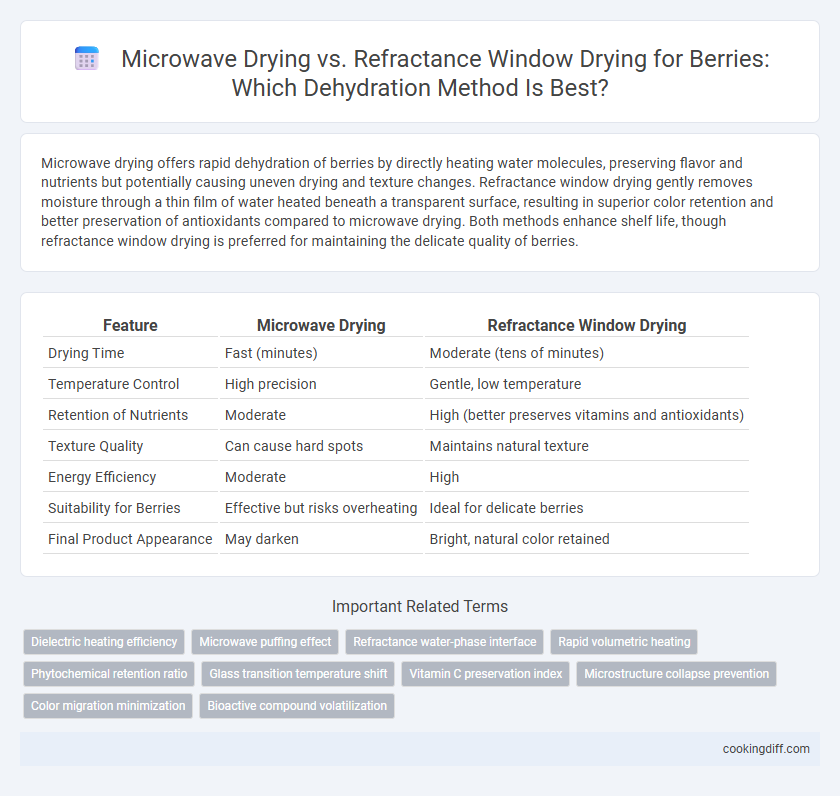
Microwave drying offers rapid dehydration of berries by directly heating water molecules, preserving flavor and nutrients but potentially causing uneven drying and texture changes. Refractance window drying gently removes moisture through a thin film of water heated beneath a transparent surface, resulting in superior color retention and better preservation of antioxidants compared to microwave drying. Both methods enhance shelf life, though refractance window drying is preferred for maintaining the delicate quality of berries.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microwave Drying | Refractance Window Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes) | Moderate (tens of minutes) |
| Temperature Control | High precision | Gentle, low temperature |
| Retention of Nutrients | Moderate | High (better preserves vitamins and antioxidants) |
| Texture Quality | Can cause hard spots | Maintains natural texture |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Suitability for Berries | Effective but risks overheating | Ideal for delicate berries |
| Final Product Appearance | May darken | Bright, natural color retained |
Introduction to Dehydration Methods for Berries
Microwave drying uses electromagnetic waves to rapidly remove moisture from berries, preserving their color and nutrients effectively. Refractance window drying employs a thin film of water and transparent conveyor belts to gently dehydrate berries while maintaining texture and flavor. Both methods offer efficient alternatives to traditional drying, with microwave drying excelling in speed and refractance window drying emphasizing quality retention.
Overview of Microwave Drying Technology
How does microwave drying technology enhance the dehydration process for berries? Microwave drying uses electromagnetic waves to generate heat internally, resulting in faster moisture removal compared to conventional methods. This technique maintains better nutrient retention and color quality in berries by reducing drying time and minimizing thermal degradation.
Fundamentals of Refractance Window Drying
Refractance Window drying utilizes infrared energy transmitted through a transparent plastic film to gently and rapidly dry berries while preserving heat-sensitive nutrients and vibrant colors. The technique involves placing the berry slurry on a thin, flexible Mylar sheet that floats on hot water, allowing efficient moisture removal with minimal thermal degradation.
This method achieves faster drying rates compared to traditional Microwave drying, reducing energy consumption and preventing case hardening commonly associated with Microwave dehydration. The precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution contribute to higher-quality berry powders with improved retention of bioactive compounds.
Efficiency of Microwave Drying for Berries
Microwave drying offers rapid moisture removal from berries, significantly reducing drying time compared to traditional methods. This technique enhances energy efficiency by directly heating water molecules within berries, leading to uniform drying and preservation of nutrients. Efficiency metrics show microwave drying can decrease processing times by up to 70%, making it highly suitable for commercial berry dehydration.
Speed and Uniformity of Refractance Window Drying
Refractance window drying offers faster dehydration speeds compared to microwave drying, enabling efficient processing of berries while preserving quality. This method ensures more uniform drying by evenly distributing heat across the berry surface, reducing hotspots and inconsistencies common in microwave drying.
- Speed - Refractance window drying can reduce drying time by up to 30% compared to traditional microwave methods.
- Uniformity - It delivers consistent moisture removal across the entire berry, minimizing partial drying.
- Quality retention - Uniform heat application helps maintain berry color, flavor, and nutrient content more effectively.
Refractance window drying is a superior technique for rapid and uniform berry dehydration in commercial applications.
