Dehydrators provide consistent temperature control and faster drying times, making them ideal for efficiently preserving pet food and treats. Solar dryers rely on natural sunlight, which can be less predictable and slower but are energy-efficient and eco-friendly options. Choosing between the two depends on your priorities for speed, convenience, and environmental impact.
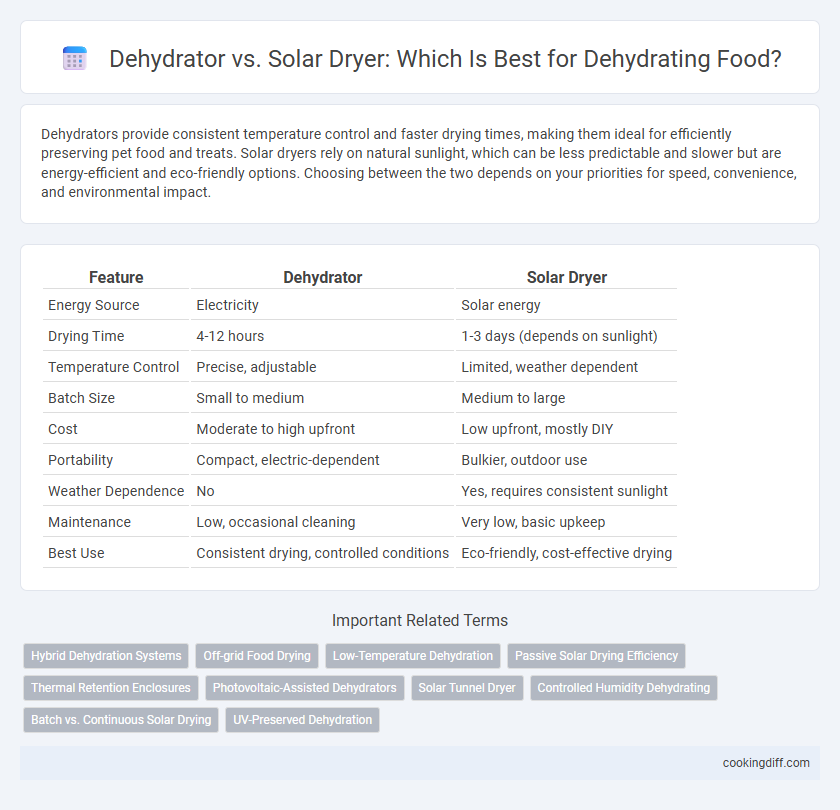
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dehydrator | Solar Dryer |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Electricity | Solar energy |
| Drying Time | 4-12 hours | 1-3 days (depends on sunlight) |
| Temperature Control | Precise, adjustable | Limited, weather dependent |
| Batch Size | Small to medium | Medium to large |
| Cost | Moderate to high upfront | Low upfront, mostly DIY |
| Portability | Compact, electric-dependent | Bulkier, outdoor use |
| Weather Dependence | No | Yes, requires consistent sunlight |
| Maintenance | Low, occasional cleaning | Very low, basic upkeep |
| Best Use | Consistent drying, controlled conditions | Eco-friendly, cost-effective drying |
Introduction to Dehydrating: Dehydrator vs Solar Dryer
Dehydrating food preserves nutrients by removing moisture, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life. Choosing between a dehydrator and a solar dryer depends on factors like energy use, drying speed, and climate suitability.
- Dehydrator Efficiency - Electric dehydrators offer consistent temperature control, speeding up the drying process regardless of weather conditions.
- Solar Dryer Sustainability - Solar dryers use renewable energy from the sun, reducing electricity consumption and lowering operating costs.
- Drying Capacity - Dehydrators typically provide uniform drying with higher capacity, while solar dryers require ample sunlight and longer drying times.
How Dehydrators Work: Mechanisms and Features
Dehydrators use electric heating elements combined with fans to circulate warm air, effectively removing moisture from food within controlled temperature ranges. Solar dryers harness solar energy through greenhouse-like enclosures, using natural convection to dry food without electricity.
- Electric Heating Element - Provides consistent and adjustable heat to facilitate efficient moisture evaporation in dehydrators.
- Air Circulation Fan - Ensures uniform airflow around food items, enhancing drying speed and preventing spoilage.
- Solar Energy Utilization - Uses sunlight and passive airflow in solar dryers, promoting eco-friendly dehydration.
Solar Dryers Explained: Principles and Designs
| Solar Dryers Explained |
| Solar dryers use greenhouse principles to trap and utilize solar radiation, creating controlled heat and airflow that enhances drying efficiency compared to traditional dehydrators. Designs vary from direct solar dryers, where the product is exposed directly to sunlight, to indirect solar dryers, which separate the drying chamber from the solar collector to prevent product damage. Key components include solar collectors, drying chambers, and ventilation systems optimized to reduce drying time and preserve nutritional quality. |
Efficiency Comparison: Dehydrator vs Solar Dryer
Electric dehydrators provide consistent temperature control, resulting in faster and more uniform drying compared to solar dryers. Solar dryers depend on variable sunlight intensity, which can lead to inconsistent moisture removal and longer drying times.
