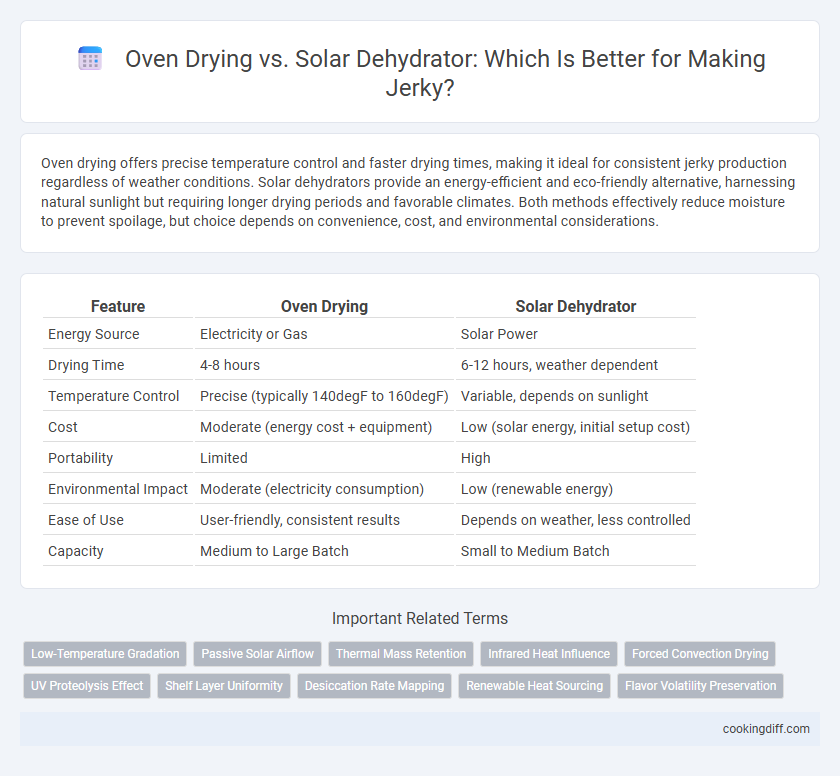
Oven drying offers precise temperature control and faster drying times, making it ideal for consistent jerky production regardless of weather conditions. Solar dehydrators provide an energy-efficient and eco-friendly alternative, harnessing natural sunlight but requiring longer drying periods and favorable climates. Both methods effectively reduce moisture to prevent spoilage, but choice depends on convenience, cost, and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oven Drying | Solar Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity or Gas | Solar Power |
| Drying Time | 4-8 hours | 6-12 hours, weather dependent |
| Temperature Control | Precise (typically 140degF to 160degF) | Variable, depends on sunlight |
| Cost | Moderate (energy cost + equipment) | Low (solar energy, initial setup cost) |
| Portability | Limited | High |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate (electricity consumption) | Low (renewable energy) |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, consistent results | Depends on weather, less controlled |
| Capacity | Medium to Large Batch | Small to Medium Batch |
Introduction to Jerky Dehydration Methods
What are the key differences between oven drying and solar dehydrators for making jerky? Oven drying offers precise temperature control and faster drying times, ensuring food safety by reaching optimal dehydration levels quickly. Solar dehydrators rely on natural sunlight, providing an energy-efficient and eco-friendly option but may require longer drying periods and depend on weather conditions.
How Oven Drying Works for Jerky
Oven drying for jerky involves setting a conventional oven to a low temperature, usually between 140degF and 170degF, to slowly remove moisture from thin strips of meat. This controlled heat dries the meat evenly, reducing the risk of bacterial growth while preserving flavor and texture.
Unlike solar dehydrators that rely on sunlight and ambient temperature, oven drying offers consistent heat regardless of weather conditions, making it reliable year-round. The process typically takes 4 to 8 hours, depending on meat thickness and oven settings.
Solar Dehydrators: An Overview
Solar dehydrators utilize renewable solar energy to dry jerky efficiently, reducing electricity costs and environmental impact. They often feature transparent panels and ventilation systems that optimize airflow and heat distribution for consistent dehydration. Unlike oven drying, solar dehydrators maintain lower temperatures that preserve flavor and nutrients while minimizing the risk of over-drying or burning the meat.
Efficiency and Speed: Oven vs Solar Dehydrator
Oven drying offers consistent temperature control and faster dehydration times, typically completing jerky in 4 to 8 hours. Solar dehydrators rely on sunlight and ambient temperatures, resulting in longer drying periods of 8 to 24 hours, making them less efficient during cloudy or low-sunlight conditions. The oven's precise heat management generally provides better speed and efficiency compared to the variable nature of solar dehydration.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Oven drying jerky typically consumes more electricity, averaging around 2 to 4 kWh per batch, depending on temperature and duration. Solar dehydrators use renewable energy, significantly reducing electrical consumption by harnessing sunlight, making them more cost-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Electric ovens maintain consistent heat but contribute to higher energy bills and carbon emissions. Solar dehydrators rely on solar radiation intensity, which can vary, but their energy consumption remains near zero during operation.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Oven drying jerky produces a consistent, evenly cooked texture with a slightly toasted flavor profile due to controlled heat. Solar dehydrators impart a unique smoky aroma and chewier texture, as the drying process is slower and influenced by environmental factors.
