Kombucha and tibicos are both popular fermented beverages but differ significantly in their fermentation process and microbial cultures. Kombucha is fermented using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) that thrives on sweetened tea, producing a tangy, slightly effervescent drink rich in probiotics and organic acids. Tibicos, also known as water kefir, uses water kefir grains composed of bacteria and yeast that ferment sugary water or fruit juices, resulting in a refreshing, mildly sweet beverage with a different probiotic profile and lower acidity.
Table of Comparison
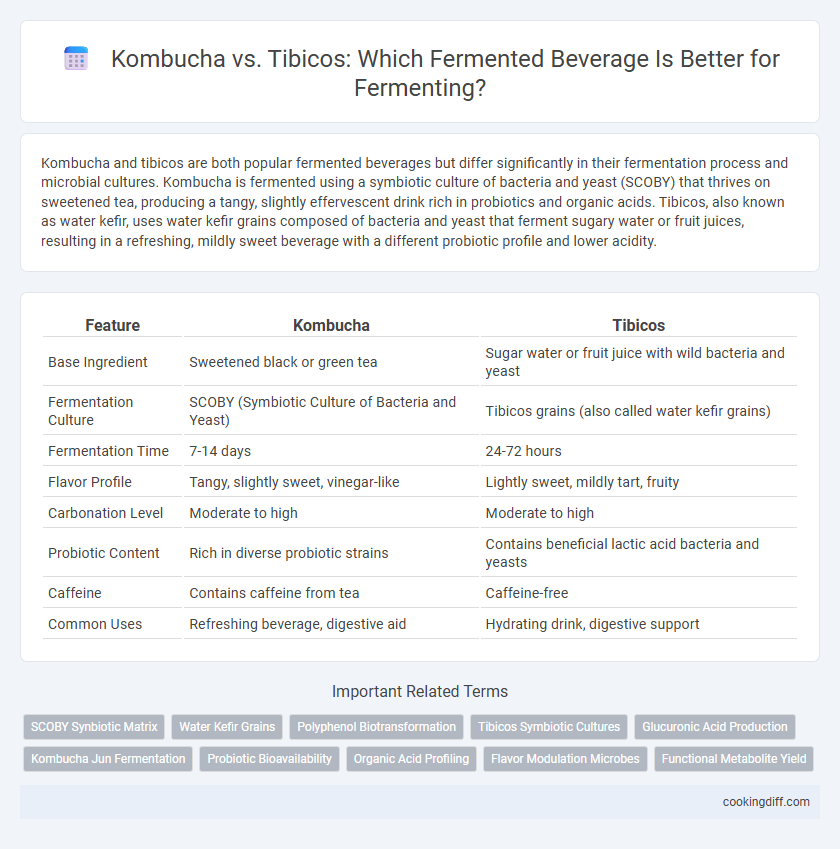
| Feature | Kombucha | Tibicos |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Sweetened black or green tea | Sugar water or fruit juice with wild bacteria and yeast |
| Fermentation Culture | SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) | Tibicos grains (also called water kefir grains) |
| Fermentation Time | 7-14 days | 24-72 hours |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, slightly sweet, vinegar-like | Lightly sweet, mildly tart, fruity |
| Carbonation Level | Moderate to high | Moderate to high |
| Probiotic Content | Rich in diverse probiotic strains | Contains beneficial lactic acid bacteria and yeasts |
| Caffeine | Contains caffeine from tea | Caffeine-free |
| Common Uses | Refreshing beverage, digestive aid | Hydrating drink, digestive support |
Introduction to Fermented Beverages
Fermented beverages like kombucha and tibicos are rich in probiotics that promote gut health and enhance digestion. Both drinks undergo natural fermentation processes involving symbiotic cultures of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY).
Kombucha is traditionally made from sweetened black or green tea, fermented by a SCOBY that produces a slightly tangy, effervescent drink loaded with organic acids and antioxidants. Tibicos, also known as water kefir, uses water kefir grains composed of bacteria and yeast to ferment sugary water or fruit juice into a refreshing, naturally carbonated beverage. This diversity in fermentation substrates results in unique microbial profiles and health benefits for each fermented drink.
