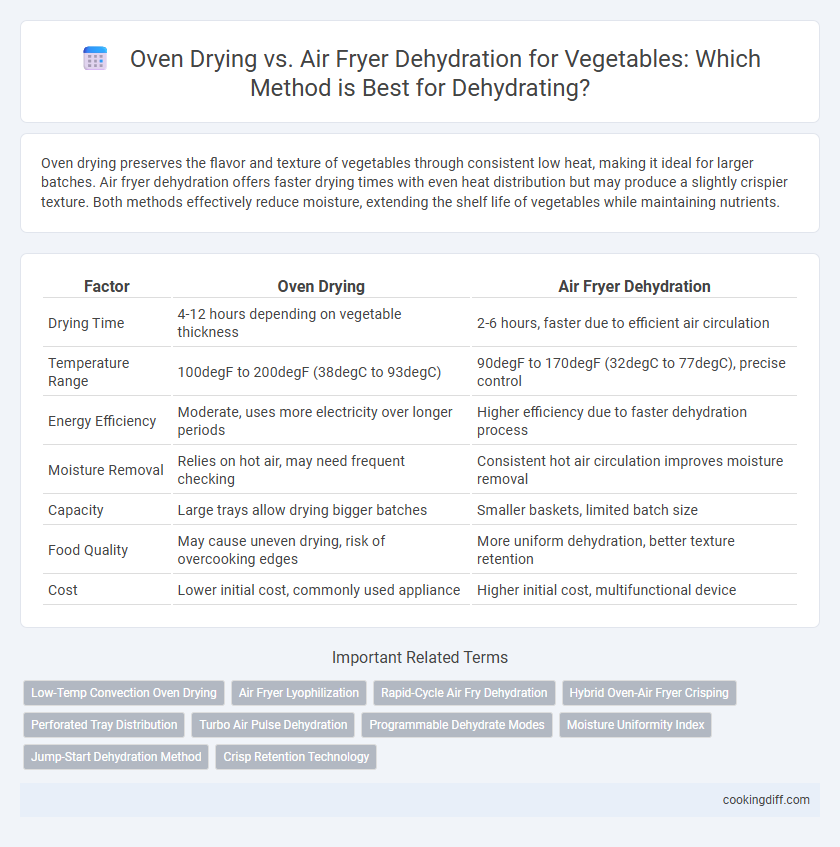
Oven drying preserves the flavor and texture of vegetables through consistent low heat, making it ideal for larger batches. Air fryer dehydration offers faster drying times with even heat distribution but may produce a slightly crispier texture. Both methods effectively reduce moisture, extending the shelf life of vegetables while maintaining nutrients.
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Oven Drying | Air Fryer Dehydration |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | 4-12 hours depending on vegetable thickness | 2-6 hours, faster due to efficient air circulation |
| Temperature Range | 100degF to 200degF (38degC to 93degC) | 90degF to 170degF (32degC to 77degC), precise control |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, uses more electricity over longer periods | Higher efficiency due to faster dehydration process |
| Moisture Removal | Relies on hot air, may need frequent checking | Consistent hot air circulation improves moisture removal |
| Capacity | Large trays allow drying bigger batches | Smaller baskets, limited batch size |
| Food Quality | May cause uneven drying, risk of overcooking edges | More uniform dehydration, better texture retention |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, commonly used appliance | Higher initial cost, multifunctional device |
Overview: Oven Drying vs. Air Fryer Dehydration for Vegetables
Oven drying and air fryer dehydration both effectively remove moisture from vegetables to preserve shelf life. Oven drying typically requires longer drying times at lower temperatures, while air fryer dehydration uses circulating hot air for faster drying.
Oven drying offers consistent temperature control ideal for drying large batches of vegetables but often consumes more energy. Air fryer dehydration provides a quicker drying process with even heat distribution, making it suitable for smaller quantities and preserving nutrient content. Both methods reduce microbial activity, extending vegetable freshness and usability when properly managed.
How Oven Drying Works for Vegetable Dehydration
Oven drying removes moisture from vegetables by circulating hot, dry air around the food at controlled temperatures, typically between 130degF and 160degF. This process gradually evaporates water, preserving the texture and nutritional content of the dehydrated vegetables.
- Consistent heat application - The oven maintains steady temperatures to ensure even dehydration without cooking the vegetables.
- Air circulation - Built-in fans or manual door openings promote airflow, preventing moisture buildup and speeding up drying time.
- Temperature control - Adjustable settings allow for precise drying tailored to various vegetable types to optimize preservation and flavor retention.
Air Fryer Dehydrators: Mechanism and Functionality
Air fryer dehydrators use rapid air circulation and controlled temperature settings to efficiently remove moisture from vegetables, preserving nutrients and texture better than conventional oven drying. This method ensures faster dehydration with less energy consumption compared to traditional oven techniques.
- Convection Technology - Utilizes high-speed fans to evenly distribute hot air around the vegetables, promoting uniform drying.
- Temperature Control - Allows precise temperature adjustments, typically between 90degF and 160degF, optimizing the dehydration process for different vegetable types.
- Compact Design - Offers a space-saving solution with multi-layer racks, enabling simultaneous dehydration of various vegetable slices efficiently.
Time Efficiency: Oven Drying vs. Air Fryer Dehydration
Oven drying vegetables typically requires 6 to 12 hours at low temperatures, making it a slower dehydration method. The air fryer significantly reduces drying time to 1 to 3 hours by utilizing rapid air circulation and higher heat efficiency.
Air fryer dehydration maintains more consistent temperature control, which enhances time efficiency without compromising the texture or nutrient retention of vegetables. Oven drying demands longer preheating and continuous monitoring, further extending the total processing time.
