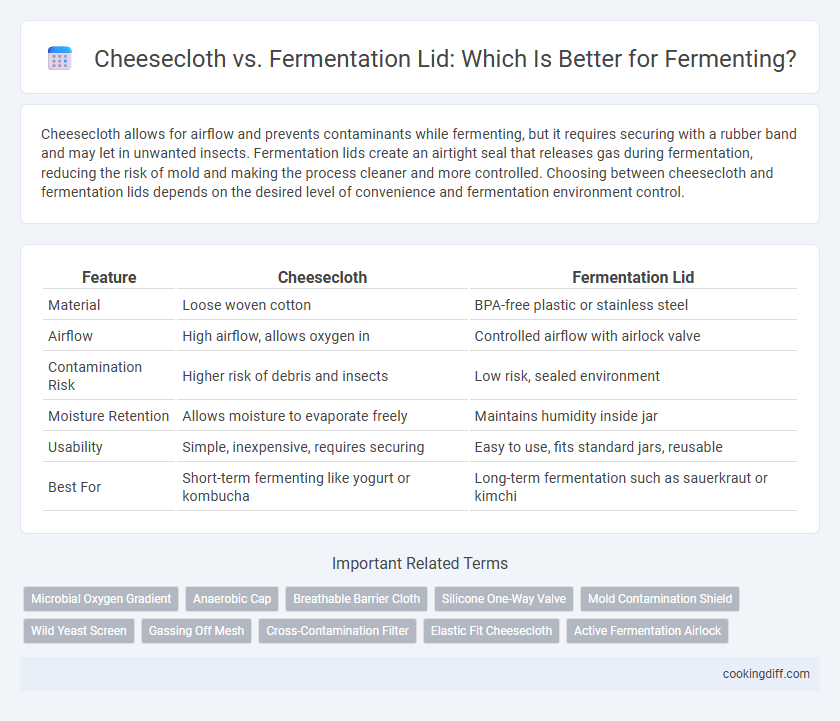
Cheesecloth allows for airflow and prevents contaminants while fermenting, but it requires securing with a rubber band and may let in unwanted insects. Fermentation lids create an airtight seal that releases gas during fermentation, reducing the risk of mold and making the process cleaner and more controlled. Choosing between cheesecloth and fermentation lids depends on the desired level of convenience and fermentation environment control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cheesecloth | Fermentation Lid |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Loose woven cotton | BPA-free plastic or stainless steel |
| Airflow | High airflow, allows oxygen in | Controlled airflow with airlock valve |
| Contamination Risk | Higher risk of debris and insects | Low risk, sealed environment |
| Moisture Retention | Allows moisture to evaporate freely | Maintains humidity inside jar |
| Usability | Simple, inexpensive, requires securing | Easy to use, fits standard jars, reusable |
| Best For | Short-term fermenting like yogurt or kombucha | Long-term fermentation such as sauerkraut or kimchi |
Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid: Key Differences Explained
| Aspect | Cheesecloth | Fermentation Lid |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability | Allows air circulation while keeping out insects, promoting aerobic fermentation. | Seals the jar to control oxygen exposure, supporting anaerobic fermentation. |
| Contamination Protection | Moderate protection; may allow dust and small particles. | Provides airtight seal, minimizing contamination risk from external elements. |
| Ease of Use | Simple to cover jars but requires securing with bands or rubber rings. | Designed to fit jars securely with built-in airlocks or valves for gas release. |
| Fermentation Type Suitability | Ideal for lacto-fermented vegetables requiring oxygen. | Best suited for kimchi, sauerkraut, and other anaerobic fermentations. |
| Cost and Reusability | Low cost, reusable with proper cleaning, but may degrade over time. | Higher initial cost, durable and reusable with easy cleaning. |
Pros and Cons of Using Cheesecloth in Fermentation
Is cheesecloth effective for fermenting foods? Cheesecloth allows airflow, preventing mold growth while keeping out insects, but its loose weave offers less protection against contaminants compared to a fermentation lid. It is inexpensive and versatile but may require a rubber band to secure and frequent monitoring during the fermentation process.
Benefits of Fermentation Lids for Home Fermenters
Fermentation lids create an airtight seal that prevents contamination and allows gases to escape, optimizing the anaerobic environment essential for successful fermenting. Their built-in airlock system reduces the risk of mold growth and spoilage compared to using cheesecloth, which only offers basic breathability.
Home fermenters benefit from fermentation lids as they require less monitoring and maintenance, ensuring consistent fermentation conditions. These lids also minimize exposure to insects and airborne particles, enhancing safety and hygiene during the fermenting process.
Airflow Control: Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid
Cheesecloth allows for maximal airflow during fermentation, promoting aerobic microbial activity essential for certain ferments like sauerkraut. Its loose weave also protects against contaminants while enabling gases to escape freely.
Fermentation lids offer controlled airflow through built-in airlocks, minimizing oxygen exposure to prevent unwanted mold and yeast growth. This creates an anaerobic environment critical for fermenting vegetables, kombucha, and other sensitive recipes.
Preventing Contamination: Which Option Works Best?
Cheesecloth allows air circulation while providing a basic barrier against dust and insects, but it does not create a sealed environment, increasing the risk of airborne contaminants. Fermentation lids, equipped with airlocks, prevent oxygen exposure and block contaminants such as mold spores and bacteria, ensuring a controlled environment. For optimal contamination prevention during fermenting, fermentation lids outperform cheesecloth by maintaining anaerobic conditions and minimizing contamination risks.
