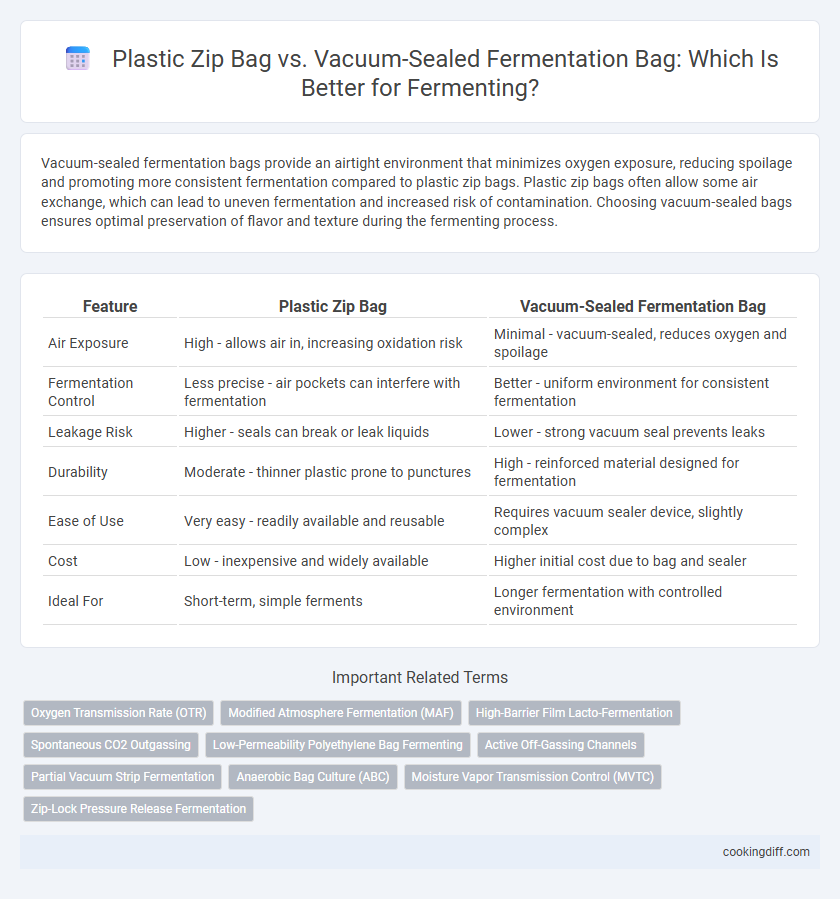
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags provide an airtight environment that minimizes oxygen exposure, reducing spoilage and promoting more consistent fermentation compared to plastic zip bags. Plastic zip bags often allow some air exchange, which can lead to uneven fermentation and increased risk of contamination. Choosing vacuum-sealed bags ensures optimal preservation of flavor and texture during the fermenting process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Zip Bag | Vacuum-Sealed Fermentation Bag |
|---|---|---|
| Air Exposure | High - allows air in, increasing oxidation risk | Minimal - vacuum-sealed, reduces oxygen and spoilage |
| Fermentation Control | Less precise - air pockets can interfere with fermentation | Better - uniform environment for consistent fermentation |
| Leakage Risk | Higher - seals can break or leak liquids | Lower - strong vacuum seal prevents leaks |
| Durability | Moderate - thinner plastic prone to punctures | High - reinforced material designed for fermentation |
| Ease of Use | Very easy - readily available and reusable | Requires vacuum sealer device, slightly complex |
| Cost | Low - inexpensive and widely available | Higher initial cost due to bag and sealer |
| Ideal For | Short-term, simple ferments | Longer fermentation with controlled environment |
Introduction: Plastic Zip Bags vs Vacuum-Sealed Fermentation Bags
| Plastic zip bags | Inexpensive, readily available, allow some air exchange, increasing risk of contamination during fermentation. |
| Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags | Designed to remove air, reducing oxidation and contamination risk, enhance anaerobic environment ideal for controlled fermentation. |
| Fermentation impact | Vacuum-sealed bags maintain consistent pressure and limit spoilage better than plastic zip bags, resulting in improved flavor and texture. |
Fermentation Science: Oxygen Exchange and Bag Choice
Plastic zip bags allow limited oxygen exchange, which can influence the growth of aerobic bacteria during fermentation, potentially affecting flavor development. Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags minimize oxygen exposure, promoting anaerobic conditions essential for lactic acid bacteria activity and consistent fermentation results.