Nutrient Retention: Microwave vs Refractance Window Drying
Microwave drying of berries preserves higher levels of vitamin C and anthocyanins due to its rapid heating process, which minimizes nutrient degradation. In contrast, refractance window drying operates at lower temperatures but exposes berries to prolonged drying times, potentially reducing some heat-sensitive nutrients.
Studies show microwave drying achieves nutrient retention rates up to 85%, while refractance window drying retains approximately 75% of key antioxidants. Both methods offer advantages in nutrient preservation, but microwave drying is generally more efficient for maintaining berry phytochemicals.
Impact on Texture and Color in Dried Berries
| Drying Method | Impact on Texture | Impact on Color |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Drying | Preserves a firmer texture due to rapid moisture removal, reducing cell damage in berries. | Maintains vibrant natural color by minimizing thermal degradation and enzymatic browning. |
| Refractance Window Drying | Produces a softer texture with slight cellular collapse, resulting in a more pliable dried berry. | Retains color effectively by using low-temperature drying, limiting pigment oxidation and color loss. |
Energy Consumption and Cost Comparison
Microwave drying of berries generally consumes less energy compared to refractance window drying, resulting in lower operational costs and faster processing times. Cost analysis reveals that despite higher initial equipment investment, microwave drying offers better long-term savings due to reduced energy use and maintenance expenses.
- Energy Consumption - Microwave drying uses approximately 30-50% less energy than refractance window drying for similar berry dehydration.
- Operational Cost - Lower electricity usage in microwave drying translates into significant annual cost savings for large-scale berry processing.
- Equipment Investment - Though microwave drying equipment may have higher upfront costs, its efficiency and durability create more cost-effective outcomes over time.
Scalability and Commercial Applications
Microwave drying offers rapid dehydration with potential for high-volume processing, making it suitable for scalable berry drying operations but may face challenges in uniformity and energy efficiency. Refractance window drying provides gentle heat and preserves berry quality, with proven scalability in commercial settings, especially for products requiring delicate handling.
- Microwave Drying Scalability - Microwave systems can be scaled up for industrial berry drying, enabling quick throughput but requiring advanced control for uniform moisture removal.
- Refractance Window Commercial Use - Widely applied in commercial berry drying, refractance window drying supports consistent product quality at scale with moderate energy consumption.
- Comparative Application - Microwave drying suits facilities prioritizing speed and high capacity, while refractance window drying is preferred where product preservation and gentle processing are critical.
Related Important Terms
Dielectric heating efficiency
Microwave drying utilizes dielectric heating to rapidly and uniformly remove moisture from berries by generating heat within the product's water molecules, resulting in higher energy efficiency and shorter drying times. Refractance window drying, while effective in preserving quality, relies on conduction and convection with less direct interaction with water molecules, leading to comparatively lower dielectric heating efficiency.
Microwave puffing effect
Microwave drying induces a rapid puffing effect in berries by generating internal steam pressure, resulting in a porous texture that enhances rehydration and preserves flavor compounds more effectively than refractance window drying. Refractance window drying offers gentle heat transfer and better nutrient retention but lacks the intense puffing action that significantly improves the sensory qualities of dehydrated berries in microwave drying.
Refractance water-phase interface
Refractance window drying preserves berry quality by gently removing moisture through a water-phase interface that minimizes thermal degradation and nutrient loss compared to microwave drying. This process maintains higher antioxidant levels and vibrant color, enhancing the sensory and nutritional profile of dried berries.
Rapid volumetric heating
Microwave drying enables rapid volumetric heating by directly exciting water molecules within berries, resulting in faster moisture removal and better retention of nutrients. Refractance window drying uses conductive and convective heat transfer through a thin film, which is less efficient in rapid volumetric heating compared to microwave methods.
Phytochemical retention ratio
Microwave drying preserves the phytochemical retention ratio in berries more effectively due to its rapid moisture removal, minimizing degradation of antioxidants and vitamin C. Refractance window drying also maintains high phytochemical levels by using low-temperature conduction, but it generally results in slightly lower retention compared to microwave drying.
Glass transition temperature shift
Microwave drying causes a rapid temperature increase that can lead to a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) shift in berries, potentially affecting texture and shelf life. Refractance window drying offers a gentler thermal profile, resulting in a smaller Tg shift that better preserves the structural integrity and nutritional quality of the dried berries.
Vitamin C preservation index
Microwave drying generally results in a higher Vitamin C preservation index for berries due to shorter drying times and lower exposure to heat, minimizing nutrient degradation. Refractance window drying, while gentle on texture, often leads to moderate Vitamin C loss because of longer drying durations and indirect heat exposure.
Microstructure collapse prevention
Microwave drying preserves berry microstructure more effectively by rapidly removing moisture with minimal thermal degradation, reducing cell wall collapse compared to slower methods. Refractance window drying also maintains structural integrity by using gentle, uniform heat transfer through a water-heated film, preventing excessive shrinkage and nutrient loss.
Color migration minimization
Microwave drying preserves berry color by rapidly removing moisture, reducing enzymatic browning and pigment degradation through shorter exposure times and uniform heating. Refractance window drying minimizes color migration by gently drying berries on a transparent film with low thermal impact, maintaining vibrant pigments and preventing the diffusion of color compounds.
Microwave drying vs Refractance window drying for berries. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com