Oven drying vegetables can be time-consuming and may lead to uneven dehydration, often affecting texture and nutrient retention. Infrared food dehydrators offer precise temperature control and faster drying times, preserving more nutrients and maintaining better flavor consistency. Choosing an infrared dehydrator enhances efficiency and results in higher quality dried vegetables compared to conventional oven drying.
Table of Comparison
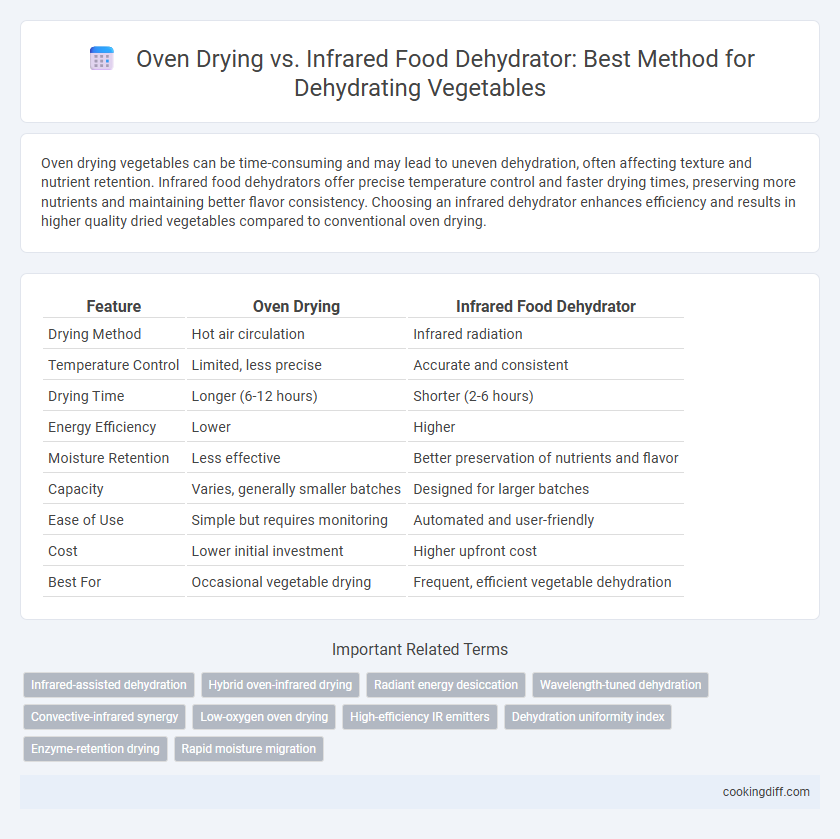
| Feature | Oven Drying | Infrared Food Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Hot air circulation | Infrared radiation |
| Temperature Control | Limited, less precise | Accurate and consistent |
| Drying Time | Longer (6-12 hours) | Shorter (2-6 hours) |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Moisture Retention | Less effective | Better preservation of nutrients and flavor |
| Capacity | Varies, generally smaller batches | Designed for larger batches |
| Ease of Use | Simple but requires monitoring | Automated and user-friendly |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost |
| Best For | Occasional vegetable drying | Frequent, efficient vegetable dehydration |
Introduction to Vegetable Dehydration Methods
Oven drying and infrared food dehydrators are popular methods for vegetable dehydration, each offering distinct advantages. Oven drying uses consistent heat to remove moisture, while infrared dehydrators employ radiation to achieve faster drying times.
Both methods help preserve nutrients and extend shelf life by reducing water content in vegetables. Choosing the best technique depends on factors like drying speed, energy efficiency, and the desired texture of the final product.
Overview of Oven Drying for Vegetables
Oven drying is a traditional method used for dehydrating vegetables by applying controlled heat over a period of time, typically ranging from several hours to a full day. This technique relies on consistent airflow and temperature settings between 120degF to 160degF to effectively remove moisture while preserving nutrients.
- Cost-effective - Uses standard kitchen ovens, eliminating the need for specialized equipment.
- Time-intensive - Drying times are longer compared to infrared dehydrators and may vary depending on vegetable type.
- Temperature control - Requires manual monitoring to prevent overheating or uneven drying of vegetables.
Oven drying offers an accessible option for vegetable dehydration but demands careful attention to temperature and drying duration to ensure quality results.
How Infrared Food Dehydrators Work
Infrared food dehydrators use infrared radiation to penetrate deeply into vegetable tissues, heating water molecules directly and facilitating efficient moisture removal. This method preserves nutrient content and color better compared to traditional oven drying, which relies on convective heat transfer from hot air.
The infrared waves target water bonds within the vegetable, enabling faster dehydration at lower temperatures, thus maintaining texture and flavor. Unlike oven drying, which may cause uneven heating and nutrient loss, infrared dehydrators offer precise temperature control and energy efficiency for optimal vegetable preservation.
Energy Efficiency: Oven vs. Infrared Dehydration
Infrared food dehydrators consume significantly less energy than conventional ovens when drying vegetables due to targeted heat application. Oven drying typically requires higher temperatures and longer durations, resulting in greater energy use and cost.
- Infrared Dehydrators Use Less Energy - Infrared technology directly heats vegetable moisture, improving dehydration speed and reducing power consumption.
- Ovens Consume More Electricity - Electric ovens maintain elevated chamber temperatures over extended periods, increasing energy expenditure.
- Energy Cost Efficiency - Using an infrared dehydrator can decrease energy costs by up to 50% compared to traditional oven drying methods.
Drying Time Comparison: Oven and Infrared Methods
Oven drying typically requires 6 to 12 hours to dehydrate vegetables depending on temperature and moisture content, while infrared food dehydrators can reduce drying time to 2 to 4 hours due to more efficient heat transfer. The infrared method preserves nutrients better by using lower temperatures and shorter exposure compared to conventional ovens.