Dehydrators offer greater efficiency in energy use with timed settings that minimize waste, whereas solar dryers rely on natural energy that is free but unpredictable. The controlled environment in dehydrators reduces the risk of food spoilage caused by humidity or pests often encountered in solar drying. Solar dryers are ideal for off-grid or low-cost drying but may require backup drying methods during cloudy conditions.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Dehydrators typically require higher upfront investment but offer consistent performance through controlled temperature and humidity, leading to predictable long-term energy costs. Solar dryers have lower initial costs but depend on weather conditions, which can extend drying times and potentially increase maintenance expenses.
- Initial Purchase Cost - Electric dehydrators often cost between $50 to $500, while solar dryers range from $20 to $200 depending on design complexity.
- Energy Consumption - Dehydrators consume electricity continuously during operation, impacting monthly utility bills.
- Maintenance and Durability - Solar dryers usually require minimal upkeep but may need structural repairs after harsh weather exposure.
Choosing between these depends on balancing upfront affordability with reliable, long-term operational efficiency.
Drying Quality and Consistency
Dehydrators provide consistent drying quality by maintaining controlled temperature and airflow, resulting in evenly dehydrated products. Solar dryers rely on natural sunlight and ambient conditions, which can cause variable drying times and uneven moisture removal. Controlled environments in dehydrators reduce contamination risk, enhancing food safety compared to unpredictable outdoor solar drying.
Suitability for Different Foods
Dehydrators provide precise temperature control, making them ideal for delicate foods such as herbs, fruits, and thinly sliced vegetables that require consistent drying conditions. Solar dryers rely on ambient sunlight and airflow, making them suitable for sturdier items like nuts, seeds, and certain fruits that can tolerate variable drying times.
Foods with high moisture content, like tomatoes and mushrooms, benefit from the controlled environment of a dehydrator to prevent spoilage during drying. Solar drying excels with drought-resistant foods and can be an eco-friendly choice in regions with consistent, strong sunlight.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Which method has a lower environmental impact: dehydrators or solar dryers? Solar dryers utilize renewable solar energy, producing zero emissions during operation, significantly reducing their carbon footprint compared to electric dehydrators. Electric dehydrators consume electricity often generated from fossil fuels, increasing environmental impact and making solar dryers a more sustainable choice for food preservation.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Dehydrators offer precise temperature control and consistent airflow, making them easier to use for predictable drying results. Solar dryers require regular monitoring and repositioning to maximize sun exposure, increasing their maintenance demands. Cleaning dehydrators is straightforward due to removable trays, while solar dryers may accumulate dust and debris, necessitating frequent cleaning.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Dehydration Systems
Hybrid dehydration systems combine the efficiency of electric dehydrators with the eco-friendly benefits of solar dryers, optimizing moisture removal while reducing energy consumption. These systems leverage solar energy during the day and switch to electric power as needed, ensuring consistent drying conditions and improved food preservation.
Off-grid Food Drying
Off-grid food drying is efficiently achieved with solar dryers that harness renewable energy, reducing electricity costs and environmental impact compared to electric dehydrators. Solar dryers also allow for larger batch drying in natural sunlight, making them ideal for sustainable preservation of fruits, vegetables, and herbs in remote or energy-limited areas.
Low-Temperature Dehydration
Low-temperature dehydration is more consistently controlled using a dehydrator, which maintains precise temperature settings typically between 95degF and 115degF, preserving nutrients and flavor during drying. Solar dryers rely on ambient sunlight and temperatures, making them less reliable for low-temperature dehydration due to fluctuations and potential overheating.
Passive Solar Drying Efficiency
Solar dryers utilize passive solar drying efficiency by harnessing sunlight and natural airflow to remove moisture, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to electric dehydrators. This method offers consistent drying with minimal operational costs, making it an eco-friendly choice for preserving fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
Thermal Retention Enclosures
Dehydrators with thermal retention enclosures maintain consistent internal temperatures, accelerating moisture removal and ensuring uniform drying, whereas solar dryers rely on ambient sunlight and often have less effective heat retention, leading to slower dehydration. Efficient thermal insulation in dehydrators reduces energy consumption and preserves product quality by preventing heat loss during the drying process.
Photovoltaic-Assisted Dehydrators
Photovoltaic-assisted dehydrators combine solar energy capture with electric control systems to optimize temperature and airflow, offering more consistent dehydration compared to traditional solar dryers. These systems enhance efficiency by using photovoltaic panels to power fans and heaters, enabling faster drying times and reduced spoilage in fruit and vegetable preservation.
Solar Tunnel Dryer
Solar Tunnel Dryers utilize greenhouse-like structures to harness solar energy, providing a controlled environment that ensures consistent drying temperatures and reduced contamination compared to traditional dehydrators. Their design promotes faster moisture removal in fruits and vegetables while conserving energy and minimizing carbon footprint.
Controlled Humidity Dehydrating
Dehydrators provide precise control over temperature and humidity levels, ensuring consistent dehydration and preventing microbial growth during the drying process. Solar dryers rely on environmental conditions, resulting in less control over humidity and temperature, which may lead to uneven drying and increased spoilage risk.
Batch vs. Continuous Solar Drying
Batch solar drying processes materials in fixed quantities, offering controlled drying conditions ideal for small-scale dehydration, while continuous solar drying systems enable ongoing material feed and extraction, maximizing efficiency and throughput for large-scale operations in solar drying applications. Dehydrators typically operate in batch mode with precise temperature control, whereas continuous solar dryers rely on sustained sunlight exposure and airflow for consistent drying performance over extended periods.
Dehydrator vs Solar dryer for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com