Air drying herbs preserves their natural aroma and flavor by slowly removing moisture through ambient airflow, making it a cost-effective and straightforward method. Vacuum drying accelerates moisture removal under reduced pressure, preventing oxidation and heat damage to delicate herbs, thus retaining more vibrant color and essential oils. Choosing between air drying and vacuum drying depends on the desired quality, processing time, and equipment availability for optimal herb preservation.
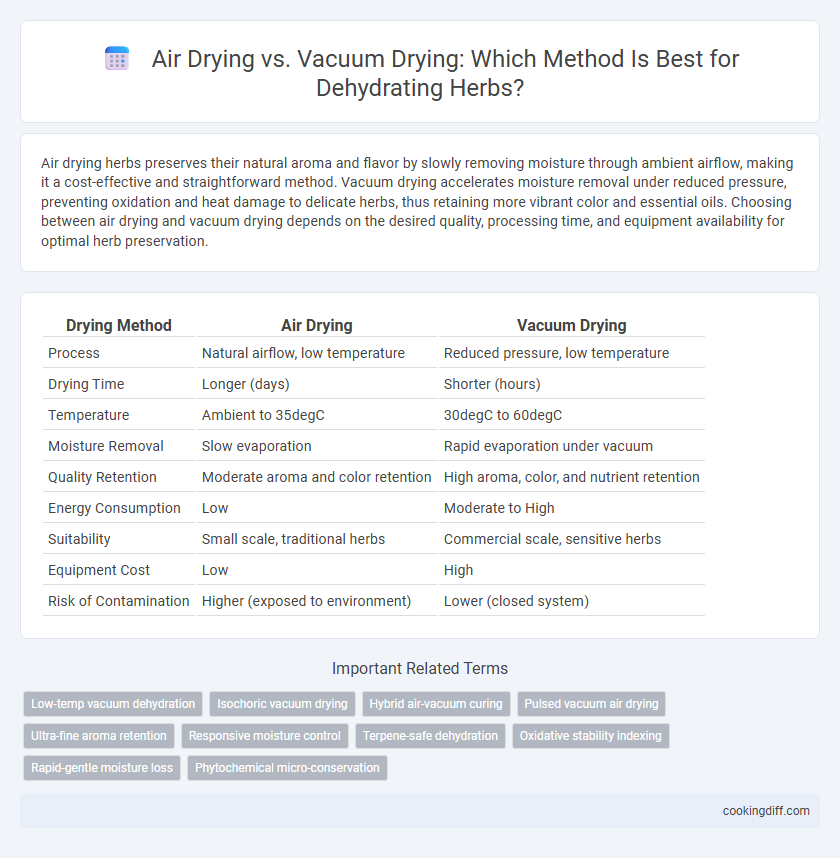
Table of Comparison
| Drying Method | Air Drying | Vacuum Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Natural airflow, low temperature | Reduced pressure, low temperature |
| Drying Time | Longer (days) | Shorter (hours) |
| Temperature | Ambient to 35degC | 30degC to 60degC |
| Moisture Removal | Slow evaporation | Rapid evaporation under vacuum |
| Quality Retention | Moderate aroma and color retention | High aroma, color, and nutrient retention |
| Energy Consumption | Low | Moderate to High |
| Suitability | Small scale, traditional herbs | Commercial scale, sensitive herbs |
| Equipment Cost | Low | High |
| Risk of Contamination | Higher (exposed to environment) | Lower (closed system) |
Introduction to Herb Drying Methods
Herb drying is essential for preserving flavor, aroma, and medicinal properties. Choosing the appropriate drying method impacts quality, shelf life, and nutrient retention.
- Air Drying - A traditional method that relies on natural airflow and ambient temperature to gradually remove moisture from herbs.
- Vacuum Drying - A controlled process using reduced pressure to lower boiling points, enabling faster drying at lower temperatures for enhanced preservation.
- Comparative Impact - Vacuum drying typically retains color and phytochemicals better than air drying but requires specialized equipment and higher energy consumption.
What is Air Drying?
Air drying is a traditional method of dehydrating herbs by hanging them in a well-ventilated, dry space at room temperature. This technique preserves the essential oils and natural flavors of herbs without the need for specialized equipment. Compared to vacuum drying, air drying is slower but cost-effective and simple for small-scale herb preservation.
What is Vacuum Drying?
| Vacuum drying | is a dehydration method that removes moisture from herbs under reduced pressure, lowering the boiling point of water to preserve delicate flavors and aromas. |
| Air drying | relies on ambient air circulation at room temperature, which can take several days and may lead to oxidation or loss of volatile oils in herbs. |
| Vacuum drying advantages | include faster drying times, enhanced retention of active compounds, and improved color and texture of dried herbs compared to traditional air drying techniques. |
Equipment Needed for Air Drying vs Vacuum Drying
Air drying herbs requires minimal equipment, typically just a well-ventilated space and breathable materials like mesh or paper bags for hanging the herbs. Vacuum drying demands specialized machinery such as vacuum chambers and heat sources to efficiently remove moisture without compromising herb quality.
- Air drying setup - Involves simple tools like string, hangers, and screens placed in a dry, airy environment to facilitate natural dehydration.
- Vacuum drying equipment - Requires a vacuum dryer machine that reduces pressure and temperature to speed up drying while preserving flavor and color.
- Cost and complexity - Air drying is low-cost and low-tech, whereas vacuum drying involves significant investment in technology and maintenance.
