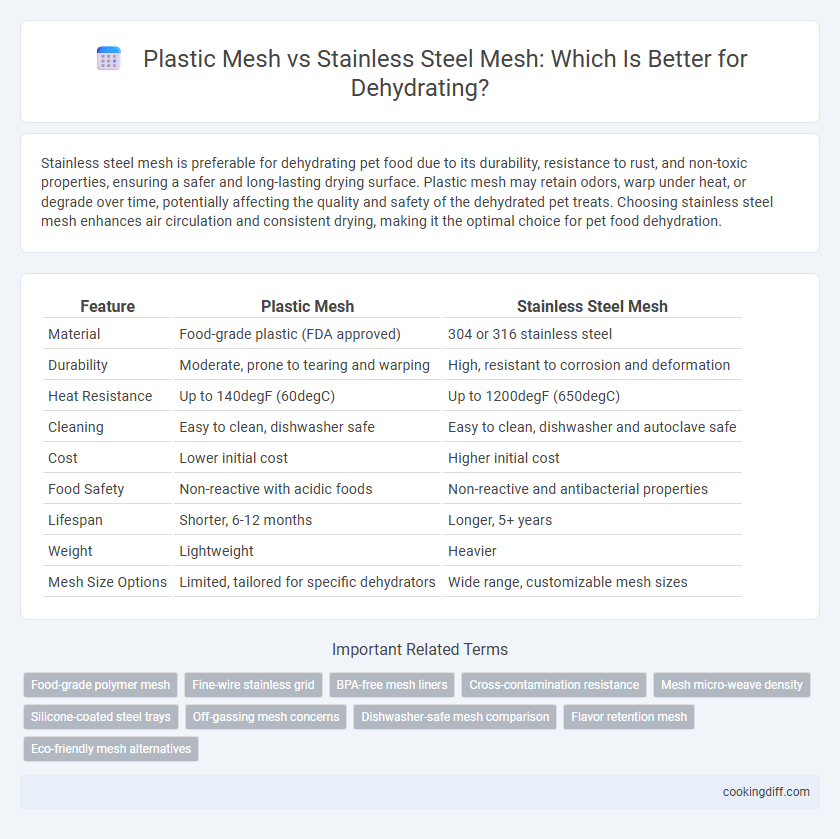
Stainless steel mesh is preferable for dehydrating pet food due to its durability, resistance to rust, and non-toxic properties, ensuring a safer and long-lasting drying surface. Plastic mesh may retain odors, warp under heat, or degrade over time, potentially affecting the quality and safety of the dehydrated pet treats. Choosing stainless steel mesh enhances air circulation and consistent drying, making it the optimal choice for pet food dehydration.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Mesh | Stainless Steel Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic (FDA approved) | 304 or 316 stainless steel |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to tearing and warping | High, resistant to corrosion and deformation |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 140degF (60degC) | Up to 1200degF (650degC) |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Easy to clean, dishwasher and autoclave safe |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Food Safety | Non-reactive with acidic foods | Non-reactive and antibacterial properties |
| Lifespan | Shorter, 6-12 months | Longer, 5+ years |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Mesh Size Options | Limited, tailored for specific dehydrators | Wide range, customizable mesh sizes |
Introduction to Dehydrating Mesh Materials
Dehydrating mesh materials play a critical role in the efficiency of drying processes, impacting airflow and food quality. Choosing between plastic mesh and stainless steel mesh depends on factors like durability, heat resistance, and ease of cleaning.
- Plastic mesh is lightweight and flexible - making it ideal for delicate foods but less durable under high temperatures.
- Stainless steel mesh offers superior heat resistance - ensuring longevity and maintaining shape during prolonged dehydrating cycles.
- Ease of cleaning varies between materials - stainless steel is generally easier to sanitize compared to plastic mesh, which can retain residues.
Plastic Mesh vs Stainless Steel Mesh: An Overview
Which mesh material offers better performance for dehydrating: plastic or stainless steel? Plastic mesh is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and ideal for drying delicate foods without imprint marks. Stainless steel mesh provides superior durability, high temperature resistance, and easier cleaning for long-term, heavy-duty dehydrating tasks.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Plastic mesh used in dehydrators offers resistance to corrosion and is lightweight but tends to wear out faster under high temperatures and frequent use. Stainless steel mesh provides superior durability, resisting rust, warping, and damage over extended periods of dehydrating various foods.
Stainless steel mesh withstands prolonged exposure to heat and moisture, ensuring longer lifespan and consistent performance during dehydrating processes. It is less prone to tearing or cracking compared to plastic mesh, making it ideal for heavy-duty or commercial dehydrating tasks. Choosing stainless steel mesh enhances overall equipment longevity and reduces replacement frequency.
Heat Resistance and Safety Factors
Stainless steel mesh offers superior heat resistance compared to plastic mesh, withstanding temperatures above 1200degF without warping or melting, making it ideal for high-temperature dehydrating processes. Plastic mesh typically degrades at temperatures above 200degF, posing risks of melting and releasing harmful chemicals into food, which raises safety concerns. The non-reactive and durable nature of stainless steel ensures food safety by preventing contamination and maintaining structural integrity during prolonged exposure to heat.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Plastic mesh trays are easier to clean due to their non-porous surface, preventing food particles from sticking and reducing residue buildup. Stainless steel mesh requires more thorough cleaning to remove trapped food debris and prevent corrosion, especially if not dried properly after washing.
