Stir frying vegetables involves cooking them quickly in a small amount of hot oil, which helps retain their crisp texture and vibrant flavor while enhancing nutrient absorption. Waterless frying uses steam and a minimal amount of oil or none at all, preserving the vegetables' natural taste and nutrients by preventing oxidation and nutrient loss. Both methods offer healthy cooking alternatives, with stir frying providing a richer flavor and waterless frying focusing on maximum nutrient retention.
Table of Comparison
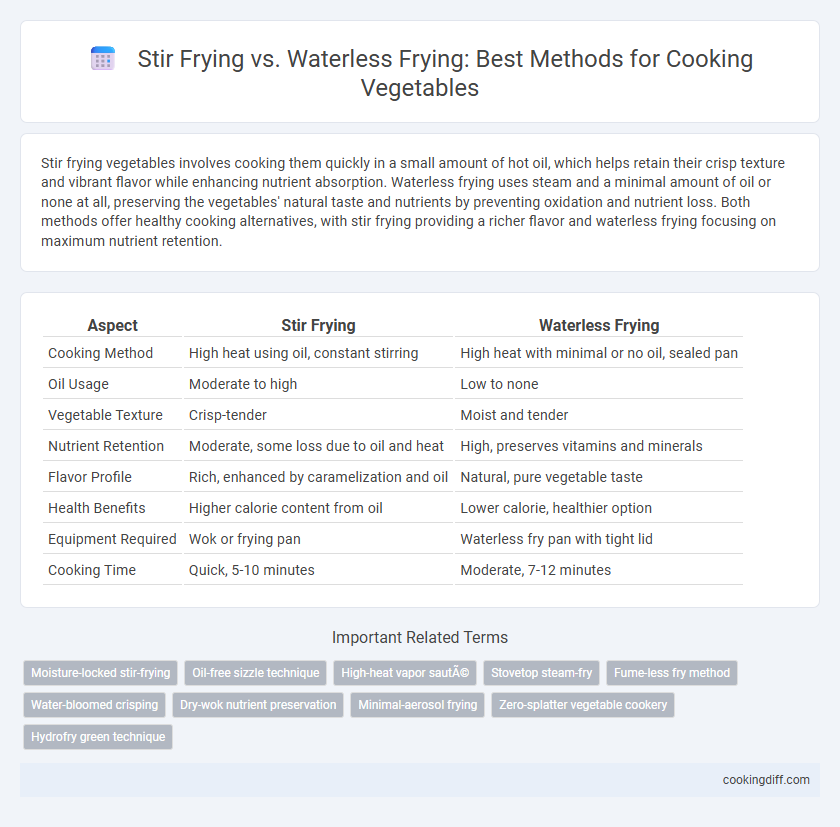
| Aspect | Stir Frying | Waterless Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High heat using oil, constant stirring | High heat with minimal or no oil, sealed pan |
| Oil Usage | Moderate to high | Low to none |
| Vegetable Texture | Crisp-tender | Moist and tender |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate, some loss due to oil and heat | High, preserves vitamins and minerals |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, enhanced by caramelization and oil | Natural, pure vegetable taste |
| Health Benefits | Higher calorie content from oil | Lower calorie, healthier option |
| Equipment Required | Wok or frying pan | Waterless fry pan with tight lid |
| Cooking Time | Quick, 5-10 minutes | Moderate, 7-12 minutes |
Introduction to Stir Frying and Waterless Frying
What are the key differences between stir frying and waterless frying for vegetables? Stir frying involves cooking vegetables quickly at high heat using a small amount of oil, which retains texture and enhances flavor. Waterless frying uses the natural moisture of vegetables to cook without added oil, preserving nutrients and providing a lower-fat alternative.
What Is Stir Frying?
Stir frying is a high-heat cooking technique where vegetables are quickly cooked in a small amount of oil while continuously being stirred. This method preserves the texture and nutrients of vegetables by cooking them rapidly, producing a crisp-tender result.
In contrast, waterless frying uses steam and natural vegetable moisture without oil, focusing on health benefits and reducing fat content. Stir frying offers enhanced flavor development due to caramelization and Maillard reactions that occur with direct heat and oil.
What Is Waterless Frying?
Waterless frying is a cooking technique that uses a sealed pan to cook vegetables with their natural moisture, eliminating the need for added oil or water. This method preserves nutrients and enhances the natural flavors and textures of the vegetables while cooking at lower temperatures.
- Definition - Waterless frying involves cooking food in a tightly covered pan that traps steam and moisture.
- Health Benefits - This method reduces fat consumption by avoiding added oils compared to traditional stir frying.
- Nutrient Retention - Waterless frying maintains higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants due to gentle heat and minimized oxidation.
Nutrient Retention: Stir Fry vs. Waterless Fry
Stir frying vegetables quickly over high heat preserves vitamins such as Vitamin C and B-complex by reducing cooking time and preventing nutrient leaching. Waterless frying, which uses steam generated from the vegetable's own moisture, minimizes nutrient loss by avoiding added water and retaining heat evenly. Studies show waterless frying retains up to 40% more antioxidants compared to traditional stir frying methods.
