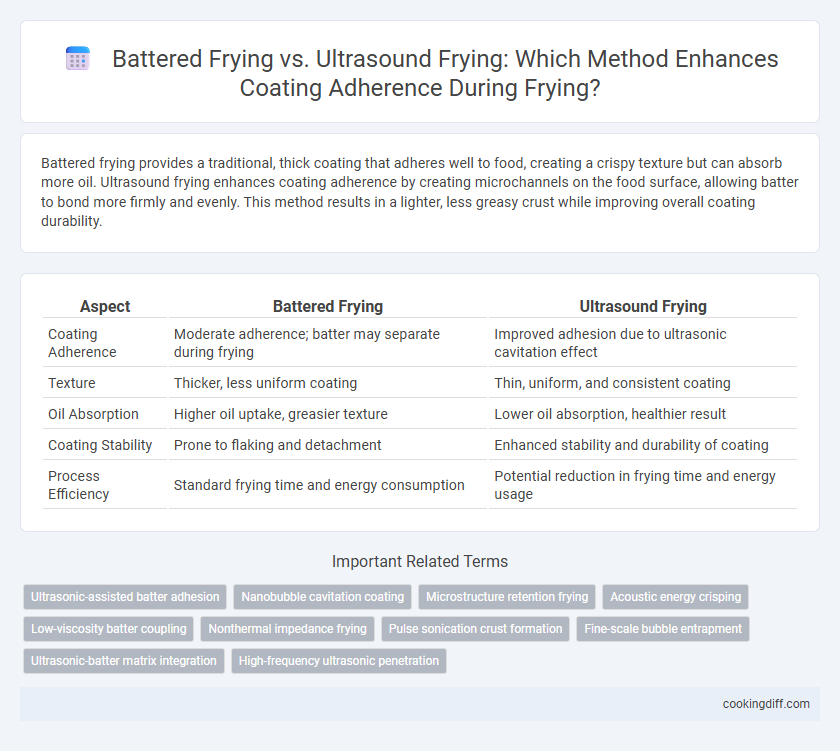
Battered frying provides a traditional, thick coating that adheres well to food, creating a crispy texture but can absorb more oil. Ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence by creating microchannels on the food surface, allowing batter to bond more firmly and evenly. This method results in a lighter, less greasy crust while improving overall coating durability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Battered Frying | Ultrasound Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Adherence | Moderate adherence; batter may separate during frying | Improved adhesion due to ultrasonic cavitation effect |
| Texture | Thicker, less uniform coating | Thin, uniform, and consistent coating |
| Oil Absorption | Higher oil uptake, greasier texture | Lower oil absorption, healthier result |
| Coating Stability | Prone to flaking and detachment | Enhanced stability and durability of coating |
| Process Efficiency | Standard frying time and energy consumption | Potential reduction in frying time and energy usage |
Introduction to Frying Techniques: Battered vs Ultrasound
Battered frying involves coating food with a thick, wet batter before submerging it in hot oil, creating a crispy and golden exterior. Ultrasound frying employs high-frequency sound waves to enhance batter adhesion and promote even frying.
Ultrasound waves generate micro-vibrations that improve the batter's penetration and bonding on the food surface, leading to a more uniform and durable coating compared to traditional methods. This technique reduces oil absorption and improves texture, offering a healthier frying alternative. Research indicates ultrasound frying can optimize coating adherence, enhancing both quality and sensory attributes of battered products.
Understanding Coating Adherence in Food Frying
| Coating Technique | Coating Adherence | Impact on Frying Quality |
| Battered Frying | Traditional batter forms a thick layer, but sometimes results in uneven adherence due to oil penetration and moisture loss during frying. | Produces a crispy texture but may lead to flaking or detachment of the coating, affecting visual appeal and mouthfeel. |
| Ultrasound Frying | Utilizes ultrasonic waves to enhance batter penetration and uniform coating adherence by reducing air bubbles and improving batter viscosity. | Results in a more consistent, firmly bonded crust with reduced oil absorption, improving texture and extending shelf life. |
What is Battered Frying? Methods and Outcomes
Battered frying involves coating food items with a liquid batter made from flour, water, and sometimes eggs before deep frying, which creates a crispy and golden outer layer. Common methods include dipping, double dipping, or swirling to ensure even batter coverage, crucial for optimal texture and flavor retention. This traditional technique results in a thick, crunchy crust that enhances the product's sensory appeal and moisture retention during frying.
What is Ultrasound Frying? Process and Innovations
Ultrasound frying utilizes high-frequency sound waves to enhance batter adhesion and create a uniform coating on food surfaces. This innovative process improves texture and reduces oil absorption compared to traditional battered frying methods.
- Ultrasound Cavitation - High-frequency sound waves generate cavitation bubbles that improve batter penetration and adherence.
- Enhanced Coating Uniformity - Ultrasound ensures even distribution of batter, leading to consistent frying results.
- Reduced Oil Uptake - The process minimizes oil absorption, producing healthier fried products with crispier coatings.
Comparing Coating Adherence: Battered vs Ultrasound Frying
Ultrasound frying significantly enhances coating adherence compared to traditional battered frying by creating microchannels that improve batter absorption and binding. The cavitation effect during ultrasound frying promotes a more uniform and stronger bond between the coating and the food surface. Studies indicate that ultrasound frying reduces coating detachment by up to 30%, resulting in a crispier and more durable crust.
