Infrared technology enhances energy efficiency and reduces drying time compared to conventional electric dehydrators, making it a superior choice for maintaining snack quality during dehydration.
Hybrid airflow dehydration
Electric dehydrators provide consistent temperature control and enhanced airflow circulation, making them ideal for uniform drying of snacks, while infrared dehydrators offer rapid heat penetration through radiant energy. Hybrid airflow dehydration combines the precise thermal regulation of electric models with the deep heat absorption of infrared technology, optimizing drying efficiency and preserving snack texture and nutritional value.
Non-thermal infrared penetration
Electric dehydrators use convection heating and circulating air to remove moisture from snacks, ensuring even drying without direct heat damage. Infrared dehydrators utilize non-thermal infrared penetration to target water molecules inside the snacks, preserving nutrients and texture while reducing drying time significantly.
Energy efficiency per batch (EEPB)
Electric dehydrators typically offer higher energy efficiency per batch (EEPB) by maintaining consistent temperatures and airflow, reducing drying time and energy consumption for snacks. Infrared dehydrators, while effective at penetrating moisture quickly, often consume more energy per batch due to variable heat distribution and longer drying cycles.
Flavor lock technology
Electric dehydrators utilize consistent low heat and controlled airflow to preserve snacks' natural flavors and nutrients, while infrared dehydrators employ radiant heat to penetrate food more deeply, enhancing flavor retention with minimal oxidation. Flavor lock technology in infrared dehydrators intensifies taste by sealing in moisture and volatile compounds, resulting in snacks with richer aroma and improved texture compared to traditional electric drying methods.
Uniform moisture gradient
Electric dehydrators provide a consistent temperature and airflow, ensuring a uniform moisture gradient that prevents uneven drying and preserves snack quality. Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat to penetrate snacks more deeply, promoting faster dehydration but may cause moisture gradients to be less uniform compared to electric models.
Nutrient-preserving infrared
Infrared dehydrators use longer wavelengths to penetrate food more evenly, preserving vitamins and antioxidants better than electric dehydrators that rely primarily on hot air circulation. Nutrient retention in snacks such as fruits and vegetables is significantly higher with infrared technology, minimizing heat-related degradation during the dehydration process.
Electric dehydrator vs Infrared dehydrator for snacks Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com