What is Kombucha?
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage created by fermenting sweetened black or green tea with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). This process produces a tangy, effervescent drink rich in probiotics, organic acids, and antioxidants.
Known for its potential health benefits, kombucha contains acetic acid and enzymes that may aid digestion and support immune health. It typically has a slight vinegar-like taste and can be flavored with various fruits and herbs during fermentation.
What are Tibicos (Water Kefir Grains)?
What are Tibicos (Water Kefir Grains)? Tibicos are symbiotic cultures of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) used to ferment sugary water, creating a naturally carbonated probiotic beverage called water kefir. They consist of polysaccharide matrices that host diverse microbial communities, resulting in a sweet, tangy flavor distinct from kombucha, which ferments tea using a different SCOBY.
Origins and History: Kombucha vs Tibicos
Kombucha originated in Northeast China around 220 B.C. and spread to Russia and Europe, known for its black tea base fermented with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). Tibicos, also called water kefir, has roots in Mexico and parts of Eastern Europe, using water kefir grains composed of a different microbial consortium to ferment sugary water or fruit juices.
- Kombucha's Origin - Traditionally brewed in East Asia, Kombucha has been consumed for its potential health benefits for over two millennia.
- Tibicos' Origins - Known as water kefir grains, Tibicos have an ancient heritage linked to indigenous fermented beverages from Mexico and Europe.
- Microbial Cultures - Kombucha uses a SCOBY mainly involving yeast and acetic acid bacteria, while Tibicos grains contain more diverse bacteria including lactic acid bacteria blended with yeast.
Both Kombucha and Tibicos represent rich fermentation traditions shaped by distinct cultural and microbial histories.
Key Ingredients and Brewing Process
Kombucha is brewed using a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) combined with sweetened tea, primarily black or green tea. The fermentation process typically lasts 7 to 14 days, where the SCOBY converts sugar into organic acids, carbonation, and trace alcohol.
Tibicos, also known as water kefir grains, consists of polysaccharide-based grains containing a complex mix of bacteria and yeasts. This culture ferments sugar water or coconut water over 24 to 48 hours, producing a lightly carbonated beverage rich in probiotics and minerals.
Flavor Profiles and Taste Comparison
Kombucha offers a tangy, slightly acidic flavor with hints of vinegar and fruity undertones, whereas Tibicos (water kefir) delivers a milder, sweeter, and more effervescent taste with subtle citrus notes. Both beverages provide a refreshing probiotic experience but cater to different flavor preferences based on their fermentation processes and sugar sources.
- Kombucha's flavor profile - Characterized by a sharp, tart taste resulting from the fermentation of sweetened tea by symbiotic cultures of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY).
- Tibicos' taste experience - Exhibits a lighter, sweeter, and gently fizzy profile due to fermentation using water kefir grains with sugar and often dried fruits.
- Flavor complexity - Kombucha generally has a deeper, more complex acidity, while Tibicos is known for its subtle fruity sweetness and smooth carbonation.
Nutritional Content and Health Benefits
Kombucha is rich in antioxidants, organic acids, and B vitamins, which support digestion and immune health, while Tibicos contains a diverse probiotic profile that promotes gut microbiota balance and boosts nutrient absorption. Both fermented beverages contribute to improved digestion and enhanced immune response through their unique fermentation processes.
- Kombucha's High Antioxidant Levels - Contains polyphenols from tea that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Tibicos' Diverse Probiotics - Features multiple strains of beneficial bacteria and yeasts supporting a healthy gut flora.
- Immune System Support - Both kombucha and tibicos enhance immune function through probiotic activity and bioactive compounds.
Probiotic Content: Kombucha vs Tibicos
Kombucha contains a diverse mix of probiotic bacteria and yeast, primarily including strains like Gluconacetobacter and Saccharomyces, which aid in gut health. Tibicos, also known as water kefir, offers a different probiotic profile rich in Lactobacillus species that promote digestion and immune support. Both beverages provide beneficial microbes, but Tibicos generally has a higher concentration of live probiotics due to its sugar-water fermentation base.
