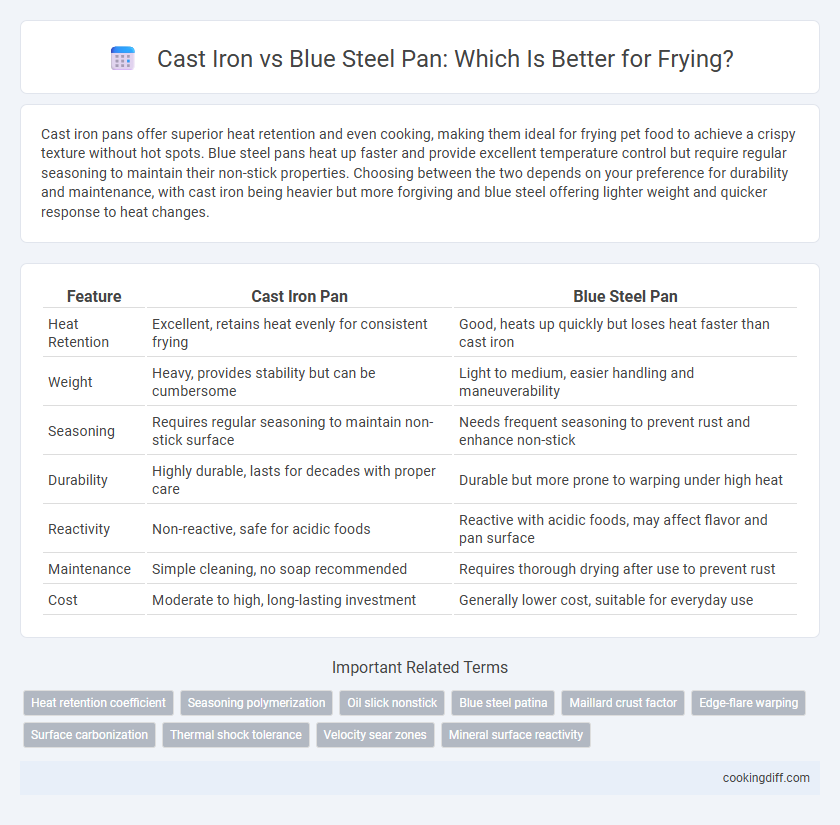
Cast iron pans offer superior heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for frying pet food to achieve a crispy texture without hot spots. Blue steel pans heat up faster and provide excellent temperature control but require regular seasoning to maintain their non-stick properties. Choosing between the two depends on your preference for durability and maintenance, with cast iron being heavier but more forgiving and blue steel offering lighter weight and quicker response to heat changes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Iron Pan | Blue Steel Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent, retains heat evenly for consistent frying | Good, heats up quickly but loses heat faster than cast iron |
| Weight | Heavy, provides stability but can be cumbersome | Light to medium, easier handling and maneuverability |
| Seasoning | Requires regular seasoning to maintain non-stick surface | Needs frequent seasoning to prevent rust and enhance non-stick |
| Durability | Highly durable, lasts for decades with proper care | Durable but more prone to warping under high heat |
| Reactivity | Non-reactive, safe for acidic foods | Reactive with acidic foods, may affect flavor and pan surface |
| Maintenance | Simple cleaning, no soap recommended | Requires thorough drying after use to prevent rust |
| Cost | Moderate to high, long-lasting investment | Generally lower cost, suitable for everyday use |
Introduction: Cast Iron vs Blue Steel Pans for Frying
Cast iron pans offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for frying at consistent temperatures. Their naturally non-stick surface improves with seasoning, enhancing food flavor and release over time.
Blue steel pans heat up quickly and provide superior heat responsiveness, perfect for precise temperature control during frying. They require regular seasoning to maintain their non-stick properties and prevent rusting, demanding more maintenance than cast iron.
Material Composition and Properties
Cast iron pans are composed primarily of carbon and iron, offering excellent heat retention and even distribution, making them ideal for frying at consistent temperatures. Blue steel pans, made from carbon steel with a blue oxide coating, heat up faster and provide a lighter, more responsive cooking experience.
- Cast Iron Material - Heavy carbon and iron alloy provides superior heat retention and durability during high-temperature frying.
- Blue Steel Composition - Carbon steel treated with a blue oxide layer reduces rust and allows quicker heat conduction for faster cooking.
- Thermal Properties - Cast iron offers slower heat response but maintains stable frying temperatures, while blue steel heats rapidly but cools down faster.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Cast iron pans excel in heat retention, maintaining steady temperatures during frying to ensure even cooking. Blue steel pans heat up faster and offer more responsive temperature control but generally have lower heat retention compared to cast iron.
- Cast iron pan retains heat exceptionally well - This allows for consistent frying temperatures, preventing sudden drops when food is added.
- Blue steel pan provides faster heat distribution - It heats quickly and responds promptly to temperature changes, ideal for delicate frying tasks.
- Cast iron's heat retention supports even cooking - Its thickness helps distribute heat evenly, minimizing hot spots during frying.
