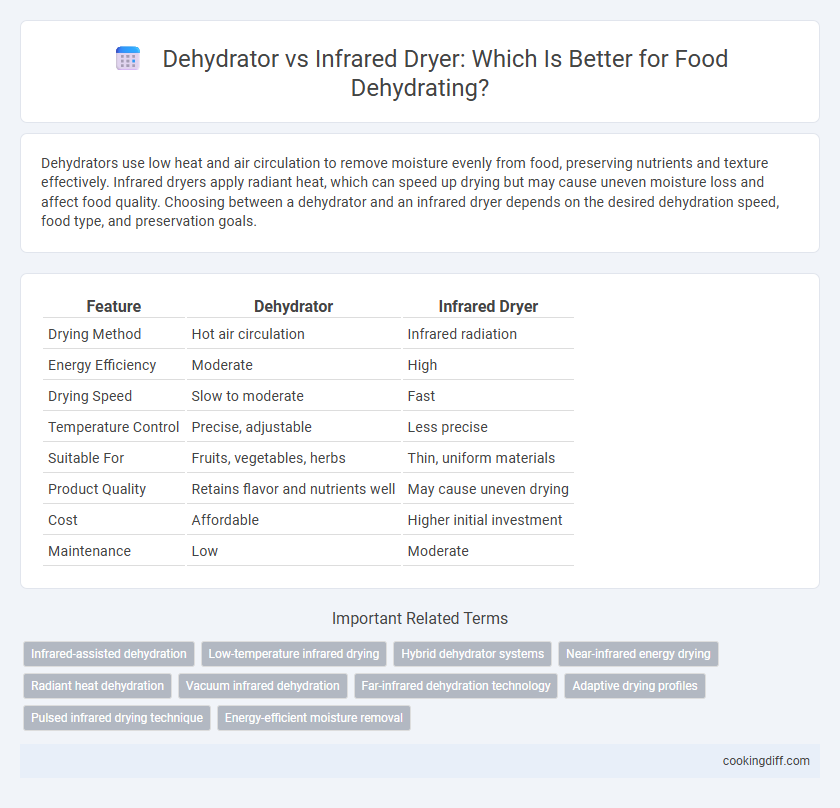
Dehydrators use low heat and air circulation to remove moisture evenly from food, preserving nutrients and texture effectively. Infrared dryers apply radiant heat, which can speed up drying but may cause uneven moisture loss and affect food quality. Choosing between a dehydrator and an infrared dryer depends on the desired dehydration speed, food type, and preservation goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dehydrator | Infrared Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Hot air circulation | Infrared radiation |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Drying Speed | Slow to moderate | Fast |
| Temperature Control | Precise, adjustable | Less precise |
| Suitable For | Fruits, vegetables, herbs | Thin, uniform materials |
| Product Quality | Retains flavor and nutrients well | May cause uneven drying |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
Overview: Dehydrator vs Infrared Dryer
Dehydrators use circulating hot air to remove moisture evenly from food, preserving nutrients and texture efficiently. Infrared dryers employ infrared radiation to penetrate the food, speeding up drying times and enhancing energy efficiency. Both methods offer distinct advantages depending on the type of food and dehydration goals, with dehydrators suited for uniform drying and infrared dryers excelling in rapid moisture removal.
How Traditional Dehydrators Work
Traditional dehydrators use heated air circulated by fans to remove moisture from food, relying on convection to evenly dry items. The temperature typically ranges between 95degF to 160degF, ideal for preserving nutrients while preventing spoilage.
Infrared dryers utilize light waves to penetrate food, heating and evaporating moisture more rapidly than conventional methods. This technology can reduce drying time but may not provide the same uniform results as traditional dehydrators.
Infrared Dryers: Technology and Process
Infrared dryers utilize infrared radiation to penetrate the material, enabling efficient moisture removal at lower temperatures compared to conventional dehydrators. This technology preserves nutritional quality and color by reducing thermal degradation during the drying process.
Infrared drying operates by emitting electromagnetic waves that cause water molecules to vibrate and evaporate quickly, resulting in reduced drying times and energy consumption. These dryers offer uniform heat distribution, minimizing surface drying and preventing case hardening. Infrared systems can be precisely controlled to optimize drying parameters for various food types, enhancing product quality and shelf life.
Drying Efficiency: Comparing Speed and Uniformity
Dehydrators typically offer more uniform drying by circulating warm air evenly around food items, ensuring consistent moisture removal. Infrared dryers provide faster drying speeds due to the direct heat penetration but may result in uneven drying if not carefully monitored.
- Dehydrator uniformity - Uses controlled airflow to maintain consistent temperature and moisture levels throughout the drying chamber.
- Infrared drying speed - Infrared radiation penetrates food surfaces quickly, accelerating the drying process compared to convection methods.
- Drying efficiency trade-off - Infrared dryers prioritize speed while dehydrators emphasize even moisture removal for improved texture and quality.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Preserves More?
Dehydrators use low heat and consistent airflow to slowly remove moisture, which helps preserve heat-sensitive nutrients better than infrared dryers. Infrared drying operates at higher temperatures and penetrates food more deeply, causing some nutrient degradation during the faster drying process.
- Lower Temperature Retention - Dehydrators maintain vitamins like C and folate more effectively due to gentler heat.
- Faster Drying Tradeoff - Infrared dryers reduce drying time but can diminish antioxidants and enzymes.
