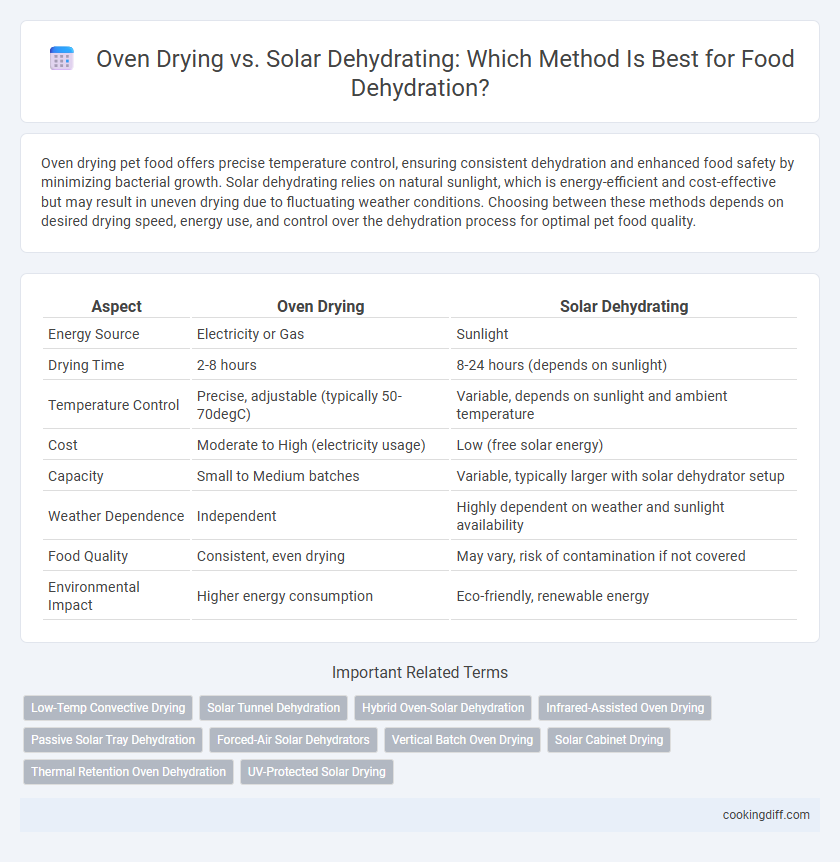
Oven drying pet food offers precise temperature control, ensuring consistent dehydration and enhanced food safety by minimizing bacterial growth. Solar dehydrating relies on natural sunlight, which is energy-efficient and cost-effective but may result in uneven drying due to fluctuating weather conditions. Choosing between these methods depends on desired drying speed, energy use, and control over the dehydration process for optimal pet food quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Oven Drying | Solar Dehydrating |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity or Gas | Sunlight |
| Drying Time | 2-8 hours | 8-24 hours (depends on sunlight) |
| Temperature Control | Precise, adjustable (typically 50-70degC) | Variable, depends on sunlight and ambient temperature |
| Cost | Moderate to High (electricity usage) | Low (free solar energy) |
| Capacity | Small to Medium batches | Variable, typically larger with solar dehydrator setup |
| Weather Dependence | Independent | Highly dependent on weather and sunlight availability |
| Food Quality | Consistent, even drying | May vary, risk of contamination if not covered |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy consumption | Eco-friendly, renewable energy |
Introduction to Food Dehydration Methods
Food dehydration is a preservation technique that removes moisture to inhibit microbial growth. Oven drying and solar dehydrating are two common methods used to achieve this, each with distinct advantages and limitations.
- Oven Drying - Utilizes controlled heat in an enclosed environment to quickly and evenly remove moisture from food.
- Solar Dehydrating - Relies on natural sunlight and airflow, offering an energy-efficient, eco-friendly method suitable for warm climates.
- Comparison - Oven drying provides consistency and speed, whereas solar dehydration is cost-effective but dependent on weather conditions.
Overview of Oven Drying for Cooking
Oven drying for cooking involves using controlled heat within a conventional kitchen oven to remove moisture from food, preserving flavor and extending shelf life. This method provides consistent temperature regulation, typically ranging between 120degF to 160degF, ensuring even dehydration of fruits, vegetables, and meats. Oven drying is preferred for its reliability and faster processing time compared to solar dehydrating, which depends on weather conditions and sunlight availability.
Understanding Solar Dehydrating Techniques
| Solar dehydrating leverages natural sunlight and ambient air to remove moisture from food, making it an energy-efficient and eco-friendly preservation method. |
| Unlike oven drying, which relies on consistent, controlled heat typically around 130degF to 150degF, solar drying depends on weather conditions and requires a well-ventilated, shaded solar dryer to prevent direct UV damage. |
| Effective solar dehydrating techniques include using solar dryers with transparent covers to trap heat and facilitate airflow, ensuring uniform drying while maintaining nutritional value and flavor integrity. |
Energy Efficiency: Oven vs. Solar Dehydration
Oven drying consumes significant electrical energy, often ranging from 500 to 1500 watts per hour, leading to higher operational costs. Solar dehydrating harnesses renewable energy from the sun, drastically reducing energy expenses and minimizing carbon footprint. Energy efficiency of solar methods depends on weather conditions, while ovens provide consistent drying regardless of climate.
Flavor and Texture Differences in Dehydrated Foods
Oven drying typically produces a more uniform texture due to controlled temperature settings, which helps retain intense flavors by reducing moisture evenly. In contrast, solar dehydrating exposes food to fluctuating temperatures and sunlight, often resulting in a chewier texture and slightly altered taste from prolonged UV exposure.