Time and Efficiency: Air Drying vs Vacuum Drying
Air drying herbs can take several days to weeks depending on humidity and airflow, making it a slower but energy-efficient method. Vacuum drying significantly reduces drying time to a few hours by lowering pressure and temperature, preserving herb quality and potency.
Air drying is cost-effective for small batches but less consistent in controlling moisture content, which can affect shelf life. Vacuum drying offers higher efficiency and uniform drying results, ideal for commercial herb processing with tight time constraints.
Impact on Herb Flavor and Aroma
How does air drying compare to vacuum drying in preserving the flavor and aroma of herbs? Air drying allows herbs to retain more natural oils, enhancing their flavor and aroma but takes longer and risks oxidation. Vacuum drying preserves delicate compounds by reducing exposure to oxygen and heat, resulting in a fresher, more vibrant herb profile.
Color and Nutrient Retention Comparison
Air drying preserves the natural color of herbs more effectively by allowing gentle moisture evaporation without heat damage, which helps maintain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments. However, this method takes longer, increasing the risk of nutrient degradation from prolonged exposure to oxygen and light.
Vacuum drying retains nutrients such as essential oils, flavonoids, and vitamins better due to reduced oxygen exposure and lower drying temperatures, minimizing oxidative stress. This method also preserves vibrant color by preventing pigment breakdown, making it ideal for high-quality herb preservation.
Cost Considerations for Home and Commercial Use
Air drying herbs is a low-cost method ideal for home use, requiring minimal equipment and energy, making it budget-friendly but slower and weather-dependent. Vacuum drying, favored in commercial settings, offers faster dehydration and better preservation of herbs' color and flavor but involves higher initial investment and operational costs due to specialized machinery. Cost considerations for choosing between these methods hinge on scale, drying speed, and quality requirements, with air drying suitable for small batches and vacuum drying optimized for high-volume production.
Best Herbs for Air Drying vs Vacuum Drying
Air drying is ideal for delicate herbs like basil, thyme, and oregano, preserving their flavor and aroma naturally. Vacuum drying suits robust herbs such as rosemary and sage, enhancing shelf life by reducing oxidation and moisture content quickly.
- Basil - Best air dried to maintain essential oils and vibrant flavor.
- Rosemary - Vacuum drying prolongs freshness by efficiently removing moisture.
- Oregano - Air drying preserves its pungent aroma and taste effectively.
Choosing the appropriate drying method depends on the herb's texture and oil content to maximize quality and longevity.
Related Important Terms
Low-temp vacuum dehydration
Low-temperature vacuum drying preserves delicate herbs by removing moisture at reduced pressure and temperatures below 40degC, maintaining volatile oils and active compounds more effectively than traditional air drying, which can degrade aroma and color due to prolonged exposure to ambient heat and oxygen. This method accelerates dehydration rates while enhancing product quality, making it ideal for high-value medicinal and culinary herbs.
Isochoric vacuum drying
Isochoric vacuum drying preserves the delicate volatile oils and active compounds in herbs more effectively than traditional air drying by maintaining constant volume and preventing cell collapse under vacuum pressure. This method accelerates moisture removal while retaining color, aroma, and nutritional value, making it superior for high-quality herb preservation.
Hybrid air-vacuum curing
Hybrid air-vacuum curing combines the gentle, natural evaporation process of air drying with the accelerated moisture removal of vacuum drying, preserving the essential oils and aromatic compounds in herbs more effectively than either method alone. This technique reduces drying time and minimizes thermal degradation, resulting in higher quality, flavor-rich, and shelf-stable herbs.
Pulsed vacuum air drying
Pulsed vacuum air drying enhances herb preservation by intermittently reducing pressure to accelerate moisture removal while maintaining air circulation, resulting in superior flavor and color retention compared to traditional air drying. This method combines the benefits of vacuum drying's low temperature efficiency with air drying's oxidative properties, optimizing drying time and quality for sensitive herbal compounds.
Ultra-fine aroma retention
Air drying preserves ultra-fine aromas in herbs by allowing natural moisture evaporation at ambient temperatures, minimizing volatile compound loss. Vacuum drying enhances aroma retention through low-pressure, low-temperature conditions that prevent oxidation and preserve essential oils more effectively than conventional methods.
Responsive moisture control
Air drying offers a natural, low-energy approach but often results in inconsistent moisture removal and longer drying times for herbs. Vacuum drying provides precise, responsive moisture control by lowering pressure and temperature, preserving herb quality and essential oils more effectively.
Terpene-safe dehydration
Air drying preserves herbal terpenes by using low temperature and gentle airflow, minimizing volatile compound loss through slow moisture evaporation. Vacuum drying enhances terpene retention by reducing oxygen exposure and evaporation temperature, ensuring faster dehydration while maintaining aroma and bioactive properties.
Oxidative stability indexing
Air drying of herbs often results in lower oxidative stability indexing due to prolonged exposure to oxygen and ambient air, which accelerates lipid oxidation and nutrient degradation. Vacuum drying limits oxygen exposure by creating a low-pressure environment, significantly preserving antioxidant compounds and enhancing the oxidative stability index in herbs.
Rapid-gentle moisture loss
Air drying herbs allows for a natural, slow moisture loss that preserves delicate flavors but can take several days, while vacuum drying accelerates moisture removal through reduced pressure and low temperatures, minimizing thermal damage and preserving essential oils for rapid-gentle dehydration. Vacuum drying typically results in higher quality herbs with retained color, aroma, and bioactive compounds compared to traditional air drying methods.
Air drying vs Vacuum drying for herbs. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com