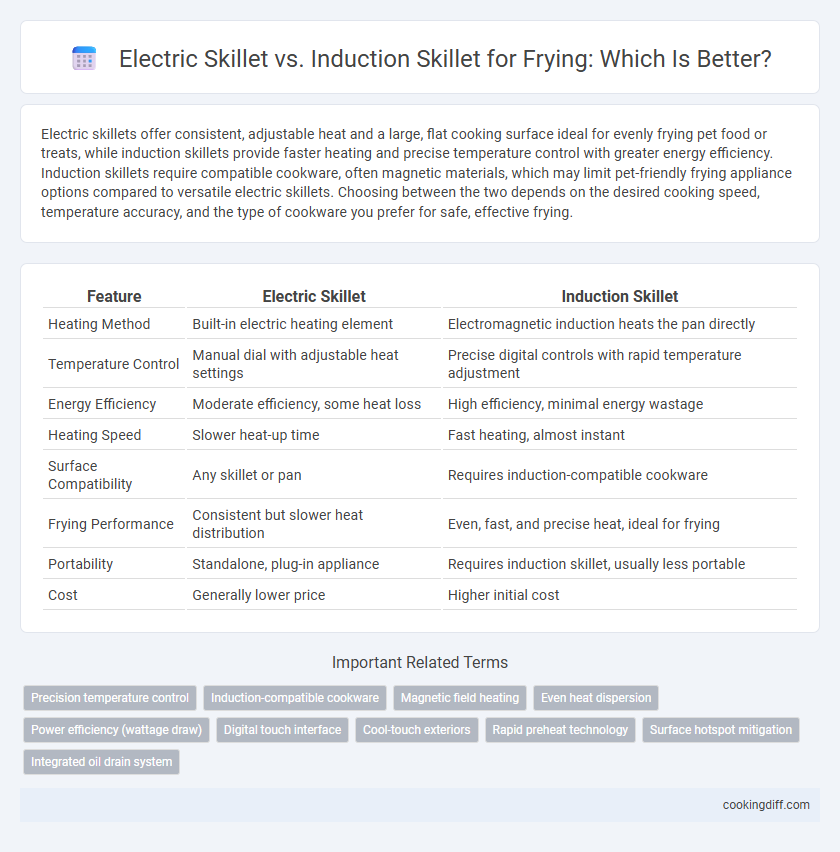
Electric skillets offer consistent, adjustable heat and a large, flat cooking surface ideal for evenly frying pet food or treats, while induction skillets provide faster heating and precise temperature control with greater energy efficiency. Induction skillets require compatible cookware, often magnetic materials, which may limit pet-friendly frying appliance options compared to versatile electric skillets. Choosing between the two depends on the desired cooking speed, temperature accuracy, and the type of cookware you prefer for safe, effective frying.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electric Skillet | Induction Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Built-in electric heating element | Electromagnetic induction heats the pan directly |
| Temperature Control | Manual dial with adjustable heat settings | Precise digital controls with rapid temperature adjustment |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate efficiency, some heat loss | High efficiency, minimal energy wastage |
| Heating Speed | Slower heat-up time | Fast heating, almost instant |
| Surface Compatibility | Any skillet or pan | Requires induction-compatible cookware |
| Frying Performance | Consistent but slower heat distribution | Even, fast, and precise heat, ideal for frying |
| Portability | Standalone, plug-in appliance | Requires induction skillet, usually less portable |
| Cost | Generally lower price | Higher initial cost |
Introduction to Electric and Induction Skillets for Frying
Electric skillets use built-in heating elements to maintain consistent temperatures, ideal for frying various foods evenly. Induction skillets rely on electromagnetic fields to heat the cookware directly, offering faster heat-up times and precise temperature control. Both types provide energy-efficient frying options but differ in heat distribution and compatibility with cookware materials.
How Electric Skillets Work for Frying
Electric skillets use an integrated heating element that evenly distributes heat across the cooking surface, ensuring consistent temperatures ideal for frying. The temperature control allows precise adjustments to maintain the perfect frying heat, reducing the risk of burning or undercooking food.
The flat, non-stick surface of electric skillets aids in even browning and easy food release, making them convenient for frying a variety of foods. Their portability and ability to maintain steady heat without fluctuating electric currents make them a reliable choice for frying compared to induction skillets.
Understanding Induction Skillets in Frying Applications
Induction skillets use electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, offering precise temperature control ideal for frying delicate foods. Electric skillets rely on a built-in heating element, which can result in less consistent heat distribution during frying processes.
- Efficient heat transfer - Induction skillets provide rapid and even heating, reducing hot spots that can cause uneven frying.
- Energy consumption - Induction units generally consume less energy compared to electric skillets, making them more eco-friendly for extended frying sessions.
- Cookware compatibility - Only ferromagnetic skillets work with induction cooktops, requiring specific materials for effective frying.
Heat Distribution: Electric vs Induction Skillets
How does heat distribution compare between electric and induction skillets for frying? Electric skillets typically use a heating element beneath a flat surface, which can result in less even heat spread and potential hot spots. Induction skillets provide rapid, uniform heating by directly inducing heat in the cookware, ensuring consistent frying temperatures across the entire surface.
Temperature Control Precision: Electric vs Induction Frying
Induction skillets offer superior temperature control precision by using electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, resulting in rapid and consistent temperature adjustments ideal for delicate frying tasks. Electric skillets rely on a built-in heating element, which often leads to slower response times and less uniform heat distribution, potentially affecting the frying quality. For precise frying temperature management, induction skillets provide greater efficiency and accuracy compared to traditional electric skillets.