Flavor and Texture Comparison
| Method | Flavor | Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Stir Frying | Enhances flavor through caramelization and Maillard reaction, producing a rich, slightly smoky taste. | Maintains a crisp-tender texture by cooking quickly over high heat. |
| Waterless Frying | Preserves the natural, subtle flavors of vegetables without added fats or browning. | Results in softer, more evenly cooked vegetables due to gentle steaming effect. |
Cooking Time Differences
Stir frying typically cooks vegetables quickly at high heat, often completing in 5 to 7 minutes, preserving crispness and color. Waterless frying uses steam generated from the vegetables' own moisture, resulting in slightly longer cooking times, usually around 8 to 12 minutes. The difference in cooking times affects texture and nutrient retention, with stir frying offering a faster method and waterless frying promoting more even heat distribution.
Oil Usage and Health Impact
Stir frying requires a moderate amount of oil to cook vegetables quickly at high heat, preserving nutrients while adding flavor. Waterless frying uses minimal to no oil, relying on the vegetables' natural moisture, which reduces fat intake and supports heart health.
- Oil Usage in Stir Frying - Typically uses 1-2 tablespoons of oil to achieve a crispy texture and enhance taste.
- Oil Usage in Waterless Frying - Uses little to no added oil, minimizing fat content and calorie consumption.
- Health Impact - Waterless frying lowers saturated fat intake and may reduce cardiovascular risks compared to oil-heavy stir frying.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Stir frying requires a wok or a large skillet that allows high heat and quick tossing of vegetables to ensure even cooking. Waterless frying demands specialized non-stick or ceramic pans designed to cook vegetables using their natural moisture without added water or oil.
- Wok or large skillet - Essential for stir frying to achieve high heat and rapid vegetable turnover.
- Non-stick or ceramic pan - Used in waterless frying to retain moisture and prevent sticking without added fats.
- High-heat source - Necessary for both methods but especially critical for stir frying to maintain crisp texture.
Proper equipment selection significantly impacts the cooking technique and the retention of nutrients in vegetables.
Best Vegetables for Stir Frying vs. Waterless Frying
Best vegetables for stir frying include bell peppers, broccoli, snap peas, and carrots due to their firm texture and ability to retain crunch under high heat. Stir frying preserves the vibrant colors and enhances the natural flavors with quick cooking over intense heat.
Waterless frying works well for tender vegetables like zucchini, mushrooms, spinach, and tomatoes, which release moisture and cook gently without added fat. This method retains nutrients by using the vegetables' own water content, resulting in softer textures and more concentrated flavors.
Related Important Terms
Moisture-locked stir-frying
Moisture-locked stir-frying preserves the natural juiciness and vibrant texture of vegetables by cooking them quickly at high heat with minimal oil, ensuring nutrients remain intact. Unlike waterless frying, which uses steam released from the vegetables to cook without added water or oil, moisture-locked stir-frying balances crispness and tenderness for optimal flavor retention.
Oil-free sizzle technique
Stir frying uses high heat and minimal oil to quickly cook vegetables, preserving texture and flavor, while waterless frying relies on the natural moisture in vegetables, steaming them without oil to maintain nutrients and offer a healthier alternative. Oil-free sizzle techniques in waterless frying create a crisp exterior by using steam and heat circulation, enhancing taste without added fats.
High-heat vapor sauté
Stir frying uses high-heat vapor saute techniques to quickly cook vegetables with minimal oil, preserving crispness and enhancing natural flavors through rapid moisture evaporation. Waterless frying, by contrast, relies on the vegetables' own moisture and lower heat, resulting in softer textures and reduced nutrient loss without added fats.
Stovetop steam-fry
Stovetop steam-fry combines high heat with minimal oil and steam to preserve nutrients and vibrant color in vegetables, offering a healthier alternative to traditional stir frying, which relies solely on oil and high heat for quick cooking. This waterless frying method reduces fat content while enhancing texture and flavor retention, making it ideal for nutrient-dense vegetable preparation.
Fume-less fry method
Stir frying vegetables involves cooking quickly at high heat with a small amount of oil, promoting crisp texture and vibrant color, but can produce smoke and fumes. Waterless frying uses the natural moisture in vegetables to cook without oil or water, minimizing smoke and fumes while preserving nutrients and flavor, making it a healthier, fume-less alternative.
Water-bloomed crisping
Waterless frying preserves the natural moisture of vegetables, resulting in water-bloomed crisping that enhances texture and flavor without the need for added oils. This technique uses high heat and steam to cook vegetables quickly, maintaining their vibrant color and nutrient content compared to traditional stir frying.
Dry-wok nutrient preservation
Dry-wok stir frying preserves the nutrients in vegetables by using high heat with minimal oil, which rapidly cooks the food while locking in vitamins such as vitamin C and antioxidants. Waterless frying further enhances nutrient retention by steaming vegetables in their own moisture without added oils or water, maintaining crisp texture and maximizing mineral and phytonutrient content.
Minimal-aerosol frying
Stir frying vegetables involves high heat and continuous stirring with minimal oil, producing a quick-cooking process that maximizes flavor and texture while generating moderate aerosol emissions. Waterless frying, using a tightly sealed pan and steam from the vegetables' own moisture, significantly reduces aerosol production and oil usage, offering a healthier and cleaner cooking method for preserving nutrient content.
Zero-splatter vegetable cookery
Stir frying uses high heat and a small amount of oil, creating flavorful, evenly cooked vegetables but often results in oil splatter, whereas waterless frying employs steam and no oil, producing tender vegetables with zero splatter and retaining maximum nutrients. Zero-splatter vegetable cooking enhances kitchen cleanliness and safety, making waterless frying an ideal method for health-conscious and mess-free meal preparation.
Stir Frying vs Waterless Frying for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com