Choosing the right bag impacts microbial activity by controlling oxygen levels, crucial for fermentation science. Vacuum-sealed bags help maintain a stable anaerobic environment, reducing contamination risks and improving shelf life. Conversely, plastic zip bags might permit slight oxygen ingress, which could alter fermentation dynamics and product quality.
Material Safety: Food-Grade Standards and Chemical Leaching
Food-grade vacuum-sealed fermentation bags are typically made from BPA-free, phthalate-free materials specifically designed to prevent chemical leaching during fermentation. Standard plastic zip bags may not meet strict food-grade standards, increasing the risk of harmful substances contaminating fermented foods.
- Vacuum-sealed bags ensure material safety - Manufactured under rigorous food-grade certifications, these bags minimize exposure to chemicals during the acidic fermentation process.
- Plastic zip bags often lack specialized safety features - Lower-grade plastics can release toxins such as BPA and phthalates when exposed to fermenting organic acids.
- Choosing compliant materials is crucial - Using certified food-grade materials preserves fermentation quality and protects consumer health from potential chemical contamination.
Ease of Use: Filling, Sealing, and Handling
Plastic zip bags offer a straightforward filling process with resealable tops that allow easy access and quick sealing, making them convenient for beginners. Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags require more effort to fill but provide superior airtight sealing, which helps maintain optimal fermentation conditions by reducing oxygen exposure. Handling vacuum-sealed bags may involve specialized equipment, while zip bags remain flexible and simple to manage during the fermentation process.
Air Removal: Manual vs Mechanical Methods
How does air removal differ between plastic zip bags and vacuum-sealed fermentation bags during fermentation? Plastic zip bags require manual squeezing to expel air, which can be inconsistent and leave pockets of oxygen, potentially affecting fermentation quality. Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags use mechanical pumps to create a near-complete air removal, providing a more controlled anaerobic environment essential for optimal fermentation results.
Contamination Risks: Mold, Spoilage, and Cross-Contamination
Plastic zip bags used for fermenting often allow minimal air exchange, increasing the risk of mold growth and spoilage due to inconsistent anaerobic conditions. These bags are also more prone to leaks and accidental openings, which can lead to cross-contamination from external bacteria or mold spores.
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags create a tightly sealed anaerobic environment that significantly reduces contamination risks by limiting exposure to oxygen and airborne pathogens. Their durable material and secure sealing mechanism minimize leaks, helping maintain optimal fermentation conditions and preventing spoilage.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes: Impact of Bag Type
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags create an anaerobic environment that enhances complex flavor development and maintains a crisp texture by preventing oxidation. Plastic zip bags may allow minimal air exchange, leading to less consistent fermentation and potential off-flavors. The controlled environment of vacuum-sealed bags results in a more robust and uniform fermentation, improving overall taste and texture outcomes.
Storage and Space Efficiency: Zip vs Vacuum-Sealed Bags
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags significantly reduce air exposure, creating an ideal anaerobic environment that enhances the fermentation process. Plastic zip bags, while convenient, often allow more air inside, which can result in slower fermentation and potential contamination risks.
- Storage Efficiency - Vacuum-sealed bags compactly store fermenting foods by removing excess air, saving valuable refrigerator space.
- Space Optimization - Zip bags tend to be bulkier due to trapped air, making them less efficient for stacking or storing multiple batches.
- Durability - Vacuum-sealed bags typically offer stronger, thicker material that resists leaks and punctures better than standard plastic zip bags.
