Stovetop frying often results in a crispy texture but can cause significant moisture loss due to direct contact with high heat, which evaporates water from the food. Steam frying, on the other hand, combines steaming and frying techniques to retain more moisture while still creating a lightly crisp exterior, preserving juiciness inside. This method reduces dryness, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables that benefit from moisture retention.
Table of Comparison
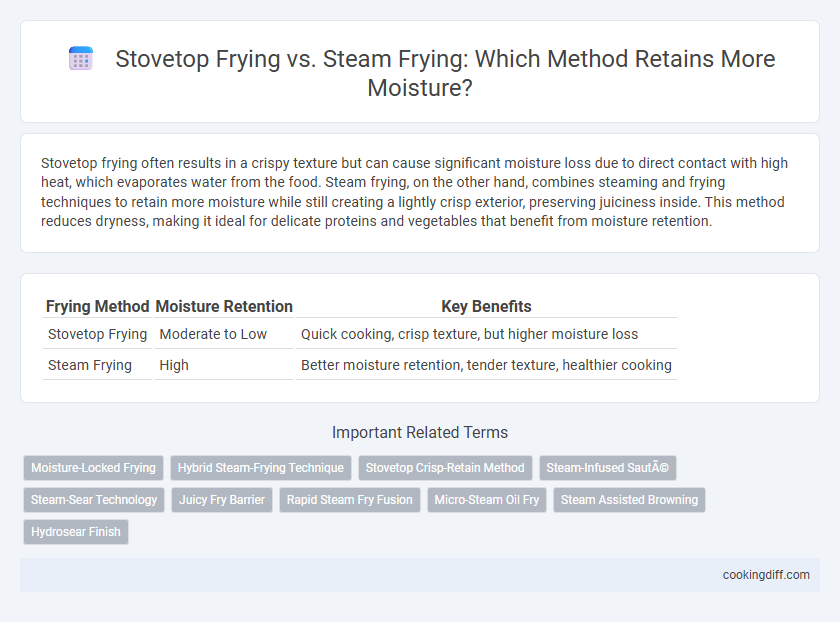
| Frying Method | Moisture Retention | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Stovetop Frying | Moderate to Low | Quick cooking, crisp texture, but higher moisture loss |
| Steam Frying | High | Better moisture retention, tender texture, healthier cooking |
Introduction to Frying Techniques: Stovetop vs Steam
Stovetop frying involves cooking food in hot oil or fat, creating a crispy exterior with intense heat. Steam frying combines frying with steam injection, promoting moisture retention and tender texture.
- Stovetop frying heats food at high temperatures - This method quickly sears the food, locking flavors while often causing moisture loss.
- Steam frying introduces steam during cooking - The steam helps maintain internal moisture, reducing dryness in the final dish.
- Moisture retention varies significantly between techniques - Steam frying generally preserves juiciness better than traditional stovetop frying.
Choosing between stovetop and steam frying depends on desired texture and moisture balance in the cuisine.
Understanding Moisture Retention in Cooking
How does stovetop frying compare to steam frying in terms of moisture retention during cooking? Stovetop frying uses direct heat, often leading to moisture loss as water evaporates rapidly from the food's surface. Steam frying, by combining heat with steam, creates a humid cooking environment that better preserves the food's internal moisture, resulting in juicier and more tender dishes.
How Stovetop Frying Affects Food Moisture
Stovetop frying uses direct heat to cook food, which often results in moisture loss due to evaporation. This method is effective for creating a crispy exterior but can dry out the interior if not carefully monitored.
- Rapid moisture evaporation - High heat causes water inside the food to quickly turn to steam and escape, reducing overall moisture content.
- Crisp texture formation - The dry heat helps develop a browned, crispy crust that contrasts with the moist interior when done properly.
- Moisture retention depends on technique - Controlling temperature and cooking time is essential to minimize excessive moisture loss during stovetop frying.
The Science Behind Steam Frying
Steam frying uses a combination of steam and oil to cook food, effectively sealing in moisture by creating a humid cooking environment that prevents drying out. This method leverages water vapor to transfer heat evenly, maintaining juiciness in meats and vegetables.
The science behind steam frying involves the water vapor slowing moisture loss by reducing surface temperature and limiting evaporation compared to traditional stovetop frying. This process enhances flavor retention and tenderness, making steam frying beneficial for moisture-sensitive ingredients.
Stovetop Frying: Pros and Cons for Juiciness
Stovetop frying allows for precise temperature control, which helps seal the exterior of foods and lock in moisture, resulting in juicier dishes. However, this method can sometimes cause uneven cooking if heat distribution is inconsistent, potentially leading to dry spots. Proper technique and the use of a suitable cooking fat are essential to maximize moisture retention when frying on the stovetop.