Pre-seasoning and Nonstick Surface
| Cast Iron Pan | Requires extended pre-seasoning to build a durable nonstick surface; seasoning involves polymerizing oil at high heat to fill pores. |
| Blue Steel Pan | Needs quicker pre-seasoning due to smoother surface; develops a naturally slick patina with fewer layers of oil polymerization. |
| Nonstick Surface | Cast iron's seasoning creates a robust, long-lasting coating ideal for high-heat frying, while blue steel offers faster responsiveness and slightly less nonstick durability over time. |
Durability and Longevity
Cast iron pans are renowned for their exceptional durability, often lasting a lifetime with proper care. Their thick, heavy construction resists warping and damage even under high heat conditions.
Blue steel pans, while also durable, require more maintenance to prevent rust and maintain seasoning. They are less resistant to chipping compared to cast iron but offer quicker heating and cooling for precise frying control.
Ease of Maintenance and Cleaning
Cast iron pans require seasoning and careful drying to prevent rust, making maintenance more involved compared to blue steel pans. Blue steel pans develop a natural non-stick patina faster and can be cleaned with less effort but need regular seasoning to avoid corrosion.
- Cast iron seasoning - Demands oiling and baking to maintain a protective layer that prevents rust and enhances non-stick properties.
- Blue steel patina - Forms quickly with use, offering a naturally slick surface that improves frying and simplifies cleaning.
- Cleaning methods - Both require hand washing without soap to preserve seasoning, but blue steel is less prone to rust if dried promptly.
Choosing between these pans depends on your willingness to maintain seasoning and care routines for optimal frying performance.
Weight and Handling in the Kitchen
Which pan offers better weight and handling for frying, cast iron or blue steel? Cast iron pans are significantly heavier, providing excellent heat retention but requiring more effort to maneuver. Blue steel pans are lighter and easier to handle, making them ideal for quick movements and tossing food during frying.
Performance with Different Foods
Cast iron pans excel at evenly distributing heat, making them ideal for frying foods that require steady, consistent temperatures like steaks and fried chicken. Blue steel pans heat up and cool down more quickly, providing superior control for delicate items such as fish fillets and eggs. Each pan's thermal properties influence cooking performance, with cast iron retaining heat longer and blue steel offering rapid temperature adjustments during frying.
Price Comparison and Value for Money
Cast iron pans generally cost more upfront, ranging from $30 to $100, while blue steel pans are typically priced between $20 and $50. Despite the higher initial investment, cast iron offers superior heat retention and durability, enhancing long-term value for money.
Blue steel pans are more affordable and heat up quickly, making them suitable for everyday frying tasks with moderate care requirements. Cast iron pans develop a natural non-stick surface over time, increasing cooking performance and lifespan. Considering durability, heat distribution, and maintenance, cast iron provides better overall value despite a higher price.
Related Important Terms
Heat retention coefficient
Cast iron pans have a higher heat retention coefficient than blue steel pans, allowing them to maintain steady, even heat during frying for better searing and consistent cooking. Blue steel pans heat up faster but lose heat more quickly, making them ideal for quick temperature adjustments but less effective for prolonged frying.
Seasoning polymerization
Cast iron pans develop a durable, non-stick surface through seasoning polymerization, where oils chemically bond to the metal, enhancing heat retention and flavor. Blue steel pans also benefit from seasoning but form a thinner, more reactive layer that requires frequent maintenance to prevent rust and maintain frying efficiency.
Oil slick nonstick
Cast iron pans develop a naturally seasoned oil slick nonstick surface that improves with use, providing excellent heat retention and durability for frying. Blue steel pans offer a smoother initial surface that quickly builds a similar nonstick patina through seasoning, making them lighter and faster to heat but requiring more maintenance to prevent rust.
Blue steel patina
A blue steel pan develops a natural patina that enhances its non-stick properties and improves heat distribution over time, making it ideal for frying delicate foods with minimal oil. Compared to cast iron, blue steel is lighter, heats up faster, and its patina forms more quickly, providing superior seasoning benefits for precise and efficient frying.
Maillard crust factor
Cast iron pans excel at maintaining high, consistent heat essential for forming a robust Maillard crust, creating a deeply caramelized and flavorful surface on fried foods. Blue steel pans heat more quickly and respond faster to temperature changes, allowing precise control over the crust development but may require more frequent reheating to sustain the intense heat needed for optimal Maillard reaction.
Edge-flare warping
Cast iron pans exhibit superior resistance to edge-flare warping due to their dense, thick construction, maintaining even heat distribution during high-temperature frying. In contrast, blue steel pans, being thinner and more prone to thermal expansion, are more susceptible to edge-flare warping, which can affect frying performance and pan lifespan.
Surface carbonization
Cast iron pans develop a durable, naturally non-stick surface through repeated surface carbonization, enhancing heat retention and flavor over time. Blue steel pans achieve surface carbonization faster, providing a smoother, slicker frying surface ideal for quick, high-heat cooking with excellent heat conductivity.
Thermal shock tolerance
Cast iron pans exhibit exceptional thermal shock tolerance due to their thick, dense construction, allowing them to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or warping. Blue steel pans, while offering quicker heat response, are more susceptible to damage from sudden thermal shifts, requiring gradual temperature adjustments for durability during frying.
Velocity sear zones
Cast iron pans provide consistent high heat retention, creating stable velocity sear zones ideal for evenly caramelizing food surfaces during frying. Blue steel pans heat up faster and develop variable velocity sear zones, enabling precise temperature control for quick searing and rapid browning.
Cast iron pan vs blue steel pan for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com