- Oven Drying Duration - Usually takes between 6 and 12 hours at 140degF to 160degF to effectively remove moisture from vegetables.
- Infrared Drying Speed - Infrared dehydrators use radiant heat that penetrates vegetables quickly, cutting drying time to as little as 2 to 4 hours.
- Nutrient Retention - Lower temperatures and faster drying in infrared methods help maintain vitamins and antioxidants better than longer oven drying processes.
Nutritional Retention in Oven vs. Infrared Dehydration
Oven drying vegetables typically exposes them to prolonged heat, which can degrade heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and certain antioxidants. Infrared food dehydrators use shorter wavelengths to penetrate food more efficiently, preserving a higher concentration of these nutrients during dehydration.
Studies indicate that infrared dehydration retains up to 20% more vitamins compared to conventional oven drying due to reduced drying times and lower overall temperatures. The precise control of heat in infrared dehydrators minimizes nutrient loss, maintaining the vegetables' natural color and flavor better. This method is particularly effective for leafy greens and other delicate vegetables prone to nutrient degradation.
Texture and Flavor Outcomes for Dehydrated Vegetables
How do oven drying and infrared food dehydrators compare in texture and flavor outcomes for dehydrated vegetables? Oven drying typically results in a firmer texture but may cause slight flavor loss due to uneven heat distribution. Infrared food dehydrators preserve more natural flavors and produce a more uniform, tender texture by evenly penetrating moisture during drying.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operating Expenses
| Method | Initial Investment | Operating Expenses |
|---|---|---|
| Oven Drying | Low to Moderate, typical home oven suffices | Higher energy consumption, increased electricity bills |
| Infrared Food Dehydrator | Moderate to High, specialized equipment required | Lower energy usage, efficient drying reduces utility costs |
Suitability for Different Vegetable Types
Oven drying is suitable for hardy vegetables like carrots and potatoes, which require longer drying times at consistent temperatures to achieve even dehydration. Infrared food dehydrators excel with delicate vegetables such as tomatoes and bell peppers, as the infrared rays penetrate efficiently, preserving color and nutrients while speeding up the drying process. Selecting the optimal method depends on the vegetable's moisture content and texture, ensuring quality retention and flavor enhancement.
Related Important Terms
Infrared-assisted dehydration
Infrared-assisted dehydration uses infrared radiation to penetrate vegetable tissues, accelerating moisture removal while preserving nutritional quality and color more effectively than conventional oven drying. This method enhances energy efficiency and reduces drying time by targeting water molecules directly, making it ideal for retaining delicate vitamins and enzymes in dehydrated vegetables.
Hybrid oven-infrared drying
Hybrid oven-infrared drying combines conventional oven heat with infrared radiation to enhance moisture removal efficiency and preserve nutrient content in vegetables better than standard oven drying or standalone infrared dehydrators. This method reduces drying time by up to 40% while maintaining texture and color, making it an optimal choice for high-quality vegetable dehydration.
Radiant energy desiccation
Oven drying uses convective heat to remove moisture from vegetables, often resulting in uneven dehydration and longer drying times; infrared food dehydrators utilize radiant energy to penetrate food surfaces, enabling faster, more efficient moisture removal while preserving nutrients and texture. Radiant energy desiccation in infrared dehydrators targets water molecules directly, offering precise temperature control and reduced oxidation compared to traditional oven drying methods.
Wavelength-tuned dehydration
Wavelength-tuned dehydration using an infrared food dehydrator targets specific absorption peaks in vegetable tissues, enhancing moisture removal efficiency and nutrient retention compared to conventional oven drying. Infrared dehydrators operate typically in the 0.75 to 2.5 micrometer wavelength range, optimizing energy transfer and reducing drying time while preserving color and texture integrity.
Convective-infrared synergy
Oven drying primarily relies on convective heat transfer, whereas infrared food dehydrators combine convective airflow with infrared radiation, creating a convective-infrared synergy that accelerates moisture removal from vegetables while preserving nutrients and color. This synergy enhances drying efficiency by penetrating vegetable tissues with infrared rays and simultaneously carrying away evaporated moisture through convection, resulting in faster dehydration and improved product quality.
Low-oxygen oven drying
Low-oxygen oven drying preserves nutrients and color in vegetables more efficiently than traditional oven drying by minimizing oxidation and enzymatic browning. Infrared food dehydrators provide rapid surface moisture removal but lack the oxygen control that prevents nutrient degradation during oven drying.
High-efficiency IR emitters
High-efficiency infrared (IR) emitters in food dehydrators deliver rapid, uniform drying of vegetables by directly heating moisture molecules, outperforming conventional oven drying which relies on slower ambient air heat transfer. IR technology enhances nutrient retention and energy efficiency, reducing dehydration time and preserving texture better than standard oven methods.
Dehydration uniformity index
Oven drying usually exhibits a lower dehydration uniformity index due to uneven heat distribution and hotspots that cause inconsistent drying of vegetables. Infrared food dehydrators enhance dehydration uniformity by delivering focused, penetrating heat, resulting in more consistent moisture removal and improved preservation of vegetable texture and nutrient content.
Enzyme-retention drying
Oven drying of vegetables often leads to significant enzyme degradation due to uneven heat distribution and prolonged exposure to high temperatures, whereas infrared food dehydrators use targeted radiant heat that preserves enzymatic activity by drying at lower, controlled temperatures. This enzyme-retention drying method enhances nutrient preservation and maintains the vegetable's natural flavor and texture more effectively than conventional oven drying.
Oven Drying vs Infrared Food Dehydrator for Vegetables Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com