Flavor profiles in oven-dried foods remain closer to the original ingredients because of consistent heat, enhancing natural sweetness and aroma without risking spoilage. Solar drying can introduce subtle smoky or earthy undertones due to open-air exposure and slower moisture removal. Texture differences grow more pronounced as oven drying yields crispier results while solar methods tend to create softer, sometimes unevenly dried products, influencing culinary uses and storage durability.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Oven drying requires a conventional oven capable of maintaining low temperatures for prolonged periods, while solar dehydrating relies on specially designed solar dryers or simple drying racks exposed to sunlight. The setup for oven drying is straightforward and convenient indoors, whereas solar dehydrating demands optimal weather conditions and well-ventilated outdoor space.
- Oven Equipment - A standard kitchen oven with temperature control between 120degF and 160degF is essential for consistent drying.
- Solar Dryer Setup - Solar dehydrators often include ventilated enclosures with transparent covers to maximize heat absorption and airflow.
- Space Requirements - Oven drying utilizes indoor kitchen space, whereas solar dehydrating needs adequate sun exposure and protection from pests outdoors.
Choosing between oven drying and solar dehydrating depends on available equipment, climate, and drying volume requirements.
Cost Comparison: Oven Drying vs. Solar Dehydrating
Oven drying requires a consistent electricity supply, leading to higher operational costs compared to solar dehydrating, which uses free solar energy. Initial investment for ovens can be significant, while solar dehydrators often require lower upfront costs, especially in sunny regions.
Energy consumption in oven drying can increase utility bills, making it less cost-effective for long-term use in food preservation. Solar dehydrating minimizes energy expenses but may need extended drying times depending on weather conditions, influencing overall efficiency.
Safety and Food Preservation Considerations
Oven drying provides precise temperature control, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and ensuring consistent food safety during dehydration. This method minimizes contamination by operating in a closed environment, while preserving nutrients and flavor effectively.
Solar dehydrating relies on natural sunlight and ambient temperatures, which can vary greatly, increasing the risk of uneven drying and potential microbial contamination. Proper ventilation and protection from insects and dust are critical for maintaining food quality and safety in solar dehydration.
Environmental Impact of Both Drying Methods
Oven drying consumes significant electrical energy, contributing to higher carbon emissions compared to solar dehydrating, which utilizes renewable solar power. Solar dehydrating reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowering environmental impact but is dependent on weather conditions and slower drying times.
- Oven Drying Energy Consumption - Electric ovens require substantial electricity, increasing the carbon footprint during food dehydration.
- Solar Dehydrating Renewable Use - Solar dehydrators harness natural sunlight, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel use.
- Environmental Trade-offs - Solar drying offers eco-friendly benefits but may result in longer processing times and inconsistent drying due to weather variability.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Convective Drying
Low-temp convective drying in oven drying offers precise temperature control and consistent airflow, enabling uniform moisture removal essential for food preservation and nutrient retention. Solar dehydrating relies on variable sunlight and ambient temperature, resulting in slower dehydration rates and less predictable drying conditions, which can lead to inconsistent product quality.
Solar Tunnel Dehydration
Solar Tunnel Dehydration offers energy-efficient, consistent drying by harnessing controlled solar heat within a tunnel structure, significantly reducing drying time compared to traditional sun drying. Unlike oven drying, it preserves nutrient content and flavor through low-temperature processing while ensuring large-scale, hygienic food dehydration with minimal carbon footprint.
Hybrid Oven-Solar Dehydration
Hybrid oven-solar dehydration combines the controlled heat of an oven with the eco-friendly energy of solar drying to maximize efficiency and preserve nutritional content in cooking. This method reduces drying time by up to 40% compared to solar or oven drying alone, ensuring consistent moisture removal while minimizing energy consumption.
Infrared-Assisted Oven Drying
Infrared-assisted oven drying accelerates moisture removal by using infrared radiation to penetrate food, ensuring faster and more uniform dehydration compared to traditional oven drying methods. This technique enhances nutrient retention and reduces drying time, contrasting with solar dehydrating methods that rely on natural sunlight and are often slower and less consistent.
Passive Solar Tray Dehydration
Passive solar tray dehydration harnesses natural sunlight and ambient heat to gently remove moisture from foods, preserving nutrients and flavors more efficiently than conventional oven drying methods. This eco-friendly technique reduces energy consumption by utilizing passive solar energy, making it a sustainable alternative to electric oven drying while maintaining optimal dehydration conditions.
Forced-Air Solar Dehydrators
Forced-air solar dehydrators utilize solar energy combined with an integrated fan system to enhance airflow and reduce drying times compared to traditional oven drying. This method preserves nutrient retention and flavor in foods by maintaining lower, more consistent temperatures, making it a sustainable and energy-efficient alternative for food dehydration.
Vertical Batch Oven Drying
Vertical batch oven drying offers precise temperature control and faster dehydration times compared to solar dehydrating, making it ideal for consistent moisture removal in cooking applications. This method ensures uniform heat distribution and energy efficiency, reducing spoilage risks associated with variable solar conditions.
Solar Cabinet Drying
Solar cabinet drying uses solar energy to efficiently remove moisture from food, preserving nutrients and flavor while reducing energy costs compared to traditional oven drying. Its design maximizes air circulation and exposure to sunlight, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable method for dehydrating fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
Thermal Retention Oven Dehydration
Oven drying offers superior thermal retention compared to solar dehydrating, maintaining consistent high temperatures around 120-160degF (49-71degC) essential for efficient moisture removal in cooking. This controlled heat environment reduces drying time and inhibits microbial growth, enhancing food safety and quality.
Oven drying vs Solar dehydrating for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com