Potential Risks and Safety Considerations
Kombucha may contain trace amounts of alcohol and caffeine, posing risks for individuals sensitive to these compounds or pregnant women. Tibicos, or water kefir, typically has lower alcohol content but can still harbor harmful bacteria if not prepared in a sterile environment. Both fermented beverages require careful attention to hygiene and fermentation time to minimize contamination and ensure safe consumption.
Related Important Terms
SCOBY Synbiotic Matrix
Kombucha and Tibicos each utilize unique SCOBY synbiotic matrices that foster diverse microbial communities essential for fermentation; Kombucha's cellulose-based SCOBY promotes a balanced symbiosis of acetic acid bacteria and yeast, while Tibicos' gelatinous polysaccharide matrix supports a robust consortium of lactic acid bacteria and yeast. These distinct microbial ecosystems drive the production of varying organic acids, vitamins, and probiotics, influencing the flavor profile, health benefits, and fermentation kinetics of their respective beverages.
Water Kefir Grains
Water kefir grains, also known as tibicos, consist of a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) that ferment sugar water into a naturally effervescent probiotic beverage with a mild, tangy flavor. Unlike kombucha, which ferments sweetened tea using a different SCOBY composed primarily of Acetobacter and yeast, tibicos produce a dairy-free, gluten-free drink rich in lactobacilli, promoting gut health and aiding digestion.
Polyphenol Biotransformation
Kombucha and Tibicos both undergo polyphenol biotransformation during fermentation, but kombucha's use of tea leaves introduces higher concentrations of catechins and flavonoids that are enzymatically modified by the symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY). Tibicos, fermented primarily with sugary substrates and diverse microbial cultures, produces distinct polyphenol derivatives, often resulting in varied antioxidant profiles compared to kombucha.
Tibicos Symbiotic Cultures
Tibicos, also known as water kefir grains, consist of a diverse symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) that ferments sugary water into a probiotic-rich beverage with a mildly sweet and tangy flavor. Unlike kombucha's tea-based fermentation driven by a specific kombucha SCOBY, tibicos cultures thrive on simple sugars, producing natural carbonation and a variety of beneficial organic acids, enzymes, and vitamins ideal for gut health and hydration.
Glucuronic Acid Production
Kombucha typically produces higher levels of glucuronic acid due to the activity of Acetobacter species during fermentation, enhancing its detoxifying properties. In contrast, Tibicos, fermented with a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY), generally yields lower glucuronic acid concentrations but offers diverse probiotic benefits.
Kombucha Jun Fermentation
Kombucha and Jun are both fermented beverages made using tea, but Jun fermentation specifically uses green tea and raw honey, resulting in a lighter, less acidic flavor compared to kombucha's black tea and sugar base. The fermentation process in Jun relies on a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) that produces beneficial probiotics, organic acids, and enzymes, enhancing gut health and digestion.
Probiotic Bioavailability
Kombucha contains a diverse range of probiotic strains primarily from Acetobacter and Saccharomyces species, offering moderate bioavailability due to the acidic environment facilitating gut colonization. Tibicos, or water kefir, harbors a symbiotic culture of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts with higher probiotic bioavailability, as the fermentation process produces a wider spectrum of live microorganisms that survive stomach acidity more effectively.
Organic Acid Profiling
Kombucha and Tibicos exhibit distinct organic acid profiles critical for their fermentation characteristics; Kombucha typically contains higher levels of acetic acid and gluconic acid, contributing to its tartness and antimicrobial properties, while Tibicos features elevated levels of lactic acid and glucuronic acid, enhancing its probiotic benefits and digestive support. Analyzing these organic acids is essential for optimizing fermentation parameters and tailoring flavor profiles in these fermented beverages.
Flavor Modulation Microbes
Kombucha's flavor modulation relies predominantly on Acetobacter and Gluconobacter bacteria, producing acetic acid and a tangy, vinegar-like taste, while tibicos, fermented by a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) including Lactobacillus and Saccharomyces species, creates a milder, slightly effervescent, and fruity profile. The microbial diversity in tibicos enables more complex flavor variations and a natural carbonation distinct from kombucha's sharper acidity and herbal undertones.
Kombucha vs Tibicos for fermented beverages. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com