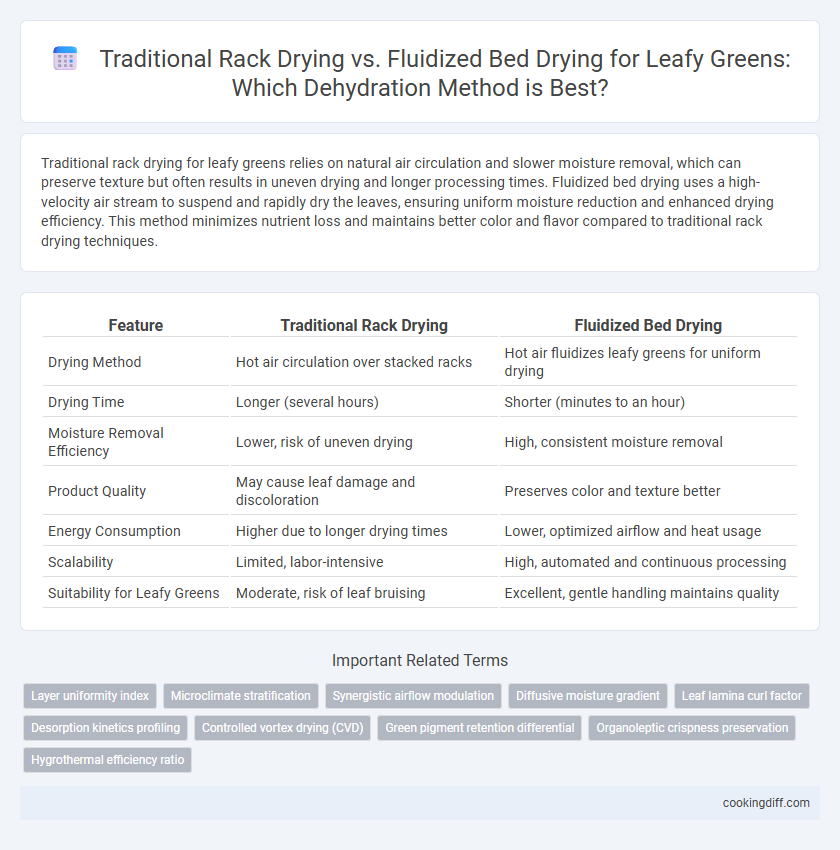
Traditional rack drying for leafy greens relies on natural air circulation and slower moisture removal, which can preserve texture but often results in uneven drying and longer processing times. Fluidized bed drying uses a high-velocity air stream to suspend and rapidly dry the leaves, ensuring uniform moisture reduction and enhanced drying efficiency. This method minimizes nutrient loss and maintains better color and flavor compared to traditional rack drying techniques.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Rack Drying | Fluidized Bed Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Hot air circulation over stacked racks | Hot air fluidizes leafy greens for uniform drying |
| Drying Time | Longer (several hours) | Shorter (minutes to an hour) |
| Moisture Removal Efficiency | Lower, risk of uneven drying | High, consistent moisture removal |
| Product Quality | May cause leaf damage and discoloration | Preserves color and texture better |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to longer drying times | Lower, optimized airflow and heat usage |
| Scalability | Limited, labor-intensive | High, automated and continuous processing |
| Suitability for Leafy Greens | Moderate, risk of leaf bruising | Excellent, gentle handling maintains quality |
Introduction to Leafy Green Dehydration Methods
Traditional rack drying and fluidized bed drying represent two primary methods for dehydrating leafy greens, each with unique mechanisms affecting moisture removal and product quality. Rack drying involves spreading leaves on screens for air circulation, making it a straightforward but slower process.
Fluidized bed drying uses heated air to suspend and dry leaves rapidly, enhancing efficiency and maintaining texture better than traditional rack drying. This method reduces drying time significantly, minimizing nutrient loss and color degradation in leafy greens. Selecting the appropriate dehydration technique depends on desired product characteristics and operational capacity.
Overview of Traditional Rack Drying
Traditional rack drying involves placing leafy greens on mesh trays and exposing them to warm air circulation for moisture removal. This method relies on passive airflow and can result in uneven drying and extended processing times.
- Low equipment cost - Traditional rack drying requires minimal investment in machinery, making it accessible for small-scale operations.
- Slow drying rate - The absence of forced air movement leads to longer dehydration times compared to advanced methods.
- Risk of product degradation - Prolonged exposure to ambient conditions can cause nutrient loss and color changes in leafy greens.
Despite its simplicity, traditional rack drying is less efficient and less suitable for maintaining the quality of leafy greens compared to fluidized bed drying.
Understanding Fluidized Bed Drying Technology
| Fluidized bed drying technology utilizes a high-velocity air stream to suspend and dry leafy greens efficiently, providing uniform heat distribution and faster moisture removal compared to traditional rack drying. |
| Traditional rack drying relies on natural or forced convection with static airflow, often resulting in uneven drying and longer processing times for delicate leafy greens. |
| Fluidized bed drying enhances product quality by reducing shrinkage and nutrient loss through precise temperature control and continuous agitation of leaves during dehydration. |
Key Differences in Drying Principles
Traditional rack drying removes moisture from leafy greens primarily through natural air circulation and passive heat transfer, relying on static layers that limit airflow and extend drying time. Fluidized bed drying uses a high-velocity air stream to suspend and agitate individual leaves, enhancing heat and mass transfer rates for more uniform and faster moisture removal.
Rack drying operates at lower air velocities with less turbulent airflow, which can lead to uneven drying and potential degradation of sensitive nutrients. Fluidized bed drying provides controlled temperature and airflow conditions that minimize nutrient loss and preserve leaf color and texture more effectively.