Ease of Use: Cheesecloth Compared to Fermentation Lids
Cheesecloth offers simplicity and flexibility for fermenting by allowing airflow while keeping contaminants out, making it easy to secure with a rubber band. Fermentation lids, however, often provide a more controlled environment with built-in airlocks to release gases automatically.
Using cheesecloth requires manual monitoring to prevent unwanted exposure and may need frequent adjustment, which can be less convenient for beginners. Fermentation lids reduce the risk of spoilage by maintaining a consistent anaerobic environment, improving fermentation reliability. Overall, cheesecloth suits casual fermenters seeking an inexpensive, low-tech solution, while fermentation lids benefit those desiring precision and ease of maintenance.
Reusability and Cleaning: Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid
Cheesecloth is highly reusable after thorough washing and drying, making it an eco-friendly option for multiple fermentation cycles. Fermentation lids often feature silicone seals and rigid materials that are easy to clean with warm, soapy water and can be sterilized for safe reuse. Both options support sustainable fermentation practices, but fermentation lids offer a more hygienic and low-maintenance solution compared to cheesecloth.
Impact on Flavor and Texture during Fermenting
Using cheesecloth during fermentation allows more air circulation, which can enhance the development of complex flavors and a slightly tangy texture. A fermentation lid creates a sealed environment that controls oxygen exposure, leading to a smoother taste and consistent texture.
- Cheesecloth promotes wild fermentation - It encourages beneficial aerobic bacteria that influence sharper, more robust flavors.
- Fermentation lids maintain anaerobic conditions - This results in less sourness and a creamier texture due to reduced oxygen contact.
- Oxygen exposure affects texture - Cheesecloth can create a drier, firmer product, while lids often yield softer, moister results.
Cost Comparison: Cheesecloth or Fermentation Lid?
Cheesecloth is an affordable option widely available for fermentation projects, typically costing just a few dollars per yard. Fermentation lids, while more expensive upfront, offer a durable, reusable solution that can save money over time.
- Cheesecloth Cost - Cheesecloth usually costs between $2 to $5 per yard, making it a low-cost disposable choice for small batches.
- Fermentation Lid Initial Investment - Fermentation lids generally range from $10 to $25 each, reflecting a higher initial purchase price compared to cheesecloth.
- Long-Term Savings - Fermentation lids provide reusable convenience that reduces recurring costs, proving more economical for frequent fermenters.
Related Important Terms
Microbial Oxygen Gradient
Cheesecloth allows more oxygen penetration, promoting aerobic microbial growth and creating a less controlled oxygen gradient, while fermentation lids limit oxygen exposure, enhancing anaerobic conditions ideal for lactic acid bacteria. Maintaining a precise microbial oxygen gradient with fermentation lids results in consistent fermentation outcomes and reduced contamination risk.
Anaerobic Cap
A fermentation lid creates a tightly sealed anaerobic cap that prevents oxygen exposure, reducing the risk of mold and contamination during fermentation, unlike cheesecloth which allows air flow and can introduce unwanted bacteria. Using a fermentation lid ensures a controlled environment essential for optimal anaerobic fermentation in foods like sauerkraut and kimchi.
Breathable Barrier Cloth
Cheesecloth serves as a breathable barrier cloth that allows gases to escape during fermentation while preventing contaminants like dust and insects from entering, promoting optimal airflow and environment for microbial activity. Fermentation lids, however, provide a more controlled fermentation atmosphere with airlocks that minimize oxygen exposure and reduce risk of spoilage, though they offer less breathability compared to cheesecloth.
Silicone One-Way Valve
A silicone one-way valve fermentation lid provides an airtight seal that efficiently releases carbon dioxide while preventing oxygen and contaminants from entering, ensuring a controlled anaerobic environment for fermenting. Unlike cheesecloth, which allows air exposure and potential contamination, the silicone valve lid maintains consistent fermentation conditions, enhancing flavor development and safety.
Mold Contamination Shield
Cheesecloth allows airflow during fermentation but can expose the batch to mold contamination due to its porous nature. Fermentation lids create an airtight seal with a one-way valve, effectively shielding fermenting foods from mold while releasing gases.
Wild Yeast Screen
Cheesecloth allows wild yeast to interact freely with fermenting liquids, enhancing natural fermentation by permitting oxygen flow and air exposure, which promotes wild microbial growth. In contrast, a fermentation lid creates an anaerobic environment that limits wild yeast access, reducing contamination risk but also restricting wild yeast-driven flavor development during fermentation.
Gassing Off Mesh
Cheesecloth allows for natural gassing off during fermentation by providing breathability while keeping contaminants out, making it ideal for short-term fermentation. Fermentation lids with built-in airlocks offer controlled gas release and prevent oxygen exposure, reducing the risk of mold and ensuring a more consistent anaerobic environment.
Cross-Contamination Filter
Cheesecloth offers a breathable barrier that allows gases to escape while minimizing large contaminants, but its loose weave may not effectively prevent smaller airborne microbes during fermentation. Fermentation lids designed with silicone gaskets and airlocks provide a more reliable cross-contamination filter by creating an airtight seal that controls oxygen exposure and prevents unwanted bacteria or mold from entering the fermenting environment.
Elastic Fit Cheesecloth
Elastic fit cheesecloth offers a breathable, secure barrier that prevents contaminants while allowing gases to escape during fermentation, maintaining an ideal environment for microbial activity. Unlike rigid fermentation lids, the stretchy material adapts to various jar sizes and shapes, enhancing convenience and reducing the risk of spoilage.
Cheesecloth vs fermentation lid for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com