Energy Efficiency in Frying: Electric vs Induction Skillets
Induction skillets deliver superior energy efficiency by directly heating the cookware through electromagnetic fields, reducing heat loss. Electric skillets rely on heating elements that transfer heat indirectly, resulting in moderate energy consumption during frying.
- Quicker Heating - Induction skillets heat up faster, minimizing cooking time and energy usage.
- Consistent Temperature - Electric skillets maintain even heat distribution but often consume more electricity to do so.
- Energy Conversion - Induction technology converts up to 90% of energy into heat, whereas electric skillets convert roughly 70%.
Safety Features for Frying: Comparing Electric and Induction Skillets
Electric skillets and induction skillets offer distinct safety features for frying that impact user experience and risk management. Induction skillets use electromagnetic fields to heat only the cookware, minimizing burn hazards, while electric skillets heat the entire surface, increasing the risk of accidental contact burns.
- Cool-to-Touch Surfaces - Induction skillets maintain cooler surfaces outside the cooking zone to reduce burn injuries.
- Automatic Shutoff - Both skillets often feature automatic shutoff mechanisms for overheating prevention, but induction models typically respond faster.
- Precise Temperature Control - Induction skillets provide rapid and accurate temperature adjustments, lowering the risk of oil overheating and fires.
Choosing an induction skillet can enhance frying safety through advanced thermal control and surface temperature management.
Versatility in Frying Techniques: Electric vs Induction Skillets
| Electric Skillet | Offers consistent, evenly distributed heat ideal for frying, sauteing, and searing various foods with adjustable temperature settings for precise control. |
| Induction Skillet | Provides rapid heating and cooling through electromagnetic technology, allowing quick temperature adjustments perfect for frying, stir-frying, and delicate cooking tasks with high energy efficiency. |
| Frying Techniques Versatility | Electric skillets excel in maintaining steady heat for deep frying and slow frying, while induction skillets enhance quick temperature shifts for diverse frying styles including crisping and sauteing. |
Cleaning and Maintenance: Frying with Electric vs Induction Skillets
Electric skillets typically feature removable, non-stick cooking surfaces that make cleaning straightforward and dishwasher-safe in many cases. Induction skillets require compatible cookware and often have more complex surfaces that may need gentle hand washing to preserve their induction functionality.
Maintenance for electric skillets is generally simpler due to fewer electronic components exposed to heat and grease. Induction skillets demand careful cleaning to avoid damage to the induction coil and sensor, often necessitating specialized cleaning products. Regular wiping of the induction base and avoiding abrasive materials extends the lifespan of these skillets, ensuring consistent frying performance.
Related Important Terms
Precision temperature control
Electric skillets offer precise temperature control through adjustable thermostats that maintain consistent heat ideal for frying delicate foods. Induction skillets provide even faster and more accurate temperature adjustments using electromagnetic technology, ensuring optimal frying results with minimal temperature fluctuations.
Induction-compatible cookware
Induction skillets require induction-compatible cookware made from magnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel to efficiently transfer heat, ensuring rapid and even frying. Electric skillets can use a wider range of cookware but often lack the precise temperature control and energy efficiency provided by induction technology.
Magnetic field heating
Electric skillets use resistive heating elements to generate heat directly, while induction skillets rely on magnetic field heating, which uses electromagnetic induction to produce heat within the cookware itself, ensuring faster and more efficient frying. The magnetic field heating of induction skillets results in precise temperature control and reduced energy consumption compared to the slower heat transfer in traditional electric skillets.
Even heat dispersion
Electric skillets provide consistent even heat dispersion due to their integrated heating elements that cover the entire cooking surface, minimizing hot spots and ensuring uniform frying. Induction skillets rely on electromagnetic fields to heat the cookware directly, offering rapid and precise temperature control with efficient heat distribution, but effectiveness depends on compatible cookware materials.
Power efficiency (wattage draw)
Electric skillets typically draw between 1200 to 1500 watts, offering consistent heat suitable for frying, whereas induction skillets operate at lower wattage, around 1000 to 1300 watts, providing faster heat-up times and greater power efficiency by directly heating the cookware. Induction skillets convert up to 90% of energy into heat, reducing electricity consumption compared to electric skillets that lose heat during transfer, making induction the more power-efficient option for frying.
Digital touch interface
The electric skillet's digital touch interface allows precise temperature control ideal for consistent frying, while the induction skillet offers a faster heat response and energy efficiency with touch controls that enhance usability. Both interfaces provide easy cleaning and accurate adjustments, but the induction skillet generally delivers more precise frying temperature regulation due to its electromagnetic heating technology.
Cool-touch exteriors
Electric skillets with cool-touch exteriors provide enhanced safety by preventing burns during frying, whereas induction skillets typically have surfaces that heat up quickly and may require additional safety measures. The cool-touch design in electric skillets ensures comfortable handling and reduces the risk of accidental contact with hot surfaces while frying various foods.
Rapid preheat technology
Electric skillets with rapid preheat technology reach optimal frying temperatures quickly, reducing wait times and ensuring even heat distribution for consistent cooking results. Induction skillets also offer fast preheating but rely on magnetic fields for precise temperature control, enhancing energy efficiency and safety during frying.
Surface hotspot mitigation
Electric skillets often exhibit uneven heating, leading to surface hotspots that can cause inconsistent frying results, whereas induction skillets utilize electromagnetic technology to distribute heat more evenly across the cooking surface, effectively minimizing hotspot formation. This precise temperature control in induction skillets enhances frying consistency and reduces the risk of burning or undercooking food.
Electric skillet vs induction skillet for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com