Steam Frying: Moisture Retention Benefits
Steam frying uses a small amount of water along with oil, creating steam that helps retain the food's natural moisture. This method prevents excessive drying, making it ideal for cooking delicate proteins and vegetables.
The steam environment reduces the risk of moisture loss compared to traditional stovetop frying, resulting in juicier and more tender dishes. Foods cooked with steam frying maintain their texture and flavor better without becoming greasy.
Flavor and Texture Differences: Stovetop vs Steam Frying
Stovetop frying creates a crispy, browned exterior with intense flavor due to Maillard reactions, while steam frying preserves moisture inside the food, resulting in a juicier texture. The dry heat of stovetop frying enhances caramelization, giving food a rich, savory taste not typically achieved with steam frying.
Steam frying combines the benefits of steaming and frying by using steam to keep food moist while utilizing hot oil to develop a slight crust, balancing tenderness and crispness. This method minimizes moisture loss, keeping vegetables vibrant and meats succulent, compared to the firmer, drier texture from traditional stovetop frying. Flavor profiles differ, with stovetop frying intensifying smoky, roasted notes and steam frying emphasizing natural freshness and subtle seasoning.
Nutritional Impact of Moisture Retention Methods
Stovetop frying typically expels more moisture from food, potentially diminishing certain heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C. Steam frying retains higher moisture levels, preserving more nutrients and enhancing the food's texture and flavor.
- Stovetop frying reduces moisture content - This process concentrates flavors but can lead to nutrient loss through dehydration.
- Steam frying preserves nutrient density - The retained moisture helps maintain vitamins and minerals often lost in dry heat methods.
- Moisture retention affects antioxidant levels - Steam frying better conserves antioxidants that protect against oxidative damage.
Best Foods for Stovetop vs Steam Frying
Stovetop frying excels with foods like chicken, steaks, and vegetables that benefit from a crispy, golden exterior due to direct heat contact. Steam frying is ideal for delicate items such as dumplings, fish, and vegetables, preserving moisture and enhancing tenderness by combining steam and frying techniques. Choosing between stovetop and steam frying depends on the desired texture and moisture retention for specific ingredients.
Related Important Terms
Moisture-Locked Frying
Stovetop frying typically results in faster moisture loss due to direct high heat exposure, while steam frying preserves moisture by creating a humid cooking environment that locks in juices. Moisture-locked frying combines steaming and frying techniques to maintain food tenderness and enhance flavor without drying out the ingredients.
Hybrid Steam-Frying Technique
Hybrid steam-frying combines the high heat of stovetop frying with controlled steam injection, preserving moisture while achieving a crispy texture. This technique reduces moisture loss compared to traditional frying, resulting in juicier, tender foods with enhanced flavor retention.
Stovetop Crisp-Retain Method
Stovetop Crisp-Retain Method excels in moisture retention by using controlled heat to quickly sear food, forming a crisp outer layer that locks internal juices. This technique preserves the natural texture and flavor more effectively than steam frying, which introduces moisture and can soften the food's exterior.
Steam-Infused Sauté
Steam-infused saute enhances moisture retention by combining high heat with controlled steam release, preventing food from drying out while maintaining a tender texture. Unlike traditional stovetop frying, this method uses a lid and a small amount of liquid to create a humid environment that locks in natural juices and flavors.
Steam-Sear Technology
Steam-Sear Technology in stovetop frying enhances moisture retention by combining high-heat searing with steam infusion, preventing moisture loss while creating a crisp exterior. This method outperforms traditional stovetop frying by sealing juices inside the food, resulting in juicier, tender dishes with superior texture and flavor.
Juicy Fry Barrier
Stovetop frying creates a crispy exterior by applying direct high heat, which can cause moisture loss but forms a Juicy Fry Barrier that seals in internal juices. Steam frying combines heat with moisture, enhancing moisture retention by infusing steam into the cooking process, resulting in juicier, tender dishes while maintaining a flavorful crust.
Rapid Steam Fry Fusion
Rapid Steam Fry Fusion combines intense stovetop heat with controlled steam injection, enhancing moisture retention by sealing juices quickly while achieving a crisp exterior. This method outperforms traditional stovetop frying by reducing moisture loss, resulting in juicier, more flavorful dishes.
Micro-Steam Oil Fry
Micro-Steam Oil Fry uses a minimal amount of oil combined with steam generated from the food's natural moisture, significantly enhancing moisture retention compared to traditional stovetop frying, which often leads to higher moisture loss due to direct high heat and oil exposure. This method preserves juiciness and texture by creating a micro-steam environment that seals in natural juices without excessive oil absorption.
Steam Assisted Browning
Steam-assisted browning during stovetop frying enhances moisture retention by creating a humid cooking environment that prevents excessive dehydration of the food's surface. This method combines the Maillard reaction with gentle steam infusion, resulting in crisp outer layers while maintaining juicy, tender interiors.
Stovetop Frying vs Steam Frying for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com