- Oven drying flavor - Offers a mild, roasted taste enhanced by steady oven temperatures.
- Solar dehydrator flavor - Develops a deeper, earthier flavor because of natural sun exposure and ambient air drying.
- Texture variations - Oven drying creates uniform chewiness, while solar drying can result in varying textures depending on humidity and temperature.
Choosing between oven drying and solar dehydrators depends on desired jerky flavor intensity and texture preference.
Food Safety Considerations
Oven drying jerky provides consistent temperatures, reaching and maintaining the critical 160degF (71degC) needed to safely kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli. This controlled environment reduces the risk of foodborne illness during the dehydration process.
Solar dehydrators rely on ambient sunlight and temperature, which can fluctuate and sometimes fail to reach safe thresholds for pathogen elimination. Uneven drying in solar dehydrators increases the chance of microbial growth, posing food safety risks. Proper airflow and monitoring are essential to ensure jerky dries thoroughly and safely when using solar methods.
Cost and Accessibility of Each Method
| Method | Cost | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|
| Oven Drying | Typically low to moderate cost, as most households already own an oven; no additional equipment purchases necessary. | Highly accessible year-round regardless of weather; requires only an electric or gas oven and basic kitchen tools. |
| Solar Dehydrator | Initial investment varies depending on design complexity; can be low-cost if homemade but may be higher for commercial models. | Dependent on sunny weather conditions and suitable outdoor space; less reliable in regions with limited sunlight or during winter months. |
Environmental Impact Analysis
Oven drying jerky consumes significant electricity, contributing to higher carbon emissions compared to solar dehydrators. Solar dehydrators utilize renewable energy, drastically reducing environmental impact and operational costs.
- Energy Source Difference - Oven drying relies on fossil-fuel-generated electricity while solar dehydrators harness free solar energy.
- Carbon Footprint - Oven drying produces more greenhouse gases due to electricity use, whereas solar dehydrators have minimal emissions.
- Sustainability - Solar dehydrators promote eco-friendly practices by minimizing reliance on non-renewable resources.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temperature Gradation
Oven drying allows precise low-temperature gradation control critical for evenly dehydrated jerky, maintaining safe temperatures typically between 130degF and 160degF to prevent bacterial growth. Solar dehydrators depend on ambient conditions, offering less consistent low-temperature control but energy-efficient drying using gradual heat exposure from 90degF to 140degF suitable for slow moisture removal.
Passive Solar Airflow
Passive solar airflow in solar dehydrators enhances moisture removal by utilizing natural convection currents, which reduces energy consumption compared to oven drying, where heat is mechanically generated and circulated by fans. Solar dehydrators with well-designed airflow systems maintain consistent drying temperatures around 130degF (54degC), critical for preserving jerky texture and preventing bacterial growth, unlike ovens that may cause uneven drying due to fluctuating heat distribution.
Thermal Mass Retention
Oven drying offers consistent thermal mass retention due to controlled heating elements that maintain steady temperatures, ensuring even moisture removal from jerky. Solar dehydrators rely on ambient solar energy, which fluctuates and results in variable thermal mass retention, potentially leading to uneven drying and inconsistent jerky texture.
Infrared Heat Influence
Oven drying jerky relies heavily on infrared heat, which penetrates meat fibers uniformly, ensuring rapid and consistent moisture evaporation for a tender yet adequately dried texture. In contrast, solar dehydrators use indirect solar heat with less infrared intensity, resulting in slower drying times and potentially uneven dehydration, which can affect jerky safety and flavor preservation.
Forced Convection Drying
Forced convection drying in oven drying for jerky ensures consistent temperature control and rapid moisture removal through circulating hot air, resulting in uniform texture and reduced spoilage risk. Solar dehydrators rely on natural air flow and solar heat, which may cause slower drying times and variable drying conditions, impacting the shelf-life and safety of the jerky.
UV Proteolysis Effect
Oven drying preserves jerky by using consistent heat without UV exposure, minimizing proteolysis and maintaining protein integrity, whereas solar dehydrators expose meat to UV rays that accelerate proteolytic breakdown, potentially impacting texture and nutrient retention. The UV proteolysis effect in solar dehydrators enhances natural enzymatic activity, which can lead to more tender jerky but may compromise shelf life and protein quality compared to oven drying.
Shelf Layer Uniformity
Oven drying for jerky typically offers more consistent heat distribution across shelf layers, ensuring uniform moisture removal and preventing uneven drying. Solar dehydrators often face challenges with fluctuating temperatures and airflow, which can result in inconsistent shelf layer uniformity and varied jerky texture.
Desiccation Rate Mapping
Oven drying offers precise temperature control and consistent heat distribution, resulting in a faster and more uniform desiccation rate for jerky compared to solar dehydrators, which depend on variable weather conditions and solar intensity. Desiccation rate mapping reveals that ovens maintain steady moisture removal throughout the drying process, while solar dehydrators exhibit fluctuations that can prolong drying time and affect texture consistency.
Renewable Heat Sourcing
Oven drying relies on electric or gas heating elements that consume non-renewable energy sources, resulting in higher carbon emissions compared to solar dehydrators. Solar dehydrators utilize renewable solar energy, significantly reducing environmental impact and operational costs while maintaining consistent heat for effective jerky dehydration.
Oven drying vs Solar dehydrator for making jerky Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com