- Moisture Control - Dehydrators provide steady airflow that prevents nutrient loss linked with overheating.
For maximum nutrient preservation, dehydrators are generally preferred over infrared dryers in food dehydration.
Energy Consumption: Cost and Sustainability Analysis
Which method consumes less energy, a dehydrator or an infrared dryer, for efficient dehydrating? Dehydrators typically use moderate electricity and maintain consistent low heat, making them cost-effective for long drying sessions. Infrared dryers, while faster, often consume more power per minute but can reduce total energy use by shortening drying time, impacting overall sustainability differently.
Versatility: Foods You Can Dry with Each Method
Dehydrators excel in versatility by efficiently drying a wide range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, herbs, and meats, through controlled low heat and airflow. Infrared dryers offer focused drying primarily for thin or uniform items like fruits and vegetables, leveraging infrared radiation for faster moisture removal. While dehydrators accommodate diverse food types with adjustable settings, infrared dryers are best suited for quicker processing of specific food categories.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Dehydrators offer straightforward controls and removable trays that simplify loading and cleaning, making them user-friendly for routine dehydration tasks. Their quiet operation and uniform heat distribution reduce monitoring needs, ensuring consistent results with minimal effort.
Infrared dryers require more careful handling due to precise temperature calibration and delicate infrared elements that can be sensitive to damage during cleaning. Maintenance often involves specialized parts replacement, which may increase downtime compared to conventional dehydrators.
Flavor and Texture Differences in Dehydrated Foods
| Flavor Preservation | Dehydrators use low heat and consistent airflow to slowly remove moisture, preserving the natural sweetness and enhancing the concentrated flavors of foods. Infrared dryers apply radiant heat that can cause slight caramelization, intensifying flavor profiles but sometimes creating a cooked taste. |
| Texture Results | Dehydrators maintain a chewy and pliable texture, retaining structural integrity ideal for fruits and vegetables. Infrared drying often results in a crispier, more brittle texture due to rapid surface drying, which may affect the food's overall mouthfeel and rehydration properties. |
| Suitability for Food Types | Dehydrators are effective for delicate items like herbs and leafy greens, ensuring minimal flavor loss and preserved nutrients. Infrared dryers excel in processing thicker items like meats, producing jerky with enhanced flavor concentration but less uniform texture. |
Related Important Terms
Infrared-assisted dehydration
Infrared-assisted dehydration uses infrared radiation to accelerate moisture removal by directly heating the water molecules within the food, offering faster drying times and better nutrient retention compared to traditional dehydrators. This method enhances energy efficiency and preserves food quality by evenly distributing heat, reducing oxidation and enzymatic degradation during the dehydration process.
Low-temperature infrared drying
Low-temperature infrared drying in dehydrators effectively preserves nutrients and color by gently removing moisture while maintaining product integrity. Compared to traditional dehydrators, infrared dryers offer faster energy-efficient drying with uniform heat distribution, reducing oxidation and microbial growth during low-temperature processes.
Hybrid dehydrator systems
Hybrid dehydrator systems combine the precise temperature control of traditional dehydrators with the rapid, energy-efficient drying capabilities of infrared dryers, resulting in faster moisture removal and improved nutrient retention. These systems optimize dehydration by balancing airflow, heat distribution, and infrared radiation to enhance texture and flavor preservation in fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
Near-infrared energy drying
Near-infrared energy drying in infrared dryers penetrates food surfaces to rapidly remove moisture, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional dehydrators that rely on convective hot air circulation. This method enhances energy efficiency and reduces drying times, making near-infrared infrared dryers superior for consistent and high-quality dehydration outcomes.
Radiant heat dehydration
Radiant heat dehydration, as utilized in infrared dryers, provides efficient moisture removal by directly heating the water molecules within food, resulting in faster drying times compared to traditional dehydrators that rely on convective heat. Infrared drying preserves nutritional content and texture better due to its precise heat control and reduced exposure to prolonged high temperatures.
Vacuum infrared dehydration
Vacuum infrared dehydration combines low-pressure vacuum and infrared heat, enhancing moisture removal efficiency while preserving food quality better than traditional dehydrators or standalone infrared dryers. This technology reduces dehydration time and minimizes nutrient loss by operating at lower temperatures with uniform heat distribution, making it ideal for sensitive food products.
Far-infrared dehydration technology
Far-infrared dehydration technology in infrared dryers penetrates food items more deeply than traditional dehydrators, enhancing moisture removal efficiency and preserving nutritional content. Infrared dryers achieve faster drying times and maintain food quality by emitting wavelengths that target water molecules directly, making them superior for precise and energy-efficient dehydration processes.
Adaptive drying profiles
Dehydrators use adaptive drying profiles by adjusting temperature and airflow to preserve nutrient quality and texture in fruits and vegetables, while infrared dryers employ targeted infrared radiation to penetrate food layers, enhancing moisture removal efficiency with precise thermal control. Infrared drying profiles adapt based on food thickness and moisture content, offering faster dehydration times compared to traditional dehydrator settings.
Pulsed infrared drying technique
Pulsed infrared drying technique in dehydrators offers precise temperature control and energy efficiency by delivering intermittent bursts of infrared radiation, enhancing moisture removal while preserving nutrient content. Compared to continuous infrared dryers, pulsed systems reduce overheating and improve product quality in dehydrating processes.
Dehydrator vs Infrared dryer for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com