Texture and Flavor: Comparing Results
Oven drying vegetables typically results in a chewier texture and a more concentrated, caramelized flavor due to the prolonged exposure to consistent heat. Air fryer dehydration often preserves a crisper texture and a fresher taste by circulating hot air rapidly, reducing drying time and preserving more nutrients. Choosing between the two methods depends on desired texture and flavor intensity, with ovens favoring richness and air fryers enhancing crispness.
Energy Consumption and Cost Considerations
Oven drying typically consumes more energy due to longer drying times and higher temperature requirements compared to air fryer dehydration, which operates efficiently with rapid hot air circulation. Air fryers reduce energy costs by shortening dehydration cycles and maintaining consistent temperature control, leading to lower electricity bills for vegetable preservation. Cost considerations favor air fryer dehydration for home use, as its compact design and energy efficiency provide a more economical option than conventional ovens.
Nutrient Retention in Both Methods
Oven drying and air fryer dehydration both reduce moisture in vegetables but differ in nutrient retention due to temperature and airflow variations. Air fryers generally preserve more vitamins and antioxidants because of shorter drying times and more efficient heat circulation.
- Oven drying - Uses steady, moderate heat over longer periods which can degrade heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C.
- Air fryer dehydration - Employs rapid air circulation and higher temperatures, reducing nutrient loss by minimizing exposure duration.
- Vitamin retention - Air frying retains up to 30% more vitamin C compared to conventional oven drying methods.
Choosing air fryer dehydration optimizes nutrient preservation in dried vegetables while maintaining texture and flavor.
Batch Size and Scalability: Which Method is Better?
Oven drying accommodates larger batch sizes, making it suitable for scalable vegetable dehydration where volume and uniform heat distribution are critical. This method typically supports continuous drying cycles, enhancing productivity for commercial-scale operations.
Air fryer dehydration is limited by smaller basket capacity, restricting batch size and scalability for substantial vegetable volumes. Its efficiency favors smaller, frequent batches, making it less ideal for large-scale vegetable dehydration despite faster drying times for limited quantities.
Ease of Use and Cleaning Differences
| Method | Ease of Use | Cleaning |
|---|---|---|
| Oven Drying | Requires manual temperature control and frequent monitoring to avoid over-drying vegetables. | Large trays and racks are often harder to clean and may retain food residues or odors. |
| Air Fryer Dehydration | Preset dehydration functions simplify temperature settings and reduce the need for constant checking. | Non-stick or removable baskets facilitate quicker cleaning and prevent buildup of food particles. |
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Convection Oven Drying
Low-temperature convection oven drying preserves more nutrients and maintains better texture in vegetables compared to air fryer dehydration by providing consistent airflow and precise temperature control around 120degF to 140degF. This method reduces moisture content efficiently while minimizing nutrient loss and oxidation, making it ideal for delicate vegetable preservation.
Air Fryer Lyophilization
Air fryer lyophilization offers superior dehydration for vegetables by combining rapid moisture removal with low-temperature airflow, preserving nutrients and enhancing texture compared to traditional oven drying. This method minimizes enzymatic degradation and oxidation, resulting in higher-quality, shelf-stable vegetable products with retained flavor and color.
Rapid-Cycle Air Fry Dehydration
Rapid-cycle air fryer dehydration accelerates moisture removal from vegetables by circulating hot air at higher velocities and controlled temperatures, preserving nutrient content and texture more effectively than traditional oven drying. Unlike oven drying, which often requires extended hours and uniform heat distribution, air fryer dehydration reduces overall drying time while maintaining flavor and color integrity through enhanced airflow dynamics.
Hybrid Oven-Air Fryer Crisping
Hybrid oven-air fryer crisping combines the even heat distribution of an oven with the rapid air circulation of an air fryer, enhancing dehydration efficiency for vegetables while preserving texture and nutrients. This method reduces drying time compared to traditional oven drying and achieves crispier results than standard air fryer dehydration, making it ideal for maintaining vegetable flavor and structure.
Perforated Tray Distribution
Oven drying uses solid trays that limit air circulation, reducing even dehydration of vegetables, while air fryer dehydration employs perforated trays that enhance airflow and promote uniform moisture removal. Perforated tray distribution in air fryers improves heat penetration and speeds up drying time compared to the denser tray structure in traditional ovens.
Turbo Air Pulse Dehydration
Turbo Air Pulse Dehydration in oven drying rapidly removes moisture from vegetables by circulating hot air evenly, preserving nutrients and texture better than traditional air fryer dehydration. Compared to air fryers, Turbo Air Pulse technology reduces drying time and energy consumption while ensuring consistent dehydration for crisp, flavorful vegetable snacks.
Programmable Dehydrate Modes
Oven drying offers programmable dehydrate modes with precise temperature control ideal for consistent vegetable dehydration, while air fryers provide quicker cycles but limited or less customizable drying settings. Programmable modes in ovens enhance nutrient retention and texture by maintaining steady low heat, compared to the faster yet less controlled dehydration in air fryer models.
Moisture Uniformity Index
Oven drying provides a consistent heat environment but often results in uneven moisture distribution in vegetables, reflected by a higher Moisture Uniformity Index, whereas air fryer dehydration utilizes rapid hot air circulation to achieve more uniform moisture removal, lowering the index and improving texture quality. The enhanced air flow in air fryers promotes faster, more homogenous drying compared to static oven conditions, optimizing dehydration efficiency and preserving nutritional content.
Jump-Start Dehydration Method
Oven drying offers consistent heat distribution and precise temperature control, enabling efficient jump-start dehydration for vegetables by quickly removing surface moisture and reducing drying time. Air fryer dehydration provides rapid air circulation and higher heat intensity, accelerating initial moisture loss but requiring careful monitoring to prevent uneven drying or overcooking.
Oven drying vs Air fryer dehydration for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com