Effects on Texture and Crispiness: A Sensory Analysis
How do battered frying and ultrasound frying compare in terms of texture and crispiness? Battered frying typically produces a thicker, crunchier coating due to the batter's ability to trap air and moisture during frying. Ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence by creating microbubbles that improve batter penetration, resulting in a lighter, crispier texture preferred in sensory evaluations.
Oil Absorption and Health Implications in Coating Methods
Battered frying typically results in higher oil absorption due to the thick coating that traps more oil during cooking. Ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence, reducing oil uptake and promoting a healthier fried product by minimizing fat content.
- Oil Absorption in Battered Frying - The dense batter layer increases oil retention, leading to higher calorie content in the final product.
- Ultrasound Frying Efficiency - Ultrasound waves improve batter penetration and adhesion, decreasing oil absorption and improving texture.
- Health Implications - Reduced oil uptake through ultrasound frying lowers fat intake, potentially decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases associated with fried foods.
Industrial Applications: Which Frying Method Wins?
Battered frying remains a widely used industrial method due to its reliable coating adherence and lower implementation costs. Ultrasound frying enhances coating uniformity and reduces oil absorption, offering innovative advantages for specialized food products.
- Battered Frying Dominance - Established technique known for consistent, thick batter layers that improve texture and flavor retention.
- Ultrasound Frying Innovation - Uses high-frequency waves to create microcavitation, promoting better batter adhesion and crispiness.
- Cost and Scalability - Battered frying is more cost-effective for large-scale operations, while ultrasound frying requires higher initial investment but offers energy savings.
Industrial food manufacturers balance cost and quality when choosing between battered and ultrasound frying methods for optimal coating adherence.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends in Coating Frying
Battered frying remains popular among consumers for its crispy texture and rich flavor, aligning with traditional preferences in coating adherence. Market trends indicate sustained demand for familiar, visually appealing coatings that enhance sensory satisfaction.
Ultrasound frying shows promise in improving coating adhesion through ultrasonic waves, offering a cleaner, more uniform crust with potential health benefits. Emerging consumer interest in innovative cooking methods and cleaner labels drives market exploration of ultrasound frying technology.
Related Important Terms
Ultrasonic-assisted batter adhesion
Ultrasonic-assisted batter adhesion significantly enhances coating adherence by promoting uniform batter distribution and increasing surface energy, resulting in a more resilient and consistent crust compared to traditional battered frying methods. This technique leverages ultrasonic cavitation to improve batter penetration and mechanical bonding, reducing coating loss during frying and ensuring superior texture and appearance.
Nanobubble cavitation coating
Nanobubble cavitation in ultrasound frying significantly enhances coating adherence by generating intense microjets that create a uniform and deeply penetrated batter layer, outperforming traditional battered frying methods. This technique improves nanobubble stability and cavitation effects, resulting in superior crispness and reduced oil absorption for coated foods.
Microstructure retention frying
Ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence by preserving the microstructure of battered foods, resulting in a uniform, crisp crust with minimal structural damage. In contrast, traditional battered frying often leads to microstructural degradation, causing uneven coating retention and increased oil absorption.
Acoustic energy crisping
Ultrasound frying leverages acoustic energy to create microbubbles that enhance batter adhesion and produce a crisper, more uniform coating compared to traditional battered frying methods. This acoustic cavitation improves coating durability by promoting better penetration and reduced oil absorption, resulting in superior texture and crunch.
Low-viscosity batter coupling
Low-viscosity batter coupled with ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence by improving batter penetration and uniformity through acoustic cavitation effects, resulting in a more consistent and durable crust compared to traditional battered frying. This technique maximizes surface interaction and reduces batter detachment, optimizing texture and coating longevity in fried products.
Nonthermal impedance frying
Nonthermal impedance frying enhances coating adherence by using electrical impedance to reduce oil absorption and maintain batter integrity better than traditional battered frying. Ultrasound frying further improves coating uniformity and texture by promoting moisture evaporation and creating microbubbles that strengthen batter adhesion without significant heat damage.
Pulse sonication crust formation
Pulse sonication during ultrasound frying significantly enhances crust formation by creating a denser, more uniform coating adherence compared to traditional battered frying methods. This technique uses high-frequency sound waves to improve the penetration and bonding of the coating, resulting in a crispier texture and reduced oil absorption.
Fine-scale bubble entrapment
Fine-scale bubble entrapment is significantly enhanced in ultrasound frying compared to traditional battered frying, promoting superior coating adherence through microcavitation effects. This ultrasound-induced bubble formation creates a porous, uniform interface facilitating stronger mechanical interlocking between the coating and the substrate.
Ultrasonic-batter matrix integration
Ultrasound frying enhances coating adherence by promoting ultrasonic-batter matrix integration, resulting in a more uniform and stronger bond between the batter and food surface compared to traditional battered frying. This technique uses high-frequency sound waves to improve batter penetration and adhesion, leading to superior crispiness and reduced oil absorption.
Battered Frying vs Ultrasound Frying for coating adherence. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com