Impact on Nutrient Retention
Traditional rack drying often results in significant nutrient loss in leafy greens due to prolonged exposure to heat and air, leading to degradation of vitamins such as vitamin C and folate. Fluidized bed drying, however, utilizes rapid hot air circulation which minimizes drying time and preserves higher levels of antioxidants and essential nutrients. Studies show fluidized bed drying retains up to 30% more nutrients compared to conventional rack drying methods.
Effects on Color, Texture, and Appearance
Traditional rack drying often results in a duller color and tougher texture in leafy greens due to prolonged exposure to heat and air. Fluidized bed drying preserves vibrant color and maintains a crisp, fresh appearance by using rapid, uniform heat transfer that minimizes thermal degradation.
- Color retention - Fluidized bed drying significantly maintains the natural green hue compared to the browning observed in rack drying.
- Texture preservation - Leafy greens dried in fluidized beds retain a delicate, less brittle texture versus the tougher, shriveled leaves from rack drying.
- Appearance quality - Uniform heating in fluidized bed drying prevents patchy discoloration and deformation seen in traditional methods.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Comparison
Fluidized bed drying demonstrates significantly lower energy consumption compared to traditional rack drying for leafy greens, enhancing operational efficiency. The uniform heat distribution in fluidized beds reduces drying time and energy waste, optimizing the dehydration process.
- Energy Consumption - Fluidized bed drying uses approximately 30-40% less energy than traditional rack drying methods.
- Drying Efficiency - Fluidized bed drying achieves faster moisture removal due to improved heat and mass transfer dynamics.
- Cost Effectiveness - Reduced energy use in fluidized bed drying leads to lower operational costs and higher throughput in leafy greens processing.
Scalability and Suitability for Different Operations
Traditional rack drying offers scalability through modular designs, making it suitable for small to medium-sized leafy green operations. Its simple setup and low initial investment favor farms with limited resources.
Fluidized bed drying excels in large-scale operations, providing uniform drying and high throughput for commercial leafy green processors. This method requires significant capital and technical expertise, making it ideal for industrial facilities.
Cost Implications: Equipment and Maintenance
Traditional rack drying for leafy greens requires lower initial equipment costs but involves higher labor and maintenance expenses due to manual handling and frequent cleaning. Fluidized bed drying systems, while entailing significant upfront investment in advanced machinery, offer reduced operational costs through automated processes and better energy efficiency. Over time, fluidized bed drying can result in substantial cost savings by minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan compared to traditional rack drying.
Related Important Terms
Layer uniformity index
Traditional rack drying for leafy greens often results in a higher layer uniformity index due to consistent air flow and slower moisture removal, preserving leaf texture and nutrients. Fluidized bed drying provides rapid drying but tends to have a lower layer uniformity index because of uneven leaf movement and variable heat exposure.
Microclimate stratification
Traditional rack drying of leafy greens often results in microclimate stratification, creating uneven moisture and temperature layers within the drying chamber that can lead to inconsistent dehydration. Fluidized bed drying minimizes microclimate stratification by suspending leaves in a uniformly heated airflow, ensuring more consistent drying and preservation of texture and nutrients.
Synergistic airflow modulation
Traditional rack drying for leafy greens relies on static, low-velocity airflow that often results in uneven moisture removal and prolonged dehydration times. Fluidized bed drying employs synergistic airflow modulation to suspend leaves in a dynamic air stream, enhancing heat and mass transfer rates for faster, more uniform dehydration while preserving leaf quality.
Diffusive moisture gradient
Traditional rack drying for leafy greens relies on surface moisture evaporation, resulting in slower moisture diffusion from inner leaf layers, while fluidized bed drying enhances convective heat and mass transfer, creating a steeper diffusive moisture gradient that accelerates internal moisture removal. This improved gradient minimizes drying time and preserves nutrient quality by maintaining better cellular structure during dehydration.
Leaf lamina curl factor
Traditional rack drying typically results in a higher leaf lamina curl factor due to uneven air distribution and slower moisture removal, causing more pronounced curling in leafy greens. Fluidized bed drying offers a more uniform drying process with rapid heat and mass transfer, minimizing leaf lamina curl and preserving the structural integrity of leafy greens.
Desorption kinetics profiling
Desorption kinetics profiling reveals that fluidized bed drying offers faster moisture removal rates for leafy greens compared to traditional rack drying, resulting in improved drying efficiency and uniformity. The enhanced heat and mass transfer in fluidized beds minimizes drying time while preserving leaf texture and nutrient content more effectively than slower, diffusion-limited rack drying methods.
Controlled vortex drying (CVD)
Controlled vortex drying (CVD) enhances traditional rack drying and fluidized bed drying by creating a uniform airflow that prevents clumping and ensures consistent dehydration of leafy greens. This method maintains product quality by minimizing oxidation and nutrient loss, resulting in improved texture and color retention compared to conventional techniques.
Green pigment retention differential
Traditional rack drying often results in significant degradation of chlorophyll pigments in leafy greens due to prolonged exposure to heat and air, causing duller, less vibrant leaves. Fluidized bed drying enhances green pigment retention by providing more uniform heat distribution and reduced drying time, preserving the bright, fresh appearance of the greens.
Organoleptic crispness preservation
Traditional rack drying often leads to uneven moisture removal and potential loss of organoleptic crispness in leafy greens due to prolonged exposure to heat. Fluidized bed drying enhances uniform airflow and temperature control, preserving the delicate texture and maintaining superior organoleptic crispness in the final product.
Traditional rack drying vs Fluidized bed drying for leafy greens. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com