Cost Comparison: Initial Investment and Reusability
Plastic zip bags have a lower initial cost but are generally single-use, increasing long-term expenses. Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags require a higher upfront investment but can be reused, reducing overall cost over time.
- Plastic zip bags are inexpensive upfront - They typically cost less per unit compared to vacuum-sealed bags.
- Vacuum-sealed bags offer reusability - Their durable material allows multiple fermentation cycles, cutting replacement frequency.
- Long-term cost efficiency favors vacuum bags - Despite the higher start price, reusability lowers total expenditure in prolonged fermentation use.
Choosing between these options depends on balancing budget constraints with the desire for sustainable, cost-effective fermentation practices.
Related Important Terms
Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR)
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags offer a significantly lower Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR) compared to plastic zip bags, ensuring minimal oxygen exposure that promotes anaerobic fermentation and reduces spoilage. Plastic zip bags have higher OTR, allowing more oxygen to permeate, which can lead to unwanted aerobic microbial activity and less consistent fermentation results.
Modified Atmosphere Fermentation (MAF)
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags create a controlled Modified Atmosphere Fermentation (MAF) environment by removing excess oxygen and retaining carbon dioxide, which enhances microbial activity and preserves flavor compounds more effectively than standard plastic zip bags. Plastic zip bags allow some air exchange, leading to inconsistent anaerobic conditions and higher risk of oxidation, reducing fermentation efficiency and product quality in MAF processes.
High-Barrier Film Lacto-Fermentation
High-barrier film vacuum-sealed fermentation bags provide superior oxygen and moisture resistance compared to plastic zip bags, ensuring an optimal anaerobic environment for lacto-fermentation. This enhanced preservation extends shelf life, preserves nutrient integrity, and reduces the risk of mold growth during the fermentation process.
Spontaneous CO2 Outgassing
Plastic zip bags allow some spontaneous CO2 outgassing during fermentation but risk seal failure and contamination, whereas vacuum-sealed fermentation bags maintain an airtight environment that effectively controls CO2 release and preserves fermentation integrity. Optimized vacuum sealing improves anaerobic conditions, reducing oxidation and ensuring consistent microbial activity during the fermenting process.
Low-Permeability Polyethylene Bag Fermenting
Low-permeability polyethylene bags offer superior oxygen and moisture barrier properties compared to plastic zip bags, ensuring an optimal anaerobic environment crucial for consistent fermentation. These vacuum-sealed fermentation bags minimize contamination risks and extend shelf life by preventing air and microbial ingress, enhancing the quality and safety of fermented products.
Active Off-Gassing Channels
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags feature active off-gassing channels that effectively release CO2 during the fermentation process, preventing pressure buildup and promoting optimal anaerobic conditions. In contrast, plastic zip bags lack specialized vents, often causing CO2 retention and potential bag deformation, which can hinder proper fermentation.
Partial Vacuum Strip Fermentation
Partial Vacuum Strip Fermentation using vacuum-sealed bags offers superior anaerobic conditions, minimizing oxygen exposure and reducing contamination risk compared to plastic zip bags. This method enhances microbial activity control, resulting in more consistent fermentation outcomes with improved flavor and texture profiles.
Anaerobic Bag Culture (ABC)
Plastic zip bags offer basic containment for fermentation but often allow limited oxygen exchange, which can hinder optimal Anaerobic Bag Culture (ABC) conditions. Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags create a near-perfect anaerobic environment by removing air, minimizing oxidation and contamination risks, thereby enhancing microbial activity and fermentation quality.
Moisture Vapor Transmission Control (MVTC)
Vacuum-sealed fermentation bags offer superior Moisture Vapor Transmission Control (MVTC) compared to plastic zip bags, minimizing oxygen exposure and preventing excess moisture loss during fermentation. This optimized MVTC ensures a stable environment that promotes consistent microbial activity and enhances flavor development in fermented products.
Plastic zip bag vs Vacuum-sealed fermentation bag for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com