- Plastic mesh resists staining - Its smooth surface allows quick rinsing and less frequent deep cleaning.
- Stainless steel mesh durability - Offers long-term use but demands regular maintenance to avoid rust and maintain hygiene.
- Cleaning tools compatibility - Plastic mesh can be cleaned with mild detergents and soft brushes, while stainless steel may require scrubbing pads to eliminate embedded particles.
Food Safety: Reactivity and Contamination Risks
Plastic mesh trays are non-reactive and resist corrosion, minimizing the risk of chemical contamination during the dehydrating process. This makes them ideal for acidic or high-moisture foods that could interact negatively with metal surfaces.
Stainless steel mesh offers excellent durability and is resistant to rust, but may pose slight risks of metal leaching if damaged or exposed to harsh cleaning agents. Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure food safety and prevent contamination from metal particles.
Mesh Size and Airflow Efficiency
| Material | Mesh Size | Airflow Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Mesh | Larger openings, typically 3-5 mm | Moderate airflow, can trap moisture causing uneven drying |
| Stainless Steel Mesh | Smaller, precise openings around 1-2 mm | Superior airflow, promotes even dehydration and faster drying times |
Impact on Food Flavor and Odor Transfer
Plastic mesh trays for dehydrators minimize odor and flavor transfer, preserving the true taste of fruits, vegetables, and herbs by preventing metallic contamination. Stainless steel mesh, although durable and easy to clean, can sometimes impart a slight metallic flavor or odor to sensitive foods during prolonged dehydration. Choosing plastic mesh is ideal for maintaining purity in dehydrated foods where flavor integrity is critical.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Plastic mesh dehydrator trays offer a lower initial cost compared to stainless steel mesh, making them budget-friendly for casual users. However, plastic tends to wear out faster and may require replacement more frequently, increasing long-term expenses.
Stainless steel mesh provides superior durability and resistance to high temperatures, often leading to better value for money over time despite a higher upfront price. Its longevity and ease of cleaning reduce maintenance costs, making it preferable for frequent or heavy-duty dehydrating tasks.
Related Important Terms
Food-grade polymer mesh
Food-grade polymer mesh offers superior flexibility and resistance to corrosion compared to stainless steel mesh, making it ideal for dehydrating delicate fruits and herbs without imprinting or damage. Its non-reactive, BPA-free composition ensures food safety and easier cleaning, while stainless steel mesh provides durability but can be heavier and prone to rust over time.
Fine-wire stainless grid
Fine-wire stainless steel mesh offers superior durability and heat resistance compared to plastic mesh, ensuring consistent airflow and optimal dehydration without warping or melting. Its tightly woven structure provides precise airflow control, enhancing moisture removal efficiency while maintaining food safety and longevity in dehydrator performance.
BPA-free mesh liners
Plastic mesh liners used for dehydrating are often BPA-free, offering a safe, non-toxic surface that prevents food from sticking while preserving flavor and nutrients. Stainless steel mesh liners, also BPA-free, provide a durable, rust-resistant option that ensures even airflow and easy cleaning, enhancing dehydration efficiency and food safety.
Cross-contamination resistance
Stainless steel mesh offers superior cross-contamination resistance compared to plastic mesh due to its non-porous surface and ability to withstand high-temperature cleaning processes, preventing bacterial buildup. In contrast, plastic mesh is more prone to harboring residues and microbial growth, increasing the risk of cross-contamination during food dehydration.
Mesh micro-weave density
Plastic mesh offers a lower micro-weave density compared to stainless steel mesh, allowing for increased airflow and faster dehydration times but potentially less durability and resistance to high temperatures. Stainless steel mesh provides a denser micro-weave structure, enhancing strength and longevity while maintaining efficient airflow for consistent dehydration results.
Silicone-coated steel trays
Silicone-coated stainless steel mesh trays provide superior durability and heat resistance compared to plastic mesh, ensuring even airflow and consistent drying during dehydration. These trays resist warping and cracking, making them ideal for long-term use in high-temperature drying environments.
Off-gassing mesh concerns
Stainless steel mesh for dehydrating is preferred over plastic mesh due to its resistance to off-gassing, which can impart unwanted odors or chemicals into dried foods. Plastic mesh may release volatile organic compounds when heated, compromising food safety and flavor during the dehydrating process.
Dishwasher-safe mesh comparison
Stainless steel mesh offers superior dishwasher safety due to its corrosion resistance and durability, maintaining structural integrity and hygiene after repeated washes. Plastic mesh, while lightweight and flexible, may degrade or retain odors over time when exposed to high dishwasher temperatures and harsh detergents.
Flavor retention mesh
Stainless steel mesh offers superior flavor retention during dehydrating by preventing the absorption of food odors and flavors, unlike plastic mesh which can sometimes retain residues and impact taste. The non-porous surface of stainless steel ensures minimal flavor transfer and easier cleaning, preserving the natural taste and aroma of dehydrated foods.
Plastic mesh vs Stainless steel mesh for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com